* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Arsuf wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
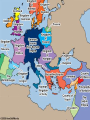
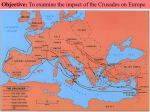
The Crusades An extended religious war fought between Christian and Muslim forces for possession of Jerusalem and the Holy Land 1095-1291 The rundown… • European Christians (England, France, Italy, Germany, & Turkey) • vs. Middle Eastern Muslims (Palestine, Syria, Egypt, & North Africa) • Fought mostly in Anatolia (Turkey), the Holy Land, & Egypt • Led to clash of Eastern vs. Western cultures and exchange of ideas, food, etc. Key Events • 634-44: Holy Land conquered by Muslims • 1095: Byzantine emperor asks Pope for help • 1096: First Crusade begins • 1099: Jerusalem captured by Christians • 1147: Second Crusade begins • 1187: Jerusalem captured by Muslims • 1189: Third Crusade begins • 1204: Crusaders sack Constantinople • 1291: Last crusader outpost in Holy Land, Acre, falls Strategy Crusaders • Recapture Holy Land in name of Christianity • Organized territory on feudal lines • Defend conquests in Holy Land with castle • Turn European aggression outward • Offer immediate forgiveness of sins to Crusaders Muslims • Repulse Christian attacks • Avoid civil wars between Muslim states Tactics Crusaders • Center of attack was charge of heavy cavalry (knights) • Shock of heavy cavalry charge was meant to shatter the enemy • Foot soldiers, archers used to support main attack Muslims • Widely used fast moving mounted archers • Main component of army was Mamluks (turkish military slaves) Technology Crusaders • Lances • Swords • Iron helmets and chain mail tunics • Kite-shaped shields • Footsoldiers armed with what they could afford • crossbows Muslims • Lightly armored, leather or horn tunics • Iron helmets • Heavy cavalry had chain mail • Composite bows Leadership Crusaders • GUY OF LUSIGNAN – King of Jerusalem 1185 – Attempted to relieve garrison at Tiberias – Marched army from sources of water – Crushed at Battle of Hattin by Saladin – Led to Muslim conquest of Jerusalem • RICHARD THE LIONHEART – King of England (spent only 6 months of his reign in England) – Led 3rd Crusade, forced to sue for peace with Saladin Muslims • SALADIN – Kurdish Muslim who unified Egypt & Syria after sezing power in 1174 – United Muslims against Crsuaders – Captured Jerusalem around 1187 – Employed scorched earth methods against Richard – His chivalrous actions led to his legend during the Crusades Logistics Crusaders • Establish bases in Holy Land • Depended on influx of European soldiers motivated by religion and/or greed • Distance from Europe made success difficult Muslims • Wear down Crusader armies • Depended on Mamluks and other soldiers from nearby Middle Eastern states • Benefitted from geographical location “home turf” Military Orders • Several religious military orders were formed in the Holy Land during the Crusades – Templars – Hospitallers – Teutonic Knights The Northern Crusade