Name_________________________ Hour
... 1. What was the greatest prize which the holy war was fought for? -Who fought who? 2. Jerusalem has a troubled past and a troubled future. It is a holy city for 3 religions: -For the Jews, it was the location of the _________________________ of Herod and Solomon. -For Muslims, it is the place where ...
... 1. What was the greatest prize which the holy war was fought for? -Who fought who? 2. Jerusalem has a troubled past and a troubled future. It is a holy city for 3 religions: -For the Jews, it was the location of the _________________________ of Herod and Solomon. -For Muslims, it is the place where ...
The Crusades
... the Holy Land (Fatimids) Turkish Muslims conquests in Europe Stories of persecuting Christians Turks attacked Byzantine Empire 1071 Turks destroy most of Byzantine army ...
... the Holy Land (Fatimids) Turkish Muslims conquests in Europe Stories of persecuting Christians Turks attacked Byzantine Empire 1071 Turks destroy most of Byzantine army ...
The crusaders - Happy Kids Cooking Healthy
... horse to his rival, Richard the Lion-heart, who lost his horse in the battle. ...
... horse to his rival, Richard the Lion-heart, who lost his horse in the battle. ...
14.1 The Crusades-teacher version
... Where would the Christians, Muslims, and Jews all consider their holy land? Called Palestine at the time, now Jerusalem in Israel ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Who gained control of Palestine (The Holy Land to Christians) during the la ...
... Where would the Christians, Muslims, and Jews all consider their holy land? Called Palestine at the time, now Jerusalem in Israel ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Who gained control of Palestine (The Holy Land to Christians) during the la ...
Pope Urban II called for a crusade after the Byzantine Emperor
... • Pope Urban II called for a crusade after the Byzantine Emperor asked for assistance against the Turks. ...
... • Pope Urban II called for a crusade after the Byzantine Emperor asked for assistance against the Turks. ...
Name Class Date The Crusades were a series of wars in which
... Pope Urban II for help, and Urban launched the Crusades to free the Holy Land. Only the First Crusade was a success for Christians, who captured Jerusalem in 1099. In the Second Crusade, Jerusalem fell to the great Muslim leader Saladin. He agreed to reopen the city to Christian pilgrims after crusa ...
... Pope Urban II for help, and Urban launched the Crusades to free the Holy Land. Only the First Crusade was a success for Christians, who captured Jerusalem in 1099. In the Second Crusade, Jerusalem fell to the great Muslim leader Saladin. He agreed to reopen the city to Christian pilgrims after crusa ...
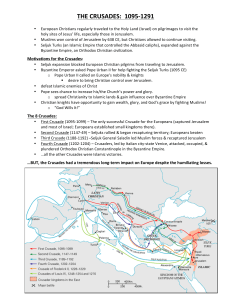
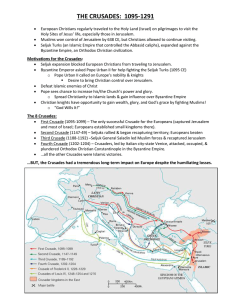
The Crusading Spirit Dwindles
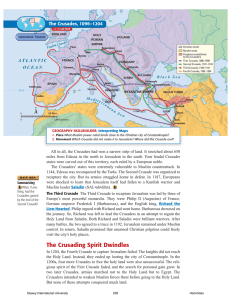
... All in all, the Crusaders had won a narrow strip of land. It stretched about 650 miles from Edessa in the north to Jerusalem in the south. Four feudal Crusader states were carved out of this territory, each ruled by a European noble. The Crusaders’ states were extremely vulnerable to Muslim countera ...
... All in all, the Crusaders had won a narrow strip of land. It stretched about 650 miles from Edessa in the north to Jerusalem in the south. Four feudal Crusader states were carved out of this territory, each ruled by a European noble. The Crusaders’ states were extremely vulnerable to Muslim countera ...
The Crusades
... • From 1189 to 1192, Barbarossa of HRE, King Phillip of Fr. And King Richard of Eng. – Barbarossa died on the way down. – Phillip and Richard fought over whose plan to use. • Phillip went home and Richard stayed. • Did not re-capture Jerusalem, signed a treaty with Saladin. • Allowed Christians to e ...
... • From 1189 to 1192, Barbarossa of HRE, King Phillip of Fr. And King Richard of Eng. – Barbarossa died on the way down. – Phillip and Richard fought over whose plan to use. • Phillip went home and Richard stayed. • Did not re-capture Jerusalem, signed a treaty with Saladin. • Allowed Christians to e ...
1. The green part on the map below shows Eurasia.
... A. Christians gained control over the Holy Land. B. Europeans learned a lot of advanced science and math from the Muslim scholars C. Trade routes grew between Europe and Asia D. Mistrust grew between Christians, Jews, and Muslims ...
... A. Christians gained control over the Holy Land. B. Europeans learned a lot of advanced science and math from the Muslim scholars C. Trade routes grew between Europe and Asia D. Mistrust grew between Christians, Jews, and Muslims ...
Humanity 258 - WordPress.com
... and the battle cry of “God wills it!” on their lips, knights and commoners were fired by religious zeal and became Crusaders. By early 1097, three armies of knights and people of all classes had gathered outside Constantinople. Most of the Crusaders were French, but Bohemians, Germans, Englishmen, S ...
... and the battle cry of “God wills it!” on their lips, knights and commoners were fired by religious zeal and became Crusaders. By early 1097, three armies of knights and people of all classes had gathered outside Constantinople. Most of the Crusaders were French, but Bohemians, Germans, Englishmen, S ...
Crusades! - honorsworld1
... and attacked and captured the city. The Western leaders held the city from 1204 until the Byzantine threw them out in 1261. – The Western Christians destroyed churches, icons, ...
... and attacked and captured the city. The Western leaders held the city from 1204 until the Byzantine threw them out in 1261. – The Western Christians destroyed churches, icons, ...
the Crusades
... Frederick Barbarossa of H.R.E, Philip II of France, and Richard I of England led 3 armies Barbarossa drowned on the way to the Holy Land; his army turned back to Europe Philip took his army back to seize English lands in France ...
... Frederick Barbarossa of H.R.E, Philip II of France, and Richard I of England led 3 armies Barbarossa drowned on the way to the Holy Land; his army turned back to Europe Philip took his army back to seize English lands in France ...
The Crusades
... The Crusades • The crusades were a series of eight wars initiated by the Christians to win back their holy lands ( Jerusalem and other sites) from the Muslims. • Around this time the kingdoms of Europe had one thing in ...
... The Crusades • The crusades were a series of eight wars initiated by the Christians to win back their holy lands ( Jerusalem and other sites) from the Muslims. • Around this time the kingdoms of Europe had one thing in ...
Dr. Franco Cardini - morganhighhistoryacademy.org
... 8. Who had already conquered two-thirds of Europe when the preaching of Crusades began in 1095? 9. Who asked for help from Western Christians from Muslim invaders? ...
... 8. Who had already conquered two-thirds of Europe when the preaching of Crusades began in 1095? 9. Who asked for help from Western Christians from Muslim invaders? ...
THE CRUSADES: 1095
... § desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o spread Christianity to Islamic lands & gain influence ov ...
... § desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o spread Christianity to Islamic lands & gain influence ov ...
the crusades: 1095-1291
... Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o Spread Christianity to Islamic lands & gain influence over Byzantine Empire Christian knights have opportunity to gain wealth, glory, and God’s ...
... Desire to bring Christian control over Jerusalem. Defeat Islamic enemies of Christ Pope sees chance to increase his/the Church’s power and glory. o Spread Christianity to Islamic lands & gain influence over Byzantine Empire Christian knights have opportunity to gain wealth, glory, and God’s ...
The Crusades - GEOCITIES.ws
... Palestine and Philip went home Richard fought but lost and made an arrangement with Saladin that Christians could still visit the Holy Land ...
... Palestine and Philip went home Richard fought but lost and made an arrangement with Saladin that Christians could still visit the Holy Land ...
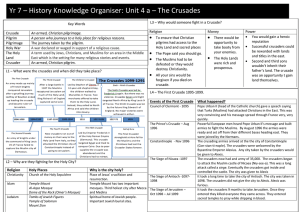
Unit 4 a – The Crusades
... Pope Urban II (head of the Catholic church) gave a speech saying that Turks (Muslims) had attacked Christians in the East. This was very convincing and his message spread through France very, very quickly. Powerful European men heard Pope Urban II’s message and built armies to fight the Muslims. By ...
... Pope Urban II (head of the Catholic church) gave a speech saying that Turks (Muslims) had attacked Christians in the East. This was very convincing and his message spread through France very, very quickly. Powerful European men heard Pope Urban II’s message and built armies to fight the Muslims. By ...
Fourth Crusade

The Fourth Crusade (1202–04) was a Western European armed expedition originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. However, in January 1203, en route to Jerusalem, the majority of the crusader leadership entered into an agreement with the Byzantine prince Alexios Angelos to divert to Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire and restore his deposed father as emperor. The intention of the crusaders was to then continue to the Holy Land with promised Byzantine financial and military assistance. On 23 June 1203 the main crusader fleet reached Constantinople. Smaller contingents continued to Acre.In August 1203, following clashes outside Constantinople, Alexios Angelos was crowned as co-Emperor (Alexios IV Angelos) with crusader support. However, in January 1204, he was deposed by a popular uprising in Constantinople. The Western crusaders were no longer able to receive their promised payments, and when Alexios IV was murdered on 8 February 1204, the crusaders and Venetians decided on the outright conquest of Constantinople. In April 1204, they captured and brutally sacked the city, and set up a new Latin Empire as well as partitioning other Byzantine territories between themselves.Byzantine resistance based on unconquered sections of the empire such as Nicaea, Trebizond, and Epirus ultimately recovered Constantinople.The Fourth Crusade is considered to be one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, and a key turning point in the decline of the Byzantine Empire.