The Peasant`s Crusade
... organized large numbers of peasants and low-ranking knights set off for Jerusalem. • Along the way they had a number of problems such as food shortages and lack of discipline. • About one-quarter of these troops died before reaching Constantinople. • Once in the Holy Land, they split up, and many we ...
... organized large numbers of peasants and low-ranking knights set off for Jerusalem. • Along the way they had a number of problems such as food shortages and lack of discipline. • About one-quarter of these troops died before reaching Constantinople. • Once in the Holy Land, they split up, and many we ...
File - Social Studies with Ms. Lyons
... (4) point of view 6) What was one direct result of the Crusades? (1) Trade increased between Europe and the Middle East. (2) Islamic kingdoms expanded into Europe. (3) Arabs and Christians divided the city of Jerusalem between them. (4) Alexander the Great became a powerful leader in Eurasia. Base ...
... (4) point of view 6) What was one direct result of the Crusades? (1) Trade increased between Europe and the Middle East. (2) Islamic kingdoms expanded into Europe. (3) Arabs and Christians divided the city of Jerusalem between them. (4) Alexander the Great became a powerful leader in Eurasia. Base ...
Middle Middle Ages - Osborne High School
... chastity, obedience, poverty, & sometimes silence nuns (called sisters) were women who did religious work from a convent & took the same vows as monks ...
... chastity, obedience, poverty, & sometimes silence nuns (called sisters) were women who did religious work from a convent & took the same vows as monks ...
File - HALDANE MUN 2016
... Four armies of Crusaders were formed from troops of different Western European regions, led by Raymond of Saint-Gilles, Godfrey of Bouillon, Hugh of Vermandois and Bohemond of Taranto (with his nephew Tancred); they were set to depart for Byzantium in August 1096. A less organized band of knights an ...
... Four armies of Crusaders were formed from troops of different Western European regions, led by Raymond of Saint-Gilles, Godfrey of Bouillon, Hugh of Vermandois and Bohemond of Taranto (with his nephew Tancred); they were set to depart for Byzantium in August 1096. A less organized band of knights an ...
Crusades Lesson Plan
... would "wear the cross of Christ on their right shoulder or back, and with one voice... cry out: 'God wills it, God wills it, God wills it!'" ii. Individual Crusaders joined for different reasons. 1. Some went to save their souls. a. They believed if they died on crusade they would go straight to hea ...
... would "wear the cross of Christ on their right shoulder or back, and with one voice... cry out: 'God wills it, God wills it, God wills it!'" ii. Individual Crusaders joined for different reasons. 1. Some went to save their souls. a. They believed if they died on crusade they would go straight to hea ...
Chapter 11 Pretest
... regain the Holy Land from the (a) Hindus. (b) Moors. (c) Jews. (d) Muslims. ...
... regain the Holy Land from the (a) Hindus. (b) Moors. (c) Jews. (d) Muslims. ...
Defending the Crusades
... Point of Criticism: The Crusaders were cruel in their conquest and in their administration of captured territories. False. Over the course of two centuries, a varied array of hundreds of thousands of European soldiers went to the Holy Land from many countries marching under a variety of kings and no ...
... Point of Criticism: The Crusaders were cruel in their conquest and in their administration of captured territories. False. Over the course of two centuries, a varied array of hundreds of thousands of European soldiers went to the Holy Land from many countries marching under a variety of kings and no ...
Middle Ages Reading Guide
... 53. Who was the most powerful of this line of kings? How old was he when he took the throne? 54. Who did this young king have great success over? 55. What honor was given to Henry’s grandson Louis IX? 56. What government body did he create? 57. What was the Estate’s General? What were the different ...
... 53. Who was the most powerful of this line of kings? How old was he when he took the throne? 54. Who did this young king have great success over? 55. What honor was given to Henry’s grandson Louis IX? 56. What government body did he create? 57. What was the Estate’s General? What were the different ...
Why were the Crusades a turning point in history?
... In the seventh century, Muslims conquered Palestine. Initially, the Muslim conquerors allowed Jews and Christians ...
... In the seventh century, Muslims conquered Palestine. Initially, the Muslim conquerors allowed Jews and Christians ...
Islamic Empires - Brookdale Community College
... dynasty at a dinner of peace, a few of them escaped, fled to Spain, and established Cordoba as their capital. The Great Mosque of Cordoba, begun in 786, contains all of the usual features of a mosque, but it is best known for its interior double set of horseshoe-shaped arches, one above the other, w ...
... dynasty at a dinner of peace, a few of them escaped, fled to Spain, and established Cordoba as their capital. The Great Mosque of Cordoba, begun in 786, contains all of the usual features of a mosque, but it is best known for its interior double set of horseshoe-shaped arches, one above the other, w ...
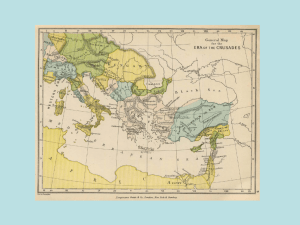
The impact of the crusades
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
the impact of the crusades
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
... formation of the crusader states in the Levant (the eastern Mediterranean), which were initially governed, and in small part populated, by settlers from Europe. Crusading in northern and eastern Europe led to the expansion of kingdoms like Denmark and Sweden, as well as the creation of brand-new pol ...
DBQ 1-10 guide
... emperor as patriarch. The Byzantine government went into exile in Nicaea and continued to fight the Latin occupiers until 1261, when they recaptured their capital. After the 4th Crusade, crusading lost much of its appeal for most Europeans. Jerusalem remained under Muslim control. ...
... emperor as patriarch. The Byzantine government went into exile in Nicaea and continued to fight the Latin occupiers until 1261, when they recaptured their capital. After the 4th Crusade, crusading lost much of its appeal for most Europeans. Jerusalem remained under Muslim control. ...
File
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
God Wills It! - cloudfront.net
... • Exchange of Ideas: Military technology, poetry and music, use of money, languages, architecture • Muslims remain in control of Jerusalem until WWI ...
... • Exchange of Ideas: Military technology, poetry and music, use of money, languages, architecture • Muslims remain in control of Jerusalem until WWI ...
First Crusade (1095-1099) Sixth Crusade
... expelled by another group called the Fatimid Muslims. The Fatimid Muslims had been friendly and accepting of Christian people, but the crusaders had come too far to be calmed. Even though the Fatimid Muslim people offered to share the city that is holy to both religions and give Christians easy acce ...
... expelled by another group called the Fatimid Muslims. The Fatimid Muslims had been friendly and accepting of Christian people, but the crusaders had come too far to be calmed. Even though the Fatimid Muslim people offered to share the city that is holy to both religions and give Christians easy acce ...
Medieval Europe - Robert Frost Middle School
... The Catholic Church Powerful rulers and devoted monks helped to spread Christianity throughout Europe. The Catholic Church became a strong and unifying force in Europe, controlling the lives of common people. Frequently, popes and kings worked together toward common goals. The Church’s wealth, effic ...
... The Catholic Church Powerful rulers and devoted monks helped to spread Christianity throughout Europe. The Catholic Church became a strong and unifying force in Europe, controlling the lives of common people. Frequently, popes and kings worked together toward common goals. The Church’s wealth, effic ...
crusade
... • Trade between Europe and Asia grew. • Muslim ideas were brought to Europe. • Some kings and nobles increased their power because others had died in the Crusades. • Due to the killings of the Jews, there was distrust between some Christians and Jews. • A mutual respect developed between some Christ ...
... • Trade between Europe and Asia grew. • Muslim ideas were brought to Europe. • Some kings and nobles increased their power because others had died in the Crusades. • Due to the killings of the Jews, there was distrust between some Christians and Jews. • A mutual respect developed between some Christ ...
7.38 crusades.pptx
... emphasis on the increasing contact by Europeans with cultures of the Eastern ...
... emphasis on the increasing contact by Europeans with cultures of the Eastern ...
The Crusades - Montgomery Township School District
... • Called for by Saint Bernard of Clairvaux in response to reports that Muslims were consolidating their forces and threatening the Christian states that had been established during the First Crusade (1144-Edessa recaptured by Muslims) • Not coordinated well between the armies of the two leaders (Kin ...
... • Called for by Saint Bernard of Clairvaux in response to reports that Muslims were consolidating their forces and threatening the Christian states that had been established during the First Crusade (1144-Edessa recaptured by Muslims) • Not coordinated well between the armies of the two leaders (Kin ...
Chapter 25
... • Many crusaders, who had lost much of their religious enthusiasm, returned home to western Europe, and some set up four feudal kingdoms called Outremer, or “the kingdom beyond the sea,” in the areas they won. • The crusaders took over the estates of rich Turkish and Arab Muslims and divided them am ...
... • Many crusaders, who had lost much of their religious enthusiasm, returned home to western Europe, and some set up four feudal kingdoms called Outremer, or “the kingdom beyond the sea,” in the areas they won. • The crusaders took over the estates of rich Turkish and Arab Muslims and divided them am ...
The Middle Ages: Europe
... Feudalism – Describe this social caste system. Vassalage – one lord swears allegiance to another in exchange for privileges. Feudalism is a hierarchy; at the top of the pyramid is the king, followed by his noble, knights, then at the bottom, the serfs or peasants Charlemagne – Why is he called the F ...
... Feudalism – Describe this social caste system. Vassalage – one lord swears allegiance to another in exchange for privileges. Feudalism is a hierarchy; at the top of the pyramid is the king, followed by his noble, knights, then at the bottom, the serfs or peasants Charlemagne – Why is he called the F ...
Church Reform and the Crusades.key
... rney eagerly for the remission sins, with the assurance of the of imperishable glory in the m of heaven. ...
... rney eagerly for the remission sins, with the assurance of the of imperishable glory in the m of heaven. ...
File
... by force Reasons for The Crusades - The Pope saw it as a chance to increase his power - Christians believed their sins would be forgiven if they fought in the Crusades and if they died they would go directly to heaven - Nobles hoped to gain wealth and land by participating and adventurers saw the Cr ...
... by force Reasons for The Crusades - The Pope saw it as a chance to increase his power - Christians believed their sins would be forgiven if they fought in the Crusades and if they died they would go directly to heaven - Nobles hoped to gain wealth and land by participating and adventurers saw the Cr ...