Key Terms and People Section Summary
... 2. Despite some initial success, the later Crusades failed. 3. The Crusades changed Europe forever. ...
... 2. Despite some initial success, the later Crusades failed. 3. The Crusades changed Europe forever. ...
Crusades review for generalization sheet
... • Leaders: Richard I the Lion Hearted of England - most successful European leader of this crusade (the only one who actually fought), kidnapped and held for ransom on his way home. • Philip II Augustus of France – fell ill and returned to France • Frederick I Barbarossa the Holy Roman Emperor – dro ...
... • Leaders: Richard I the Lion Hearted of England - most successful European leader of this crusade (the only one who actually fought), kidnapped and held for ransom on his way home. • Philip II Augustus of France – fell ill and returned to France • Frederick I Barbarossa the Holy Roman Emperor – dro ...
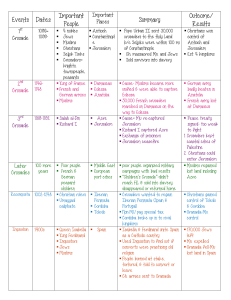
Events Dates Important People Summary Outcome/ Results
... Edessa 50,000 French crusaders marched on Damascus on the way to Edessa Cause= Mu. re-captured Jerusalem Richard I captured Acre Exchange of prisoners Jerusalem ceasefire ...
... Edessa 50,000 French crusaders marched on Damascus on the way to Edessa Cause= Mu. re-captured Jerusalem Richard I captured Acre Exchange of prisoners Jerusalem ceasefire ...
1.3 Why did the Crusades occur and how they they
... known to the Christians as the Holy Land. Christians referred to this area as the Holy Land because it was where Jesus had lived and taught. Muslims and Jews also considered the land holy. The leader of the Byzantine Empire, Alexius I, asked the pope for help in defeating the Turks. Under the leader ...
... known to the Christians as the Holy Land. Christians referred to this area as the Holy Land because it was where Jesus had lived and taught. Muslims and Jews also considered the land holy. The leader of the Byzantine Empire, Alexius I, asked the pope for help in defeating the Turks. Under the leader ...
Slide 1
... The crusades were a series of religious wars between Muslims and Christians, beginning in 1096. They started when the Seljuk Turks invaded the Holy Land (Palestine). The Byzantine emperor wanted to recover this land by fighting in a holy war in the name of God. ...
... The crusades were a series of religious wars between Muslims and Christians, beginning in 1096. They started when the Seljuk Turks invaded the Holy Land (Palestine). The Byzantine emperor wanted to recover this land by fighting in a holy war in the name of God. ...
Study Guide mIddle ages
... SAD cycle for Charlemagne’s Empire #33 Test Date: Wed. Dec. How the Viking and other invasions led to 16th Feudalism #34 See my Jeopardy Review on Feudalism/ Draw the Feudal Pyramid #34 my I-Learn Site to help How Manorialism Works #34 ...
... SAD cycle for Charlemagne’s Empire #33 Test Date: Wed. Dec. How the Viking and other invasions led to 16th Feudalism #34 See my Jeopardy Review on Feudalism/ Draw the Feudal Pyramid #34 my I-Learn Site to help How Manorialism Works #34 ...
The Crusades
... In the seventh century, Muslims conquered Palestine. Initially, the Muslim conquerors allowed Jews and Christians ...
... In the seventh century, Muslims conquered Palestine. Initially, the Muslim conquerors allowed Jews and Christians ...
High Middle Ages - Ms. Mac`s Class
... C. Capetian dynasty ruled France 1. By 1000, France was divided into about 30 feudal territories. 2. Hugh Capet - chosen ruler of France by France’s most powerful nobles in 987. a. He began the Capetian dynasty. ...
... C. Capetian dynasty ruled France 1. By 1000, France was divided into about 30 feudal territories. 2. Hugh Capet - chosen ruler of France by France’s most powerful nobles in 987. a. He began the Capetian dynasty. ...
The Crusades
... chance to fight, gain territory, riches, possibility of a title – Pope and kings saw it as an opportunity to free Europe from young nobles who disturbed the peace and wasted lives and energy fighting one another ...
... chance to fight, gain territory, riches, possibility of a title – Pope and kings saw it as an opportunity to free Europe from young nobles who disturbed the peace and wasted lives and energy fighting one another ...
Year 7 History Knowledge Organiser Term 3/4
... In 1071, Muslim Turks defeated the army of the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert and Turkish nomads settled in the Christian Byzantine Empire. In 1095, the Emperor of Byzantium appealed to Pope Urban II for help. Pope Urban II asked the knights of Europe to go on a pilgrimage which later b ...
... In 1071, Muslim Turks defeated the army of the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert and Turkish nomads settled in the Christian Byzantine Empire. In 1095, the Emperor of Byzantium appealed to Pope Urban II for help. Pope Urban II asked the knights of Europe to go on a pilgrimage which later b ...
If YOU were there `~
... do. Adventure called to them. The First Crusade About 5,000 Crusaders left Europe for the Holy Land in 1096. Some of the first ones to set out were peasants, not soldiers. On their way to the Holy Land, these peasant Crusaders attacked jews in Germany. They blamed the jews for jesus's death. ...
... do. Adventure called to them. The First Crusade About 5,000 Crusaders left Europe for the Holy Land in 1096. Some of the first ones to set out were peasants, not soldiers. On their way to the Holy Land, these peasant Crusaders attacked jews in Germany. They blamed the jews for jesus's death. ...
Medieval Study Guide1
... the crusades. Name the negative effects of the crusades. How did the Crusades affect the Jewish and Muslim populations? ...
... the crusades. Name the negative effects of the crusades. How did the Crusades affect the Jewish and Muslim populations? ...
Chapter 14.1
... Muslims had seized control of the Holy Land, including the holy city of Jerusalem The Holy Land (present- day Israel and Palestine) was considered holy and cherished by the three great monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam There were obviously religious motives, but there wer ...
... Muslims had seized control of the Holy Land, including the holy city of Jerusalem The Holy Land (present- day Israel and Palestine) was considered holy and cherished by the three great monotheistic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam There were obviously religious motives, but there wer ...
MEDIEVAL VOCABULARY ACTIVITY
... 1. ________________ were heavily armored soldiers who fought on horses. 2. First built out of wood, then later stone, _________________ were built for defense. 3. Wealth was based on owning ______________________. 4. The ___________________ were invaders from central Asia. 5. England was invaded by ...
... 1. ________________ were heavily armored soldiers who fought on horses. 2. First built out of wood, then later stone, _________________ were built for defense. 3. Wealth was based on owning ______________________. 4. The ___________________ were invaders from central Asia. 5. England was invaded by ...
group1powerpoint
... Roman popes and Byzantine emperors were rivals, but Urban still agreed. AT the Council of Clermont in 1095, Urban incited bishops ad nobles to action. He then called for a crusade to free the Holy Land. By 1096, thousands of knights were on their way to the Holy Land. Armies of ordinary men and wome ...
... Roman popes and Byzantine emperors were rivals, but Urban still agreed. AT the Council of Clermont in 1095, Urban incited bishops ad nobles to action. He then called for a crusade to free the Holy Land. By 1096, thousands of knights were on their way to the Holy Land. Armies of ordinary men and wome ...
Discipline History Course Title Bachelor of Arts (Omnibus
... This seminar examines the so-called ‘First Crusade’ in its 11th- & early 12th-century context through close analysis of contemporary documents & narrative accounts of events (in translation), including several written by crusaders & some by Greek, Muslim & Jewish commentators. It opens with discussi ...
... This seminar examines the so-called ‘First Crusade’ in its 11th- & early 12th-century context through close analysis of contemporary documents & narrative accounts of events (in translation), including several written by crusaders & some by Greek, Muslim & Jewish commentators. It opens with discussi ...
000A
... The Crusades were a long series of wars between Christians and Muslims in Southwest Asia. The Europeans fought the Muslims to retake Palestine. Christians call the region the Holy Land because it was where Jesus had lived, preached, and died. For many years Palestine had been ruled by Muslims. In ge ...
... The Crusades were a long series of wars between Christians and Muslims in Southwest Asia. The Europeans fought the Muslims to retake Palestine. Christians call the region the Holy Land because it was where Jesus had lived, preached, and died. For many years Palestine had been ruled by Muslims. In ge ...
The Causes of the Crusades
... The possibility of opening up new trade routes between Europe and the Middle East. Take another look at the reasons why Europeans were willing to fight. Which one would have convinced you most to go on a crusade? Why? ...
... The possibility of opening up new trade routes between Europe and the Middle East. Take another look at the reasons why Europeans were willing to fight. Which one would have convinced you most to go on a crusade? Why? ...
Ch. 14 Power Point
... each other and began to respect each other European Christians held onto Palestine for almost 100 years Turks eventually won back lands ...
... each other and began to respect each other European Christians held onto Palestine for almost 100 years Turks eventually won back lands ...
13-1 The Crusades screencast sheet
... IMPACTS OF THE CRUSADES All together, there were a total of nine Crusades that spanned the course of about 200 years. Militarily, they were a __________ because they did not ______________________________________. However, the Crusades would ultimately have a much larger and more important impact o ...
... IMPACTS OF THE CRUSADES All together, there were a total of nine Crusades that spanned the course of about 200 years. Militarily, they were a __________ because they did not ______________________________________. However, the Crusades would ultimately have a much larger and more important impact o ...
The Crusades
... • 11th & 13th centuries, European Christians carried out a series of military expeditions to take back the holy land from the Muslims • Seljuk Turks won the battle of Manzikert & threatened Constantinople • Crusades began when Pope Urban II responded to the request of Alexius I to liberate Jerusalem ...
... • 11th & 13th centuries, European Christians carried out a series of military expeditions to take back the holy land from the Muslims • Seljuk Turks won the battle of Manzikert & threatened Constantinople • Crusades began when Pope Urban II responded to the request of Alexius I to liberate Jerusalem ...
The Third Crusade
... crossing a river on horseback. German army disperses despite Leopold Richard, Phillip and the rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
... crossing a river on horseback. German army disperses despite Leopold Richard, Phillip and the rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
The Crusades The Crusades were a series of wars during
... from the Turks and to help push them out of the Holy Land. The Pope helped to gather an army, primarily with the help of the Franks and the Holy Roman Empire. ...
... from the Turks and to help push them out of the Holy Land. The Pope helped to gather an army, primarily with the help of the Franks and the Holy Roman Empire. ...
The Crusades
... journeyed to the holy land to fight in the name of God. Muslim Turks- group who had control of the Holy Land at the start of the 1st Crusade. King Richard I- called “Lion Heart” for his courage fought against the Muslims during the 3rd Crusade. Saladin-known as one of the greatest generals of ...
... journeyed to the holy land to fight in the name of God. Muslim Turks- group who had control of the Holy Land at the start of the 1st Crusade. King Richard I- called “Lion Heart” for his courage fought against the Muslims during the 3rd Crusade. Saladin-known as one of the greatest generals of ...
Crusades
... • King Richard and Saladin admired each other and made compromises. Though King Richard conquered some lands, he left with Jerusalem in Muslim hands. ...
... • King Richard and Saladin admired each other and made compromises. Though King Richard conquered some lands, he left with Jerusalem in Muslim hands. ...