Slide 1
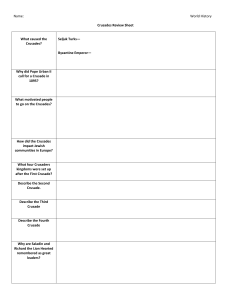
... 4. What happens when they first get to Jerusalem? 5. How long did fighting last? 6. Who declared a Jihad? 7. What is the ultimate prize taken by the Muslims in 1188? ...
... 4. What happens when they first get to Jerusalem? 5. How long did fighting last? 6. Who declared a Jihad? 7. What is the ultimate prize taken by the Muslims in 1188? ...
The Fall and Influence of the Byzantines
... • Instead attacks port of Zara in Dalmatia – then moves onto Constantinople (Alexios III offered to pay for Egyptian attack) • In 1204 they ransacked the city and burned most of it to the ground. • They raped, pillaged, and stole priceless artifacts. • Byzantines went through three Emperors in a mat ...
... • Instead attacks port of Zara in Dalmatia – then moves onto Constantinople (Alexios III offered to pay for Egyptian attack) • In 1204 they ransacked the city and burned most of it to the ground. • They raped, pillaged, and stole priceless artifacts. • Byzantines went through three Emperors in a mat ...
The Third Crusade
... Who was involved? -Richard I of England -Phillip II Augustus of France Frederick I (Barbarossa) the Holy Roman Emperor Saladin ...
... Who was involved? -Richard I of England -Phillip II Augustus of France Frederick I (Barbarossa) the Holy Roman Emperor Saladin ...
The Crusades
... Barbarossa drowned negotiate a and his army fell settlement with apart Saladin to allow Richard and Phillip Christian pilgrims free had some success access to Jerusalem along the coast, but failed miserably inland Phillip goes back home ...
... Barbarossa drowned negotiate a and his army fell settlement with apart Saladin to allow Richard and Phillip Christian pilgrims free had some success access to Jerusalem along the coast, but failed miserably inland Phillip goes back home ...
chapter 11 religion
... THEY ACT IN DIRESPECTFUL WAYS TO PEOPLE OF OTHER RELIGIONS. THE GOSPEL OF JESUS CHRIST NEVER CALLS UPON US TO DISRESPECT ANYONE FOR ANY REASON! ...
... THEY ACT IN DIRESPECTFUL WAYS TO PEOPLE OF OTHER RELIGIONS. THE GOSPEL OF JESUS CHRIST NEVER CALLS UPON US TO DISRESPECT ANYONE FOR ANY REASON! ...
The Crusades: Origins, Motivations, and Ideals
... crusade in the 13th century; that endeavor, known as the Fourth Crusade, resulted in the sack of Christian Constantinople by Christian European knights. The Europeans were eventually ousted from Constantinople, but the capital of Eastern Christendom never quite recovered from the blow. Its weakened ...
... crusade in the 13th century; that endeavor, known as the Fourth Crusade, resulted in the sack of Christian Constantinople by Christian European knights. The Europeans were eventually ousted from Constantinople, but the capital of Eastern Christendom never quite recovered from the blow. Its weakened ...
The Crusades - Nutley Public Schools
... • Made up of untrained and illiterate mostly peasants with some knights. • Lacked military discipline and knowledge and were massacred in Asia Minor by the Turks. ...
... • Made up of untrained and illiterate mostly peasants with some knights. • Lacked military discipline and knowledge and were massacred in Asia Minor by the Turks. ...
Cause and Effects of The Crusades
... Pope Urban thought by helping Alexius he would also: • Increase his power in Europe • Heal the split (schism) between the Roman an Byzantine churches • Unite the Christians in fighting the Muslims rather than each other ...
... Pope Urban thought by helping Alexius he would also: • Increase his power in Europe • Heal the split (schism) between the Roman an Byzantine churches • Unite the Christians in fighting the Muslims rather than each other ...
The Crusades
... – King of England (spent only 6 months of his reign in England) – Led 3rd Crusade, forced to sue for peace with Saladin ...
... – King of England (spent only 6 months of his reign in England) – Led 3rd Crusade, forced to sue for peace with Saladin ...
11.4 Christians and the Crusades
... powerful, as nobles and knights left home to fight in the Middle East. The increasing power of monarchs weakened feudalism. Contact with Middle Eastern cultures had a major impact on Christians’ way of life. In the Holy Land, Christians learned about new foods and other goods. They dressed in clothi ...
... powerful, as nobles and knights left home to fight in the Middle East. The increasing power of monarchs weakened feudalism. Contact with Middle Eastern cultures had a major impact on Christians’ way of life. In the Holy Land, Christians learned about new foods and other goods. They dressed in clothi ...
The Earth and Its Peoples: Chapter 9 – Christian Europe Emerges
... Norman Christians/European nobles’ younger sons desired new lands to conquer and titles to maintain their status Italian city-states wanted to increase Mediterranean trade and establish trading posts in Muslim lands Pope’s political struggle with kings also a factor, as church constantly seeki ...
... Norman Christians/European nobles’ younger sons desired new lands to conquer and titles to maintain their status Italian city-states wanted to increase Mediterranean trade and establish trading posts in Muslim lands Pope’s political struggle with kings also a factor, as church constantly seeki ...
The Crusades Info Page
... Jerusalem’s fall in 1187 to Salah al-‐Din (Saladin). Saladin’s victory shocked the European world. On hearing the news, Pope Urban III had a heart attack and died. Richard the Lion-‐hearted of Eng ...
... Jerusalem’s fall in 1187 to Salah al-‐Din (Saladin). Saladin’s victory shocked the European world. On hearing the news, Pope Urban III had a heart attack and died. Richard the Lion-‐hearted of Eng ...
File - Mr. Miller`s Online Classroom
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantium Empire Greek Orthodox and Roman Catholic Church split from one another. Turkish Muslims had taken control of the Holy Land—No more pilgrimages! ...
... Holy Roman Empire and Byzantium Empire Greek Orthodox and Roman Catholic Church split from one another. Turkish Muslims had taken control of the Holy Land—No more pilgrimages! ...
The Crusades Notes (295-302)
... Pope Gregory called for a third Crusade which went badly from the beginning. ...
... Pope Gregory called for a third Crusade which went badly from the beginning. ...
The Middle Ages
... the Islamic groups out of the holy land First Crusade: fought by a combined total of over ...
... the Islamic groups out of the holy land First Crusade: fought by a combined total of over ...
Chapter 9
... Justinian codification of Roman law resulted in The Body of Civil Law. Under early Germanic law, a wrongdoer had to pay wergild, or “money for a man,” to the family of the person he injured or killed. Under Germanic law, if an accused person was unharmed after a physical trial, or ordeal, he or s ...
... Justinian codification of Roman law resulted in The Body of Civil Law. Under early Germanic law, a wrongdoer had to pay wergild, or “money for a man,” to the family of the person he injured or killed. Under Germanic law, if an accused person was unharmed after a physical trial, or ordeal, he or s ...
The Crusades
... • Barbarossa drowned while swimming in a river • English & French had success with their naval fleets against coastal cities, but failed as they moved inland • Richard I negotiated a settlement with Saladin to allow Christian pilgrims free access to Jerusalem ...
... • Barbarossa drowned while swimming in a river • English & French had success with their naval fleets against coastal cities, but failed as they moved inland • Richard I negotiated a settlement with Saladin to allow Christian pilgrims free access to Jerusalem ...
The Crusades - Cobb Learning
... • The Crusades had economic, social, and political goals as well as religious motives. • Muslims had control of Palestine and threatened Constantinople. • Offered kings & the Church both an opportunity to rid of quarrelsome knights who fought each other. • Younger sons were seeking land and fame. • ...
... • The Crusades had economic, social, and political goals as well as religious motives. • Muslims had control of Palestine and threatened Constantinople. • Offered kings & the Church both an opportunity to rid of quarrelsome knights who fought each other. • Younger sons were seeking land and fame. • ...
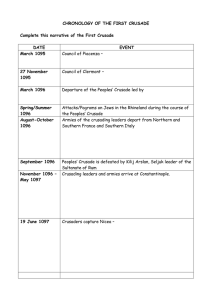
chronology of the first crusade
... Peoples’ Crusade is defeated by Kilij Arslan, Seljuk leader of the Sultanate of Rum Crusading leaders and armies arrive at Constantinople. ...
... Peoples’ Crusade is defeated by Kilij Arslan, Seljuk leader of the Sultanate of Rum Crusading leaders and armies arrive at Constantinople. ...
Fourth Crusade

The Fourth Crusade (1202–04) was a Western European armed expedition originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. However, in January 1203, en route to Jerusalem, the majority of the crusader leadership entered into an agreement with the Byzantine prince Alexios Angelos to divert to Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire and restore his deposed father as emperor. The intention of the crusaders was to then continue to the Holy Land with promised Byzantine financial and military assistance. On 23 June 1203 the main crusader fleet reached Constantinople. Smaller contingents continued to Acre.In August 1203, following clashes outside Constantinople, Alexios Angelos was crowned as co-Emperor (Alexios IV Angelos) with crusader support. However, in January 1204, he was deposed by a popular uprising in Constantinople. The Western crusaders were no longer able to receive their promised payments, and when Alexios IV was murdered on 8 February 1204, the crusaders and Venetians decided on the outright conquest of Constantinople. In April 1204, they captured and brutally sacked the city, and set up a new Latin Empire as well as partitioning other Byzantine territories between themselves.Byzantine resistance based on unconquered sections of the empire such as Nicaea, Trebizond, and Epirus ultimately recovered Constantinople.The Fourth Crusade is considered to be one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, and a key turning point in the decline of the Byzantine Empire.