1 Social Studies Name: Directions: Complete the
... approached Jerusalem, though he refused to lay siege to the city. In September 1192, ____________________________________________ that reestablished the Kingdom of Jerusalem (though without the city of Jerusalem) and ended the Third Crusade. 16. During the “Fourth Crusade”, explain where the crusade ...
... approached Jerusalem, though he refused to lay siege to the city. In September 1192, ____________________________________________ that reestablished the Kingdom of Jerusalem (though without the city of Jerusalem) and ended the Third Crusade. 16. During the “Fourth Crusade”, explain where the crusade ...
The Third Crusade
... Richard, Phillip and the rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
... Richard, Phillip and the rest of the German army defeat Saladin at the Battle of Acre. Phillip and Leopold leave b/c Richard is being difficult slaughters 3,000 Muslims when Saladin is slow to pay. ...
Ch 6.2 Powerpoint
... Another group of monks called the Franciscans was started by St. Francis of Assissi. They lived among the people, preaching repentance and aiding the people. Another group the Dominicans wanted to defend the church from heresy - the denial of basic church doctrines. The became the examiners of peop ...
... Another group of monks called the Franciscans was started by St. Francis of Assissi. They lived among the people, preaching repentance and aiding the people. Another group the Dominicans wanted to defend the church from heresy - the denial of basic church doctrines. The became the examiners of peop ...
ED–The_Middle_Ages - Reeths
... • In the Fourth Crusade, crusaders attacked and plundered Constantinople, the city they had originally come to protect! • For the next 68 years, four more crusades were fought, but the Holy Land remained under Muslim control. • Crusaders had ruined much of the land through which they traveled, inclu ...
... • In the Fourth Crusade, crusaders attacked and plundered Constantinople, the city they had originally come to protect! • For the next 68 years, four more crusades were fought, but the Holy Land remained under Muslim control. • Crusaders had ruined much of the land through which they traveled, inclu ...
Standard: SSWH5 - Mr. Holmes Wonderful World of History
... the Crusaders reversed a seemingly hopeless situation when a peasant found a ________ that had pierced the side of Christ’s side hidden under a church, thereby raising morale enough to win the day. By 1100CE European nobles held both Antioch and Jerusalem as ________ Christian kingdoms (most Christi ...
... the Crusaders reversed a seemingly hopeless situation when a peasant found a ________ that had pierced the side of Christ’s side hidden under a church, thereby raising morale enough to win the day. By 1100CE European nobles held both Antioch and Jerusalem as ________ Christian kingdoms (most Christi ...
The crusader States
... soldiers were so upset that they returned home. Only a fraction of the original army made it to the Holy land. Barbarossa’s death was a bitter blow to the crusaders. Eventually both Kings set off, travelling by sea rather than overland. Their journey was slow. At Acre they met Guy of Jerusalem. He ...
... soldiers were so upset that they returned home. Only a fraction of the original army made it to the Holy land. Barbarossa’s death was a bitter blow to the crusaders. Eventually both Kings set off, travelling by sea rather than overland. Their journey was slow. At Acre they met Guy of Jerusalem. He ...
The Crusades - Union Academy
... and drove all Christians out of Jerusalem. Led by three men King Richard the Lion ...
... and drove all Christians out of Jerusalem. Led by three men King Richard the Lion ...
The Crusades were military campaigns sanctioned by
... Crusade was the last crusade sponsored by the papacy. Jerusalem was held for nearly a century after the Fourth Crusade and other strongholds in the Near East would remain in Christian possession much longer, but the crusades in the Holy Land ultimately failed to establish permanent Christian kingdom ...
... Crusade was the last crusade sponsored by the papacy. Jerusalem was held for nearly a century after the Fourth Crusade and other strongholds in the Near East would remain in Christian possession much longer, but the crusades in the Holy Land ultimately failed to establish permanent Christian kingdom ...
THE CRUSADERS
... 4. Why did the Crusaders want to seize Antioch prior to moving on toward Jerusalem? What would have been the likely result if they had not taken Antioch? How did Bohemond finally make entry into Antioch, fostering the eventual Christian takeover? ...
... 4. Why did the Crusaders want to seize Antioch prior to moving on toward Jerusalem? What would have been the likely result if they had not taken Antioch? How did Bohemond finally make entry into Antioch, fostering the eventual Christian takeover? ...
Challenges to Islam
... a serious blow to the Byzantine Empire Much of Anatolia is now under Seljuk Turk control ...
... a serious blow to the Byzantine Empire Much of Anatolia is now under Seljuk Turk control ...
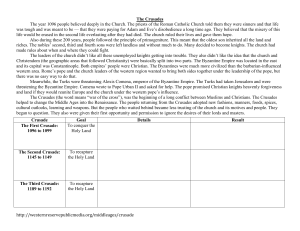
From 1189-1192 – Richard I of England, Philip II of France, and
... and Norman nobles led the first Crusade, which turns out to be only successful one. The Byzantine emperor worried about the Christian armies, but finally allowed them to pass through. ( he had reason to worry). The Crusaders captured Antioch, Jersusalem, Edessa and Tripoli. The 2nd Crusade beg ...
... and Norman nobles led the first Crusade, which turns out to be only successful one. The Byzantine emperor worried about the Christian armies, but finally allowed them to pass through. ( he had reason to worry). The Crusaders captured Antioch, Jersusalem, Edessa and Tripoli. The 2nd Crusade beg ...
The Crusades - Living in Medieval Europe
... shall not fall into the hands of the Turks. . . . Therefore act while there is still time lest the kingdom of the Christians shall vanish from your sight and, what is more important, the Holy Sepulchre [the tomb where Jesus was buried] shall vanish. And in your coming you will find your reward in he ...
... shall not fall into the hands of the Turks. . . . Therefore act while there is still time lest the kingdom of the Christians shall vanish from your sight and, what is more important, the Holy Sepulchre [the tomb where Jesus was buried] shall vanish. And in your coming you will find your reward in he ...
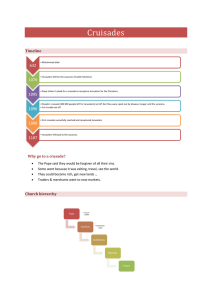
The Crusades The year 1096 people believed deeply in the Church
... and its capital was Constantinople. Both empires’ people were Christian. The Byzantines were much more civilized than the barbarian-influenced western area. Rome’s pope and the church leaders of the western region wanted to bring both sides together under the leadership of the pope, but there was no ...
... and its capital was Constantinople. Both empires’ people were Christian. The Byzantines were much more civilized than the barbarian-influenced western area. Rome’s pope and the church leaders of the western region wanted to bring both sides together under the leadership of the pope, but there was no ...
The Middle Ages
... • The letter to the pope begged for help, so that the Holy Sepulcher, Christ’s tomb in Jerusalem, would not be destroyed. – At the Council of Clermont, Pope Urban II declared a holy war in the East – The pope called for this crusade to help the Byzantine Empire, to assert his own leadership in the W ...
... • The letter to the pope begged for help, so that the Holy Sepulcher, Christ’s tomb in Jerusalem, would not be destroyed. – At the Council of Clermont, Pope Urban II declared a holy war in the East – The pope called for this crusade to help the Byzantine Empire, to assert his own leadership in the W ...
Word - Saint Mary`s Press
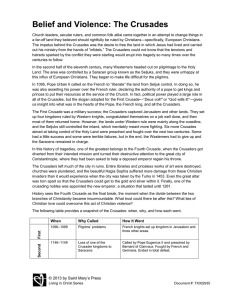
... Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the land in which Jesus had lived and ...
... Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the land in which Jesus had lived and ...
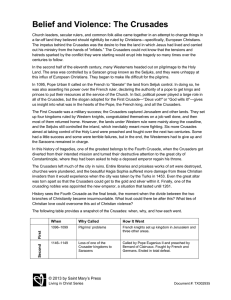
Belief and Violence: The Crusades
... Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the land in which Jesus had lived and ...
... Church leaders, secular rulers, and common folk alike came together in an attempt to change things in a far-off land they believed should rightfully be ruled by Christians—specifically, European Christians. The impetus behind the Crusades was the desire to free the land in which Jesus had lived and ...
Crusades Practice Test Questions
... 1. Which of the following Crusades was the ONLY one to capture Jerusalem? A. First B. Second C. Third D. Fourth 2. Which of the following popes called the First Crusade in an effort to take Jerusalem from the Muslims? A. Leo X B. Urban II C. Julius III D. Boniface VII 3. Which of the following Musli ...
... 1. Which of the following Crusades was the ONLY one to capture Jerusalem? A. First B. Second C. Third D. Fourth 2. Which of the following popes called the First Crusade in an effort to take Jerusalem from the Muslims? A. Leo X B. Urban II C. Julius III D. Boniface VII 3. Which of the following Musli ...
The Crusades
... ▫ It represented God and the righteous beliefs with which the Crusaders fought their campaign ...
... ▫ It represented God and the righteous beliefs with which the Crusaders fought their campaign ...
The Crusades!
... We believe that the Greeks have been punished through [the Crusades] by the just judgement of God: these Greeks who have striven to rend the Seamless Robe of Jesus Christ ... Those who would not join Noah in his ark perished justly in the deluge; and these have justly suffered famine and hunger who ...
... We believe that the Greeks have been punished through [the Crusades] by the just judgement of God: these Greeks who have striven to rend the Seamless Robe of Jesus Christ ... Those who would not join Noah in his ark perished justly in the deluge; and these have justly suffered famine and hunger who ...
The Crusades - WordPress.com
... tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When th ...
... tragedy. Many thousands of French and German children died trying to reach Jerusalem. They believed God would help them because they were children. Many died of hunger. Other froze to death. When the survivors reached the Mediterranean Sea, they expected the waters to part and let them pass. When th ...
Document
... • Richard, Saladin admired each other as military leaders, gentlemen • Made proposals for peace, including marriage alliance of Richard’s sister, Saladin’s brother; never took place because of religious differences ...
... • Richard, Saladin admired each other as military leaders, gentlemen • Made proposals for peace, including marriage alliance of Richard’s sister, Saladin’s brother; never took place because of religious differences ...
TCI CH10 Interactive Notebook Answer Key
... Some of the Crusaders stayed in the Holy Land to establish four Crusader kingdoms. Second Crusade: As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in An ...
... Some of the Crusaders stayed in the Holy Land to establish four Crusader kingdoms. Second Crusade: As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in An ...
TCI CH10 Interactive Notebook Answer Key
... Some of the Crusaders stayed in the Holy Land to establish four Crusader kingdoms. Second Crusade: As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in An ...
... Some of the Crusaders stayed in the Holy Land to establish four Crusader kingdoms. Second Crusade: As Muslims banded together, they fought against the Crusader kingdoms, which led Christians to call for a Second Crusade. The Crusade ended in failure after German and French armies were defeated in An ...
The Crusades
... • Christians lost foothold in Holy Land • Saladin ruler of Egypt took Jerusalem in 1187 ...
... • Christians lost foothold in Holy Land • Saladin ruler of Egypt took Jerusalem in 1187 ...
Fourth Crusade

The Fourth Crusade (1202–04) was a Western European armed expedition originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. However, in January 1203, en route to Jerusalem, the majority of the crusader leadership entered into an agreement with the Byzantine prince Alexios Angelos to divert to Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire and restore his deposed father as emperor. The intention of the crusaders was to then continue to the Holy Land with promised Byzantine financial and military assistance. On 23 June 1203 the main crusader fleet reached Constantinople. Smaller contingents continued to Acre.In August 1203, following clashes outside Constantinople, Alexios Angelos was crowned as co-Emperor (Alexios IV Angelos) with crusader support. However, in January 1204, he was deposed by a popular uprising in Constantinople. The Western crusaders were no longer able to receive their promised payments, and when Alexios IV was murdered on 8 February 1204, the crusaders and Venetians decided on the outright conquest of Constantinople. In April 1204, they captured and brutally sacked the city, and set up a new Latin Empire as well as partitioning other Byzantine territories between themselves.Byzantine resistance based on unconquered sections of the empire such as Nicaea, Trebizond, and Epirus ultimately recovered Constantinople.The Fourth Crusade is considered to be one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, and a key turning point in the decline of the Byzantine Empire.