Motion Unit - Dickinson ISD
... hill covered with snow and ice. Since there’s not much friction, the sled gains speed the whole way down the hill. ...
... hill covered with snow and ice. Since there’s not much friction, the sled gains speed the whole way down the hill. ...
Quiz_MATH.rtf
... D) decreases at high temperature, increases at low E) stays the same 13. (C) Two monatomic ideal gases are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m. The ratio of the average molecular kinetic energy KA/KB is ...
... D) decreases at high temperature, increases at low E) stays the same 13. (C) Two monatomic ideal gases are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Gas A is composed of molecules with mass m while gas B is composed of molecules with mass 4m. The ratio of the average molecular kinetic energy KA/KB is ...
The history of thoughta and science
... guardian of propriety, ensuring that causality causes only legitimate actions because energy is conserved. Newton’s second law proves the fact that total energy is constant. The conservation of energy is related with the symmetry of spacetime. Heat is energy transferred between two objects as a resu ...
... guardian of propriety, ensuring that causality causes only legitimate actions because energy is conserved. Newton’s second law proves the fact that total energy is constant. The conservation of energy is related with the symmetry of spacetime. Heat is energy transferred between two objects as a resu ...
Zero Torque and Static Equilibrium
... Conservation of Energy If these two objects, of the same mass and radius, are released simultaneously, the disk will reach the bottom first – more of its gravitational potential energy becomes translational kinetic energy, and less rotational. ...
... Conservation of Energy If these two objects, of the same mass and radius, are released simultaneously, the disk will reach the bottom first – more of its gravitational potential energy becomes translational kinetic energy, and less rotational. ...
Kinetic Energy is Energy Due to Motion When the potential energy of
... make your eardrum vibrate. Any moving object has kinetic energy. When a solid object moves, all the molecules move in unison. The kinetic energy of such an object is often called mechanical kinetic energy. Even when molecules are not physically attached to each other, they can still move together li ...
... make your eardrum vibrate. Any moving object has kinetic energy. When a solid object moves, all the molecules move in unison. The kinetic energy of such an object is often called mechanical kinetic energy. Even when molecules are not physically attached to each other, they can still move together li ...
Thermodynamic functions - Phase Transformations Group
... The Helmholtz free energy F is the corresponding term at constant volume, when H is replaced by U in equation 9. A process can occur spontaneously if it leads to a reduction in the free energy. Quantities such as H, G and S are path independent and therefore are called functions of state. More About ...
... The Helmholtz free energy F is the corresponding term at constant volume, when H is replaced by U in equation 9. A process can occur spontaneously if it leads to a reduction in the free energy. Quantities such as H, G and S are path independent and therefore are called functions of state. More About ...
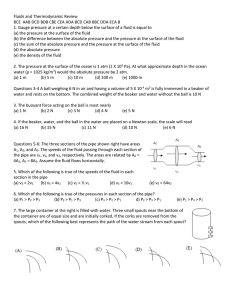
Fluids and Thermodynamic Review BCE AAB DCD BDB CBE CEA
... hot sun on a summer day. The order of heat transfers during the entire process is (A) conduction, convection, radiation (B) convection, radiation, conduction (C) radiation, convection, conduction (D) conduction, radiation, convection (E) radiation, conduction, convection 15. Which of the following i ...
... hot sun on a summer day. The order of heat transfers during the entire process is (A) conduction, convection, radiation (B) convection, radiation, conduction (C) radiation, convection, conduction (D) conduction, radiation, convection (E) radiation, conduction, convection 15. Which of the following i ...
Matter and Energy unit review answer key
... Describe the molecules for each of the following states of matter. Include the arrangement of the molecules, their movement, and their shape, and volume. ...
... Describe the molecules for each of the following states of matter. Include the arrangement of the molecules, their movement, and their shape, and volume. ...
Part VI
... • The work-kinetic energy theorem in rotational language states that the net work done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational kinetic energy ...
... • The work-kinetic energy theorem in rotational language states that the net work done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational kinetic energy ...
Temperature
... calibration points The discrepancies between the two thermometers are especially large when the temperatures being measured are far from the calibration points, because mercury and alcohol have different thermal expansion properties. ...
... calibration points The discrepancies between the two thermometers are especially large when the temperatures being measured are far from the calibration points, because mercury and alcohol have different thermal expansion properties. ...
Section 1 – Thermal Energy
... Matter in Motion º All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. º All materials (solid, liquid, and gas) are in constant motion. º Just like other objects in motion atoms have kinetic energy. º Cool objects are moving slower so they have less kinetic energy than warmer ones. Temperature º D ...
... Matter in Motion º All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms. º All materials (solid, liquid, and gas) are in constant motion. º Just like other objects in motion atoms have kinetic energy. º Cool objects are moving slower so they have less kinetic energy than warmer ones. Temperature º D ...
Homework 3
... gets converted to heat or both. Examples would be compressing a spring or a pocket of air. Since dW is defined as work done by the system, when work is done on the system, such as compressing it, dW is negative and positive when the system expands. Part B Conservation of energy states that energy ca ...
... gets converted to heat or both. Examples would be compressing a spring or a pocket of air. Since dW is defined as work done by the system, when work is done on the system, such as compressing it, dW is negative and positive when the system expands. Part B Conservation of energy states that energy ca ...
D12E12Safety1\4Curr\emet
... 7.2.7 state that energy in transition between bodies or systems can only be heat flow (or heat transfer) (Q) and work flow (or work transfer) (W) 7.2.8 define the first law of thermodynamics as “the energy stored in any given thermodynamics system can only be changed by the transition of energies Q ...
... 7.2.7 state that energy in transition between bodies or systems can only be heat flow (or heat transfer) (Q) and work flow (or work transfer) (W) 7.2.8 define the first law of thermodynamics as “the energy stored in any given thermodynamics system can only be changed by the transition of energies Q ...
Problem Set V
... and find and for the coin flip example. f) What is the limiting value of the ratio / for large n. Interpret the result. 4) Two-dimensional problems are relevant in materials science. Derive expressions for the following quantities of a two-dimensional ideal gas: a) the average speed b) the roo ...
... and find and for the coin flip example. f) What is the limiting value of the ratio / for large n. Interpret the result. 4) Two-dimensional problems are relevant in materials science. Derive expressions for the following quantities of a two-dimensional ideal gas: a) the average speed b) the roo ...
Introduction in energy systems - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
... surrounding objects (Kelvin statement). Third law of thermodynamics The system is not possible cooled, in a finite number of steps, to absolute zero. ...
... surrounding objects (Kelvin statement). Third law of thermodynamics The system is not possible cooled, in a finite number of steps, to absolute zero. ...