Thermodynamic Symbols and Constants
... HoT - Ho298 is the enthalpy at the standard state T less the enthalpy at the standard state at 298.15 K. (GoT - Ho298)/T is the Gibbs energy function and is equal to (HoT - Ho298)/T - SoT. This function is tabulated because it shows greater linearity than GoT thus facilitating interpolation between ...
... HoT - Ho298 is the enthalpy at the standard state T less the enthalpy at the standard state at 298.15 K. (GoT - Ho298)/T is the Gibbs energy function and is equal to (HoT - Ho298)/T - SoT. This function is tabulated because it shows greater linearity than GoT thus facilitating interpolation between ...
Course 2 – Mathematical Tools and Unit Conversion Used in
... It is energy in transit, not stored in the system as heat but as kinetic and potential energy of the atoms The rate of heat transfer from one body to another is proportional to the difference in temperature 1 calorie = the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 °C ...
... It is energy in transit, not stored in the system as heat but as kinetic and potential energy of the atoms The rate of heat transfer from one body to another is proportional to the difference in temperature 1 calorie = the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 °C ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a t ...
... observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a t ...
název projektu
... If two or more objects are in thermodynamic equilibrium with other object, all these objects are in equilibrium ...
... If two or more objects are in thermodynamic equilibrium with other object, all these objects are in equilibrium ...
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter
... The total KE of a substance is equal to the thermal energy of the substance. • Predict: What happens to the temperature when molecules speed up? • Predict: What happens to the temperature when more molecules are added? • Do the results seem reasonable? • Tub of hot water vs glass of hot water… • Wh ...
... The total KE of a substance is equal to the thermal energy of the substance. • Predict: What happens to the temperature when molecules speed up? • Predict: What happens to the temperature when more molecules are added? • Do the results seem reasonable? • Tub of hot water vs glass of hot water… • Wh ...
Thermodynamics - WordPress.com
... Latent Heat Latent heat of fusion: energy needed to melt a solid without a temperature rise Latent heat of vaporization: energy needed to boil a liquid without a temperature rise. Energy = mass × spedific latent heat ...
... Latent Heat Latent heat of fusion: energy needed to melt a solid without a temperature rise Latent heat of vaporization: energy needed to boil a liquid without a temperature rise. Energy = mass × spedific latent heat ...
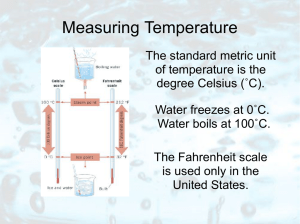
Measuring Temperature
... average kinetic energy of moving molecules. The faster the molecules move, the higher the temperature. ...
... average kinetic energy of moving molecules. The faster the molecules move, the higher the temperature. ...
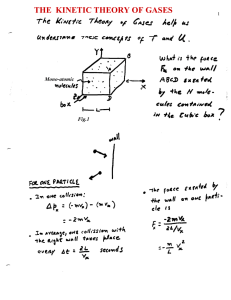
the kinetic theory of gases
... differently. A constant conversion factor k is introduced between the average kinetic energy of a molecule < ½ mv2 > and the , thus defined, absolute temperature scale T. < ½ mv2 > ≡ 3/2 k T ...
... differently. A constant conversion factor k is introduced between the average kinetic energy of a molecule < ½ mv2 > and the , thus defined, absolute temperature scale T. < ½ mv2 > ≡ 3/2 k T ...
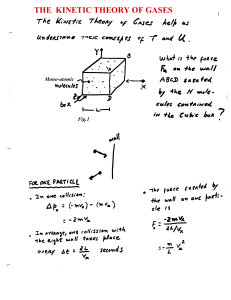
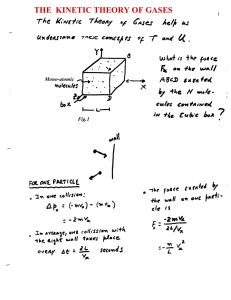
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
... differently. A constant conversion factor k is introduced between the average kinetic energy of a molecule < ½ mv2 > and the , thus defined, absolute temperature scale T. < ½ mv2 > ≡ 3/2 k T ...
... differently. A constant conversion factor k is introduced between the average kinetic energy of a molecule < ½ mv2 > and the , thus defined, absolute temperature scale T. < ½ mv2 > ≡ 3/2 k T ...
state of matter - Mayfield City Schools
... - In both the above examples, the molecules are made to race back and forth faster. In other words, they gain kinetic energy. In general, the warmer an object, the more kinetic energy its atoms and molecules possess. - Temperature, the degree of “hotness” or “coldness” of an object, is proportional ...
... - In both the above examples, the molecules are made to race back and forth faster. In other words, they gain kinetic energy. In general, the warmer an object, the more kinetic energy its atoms and molecules possess. - Temperature, the degree of “hotness” or “coldness” of an object, is proportional ...
IB 3.2 Gases Feb 16 Agenda
... Three types of “average speed” values for the particles of an ideal gas ...
... Three types of “average speed” values for the particles of an ideal gas ...
Relationships Between Heat and Work
... • Internal energy is constant in a constanttemperature process • Isothermal process – a thermodynamic process that takes place at constant temperature and in which the internal energy of a system remains unchanged – Similar to a balloon expanding as the pressure drops before a storm hits • The ballo ...
... • Internal energy is constant in a constanttemperature process • Isothermal process – a thermodynamic process that takes place at constant temperature and in which the internal energy of a system remains unchanged – Similar to a balloon expanding as the pressure drops before a storm hits • The ballo ...
File
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
(the energy due to rotational motion), and translational (the energy
... Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. An object that has motion - whether it is vertical or horizontal motion - has kinetic energy. There are many forms of kinetic energy - vibrational (the energy due to vibrational motion), rotational (the energy due to rotational motion), and translational (the ...
... Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. An object that has motion - whether it is vertical or horizontal motion - has kinetic energy. There are many forms of kinetic energy - vibrational (the energy due to vibrational motion), rotational (the energy due to rotational motion), and translational (the ...
Verdana 30 pt
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...