4.14.1 Kinetic Energy Energy is the ability to do work. When a force
... changes from an initial value v0 to a final value v over a time interval. We can relate Newton’s second law to speed by way of (4.23), v 2 = 2as + v 02 , as follows. First, because of (4.26) and because F = ma, we can write W = Fs = mas. Note that both (4.23) and the above equation contain the term ...
... changes from an initial value v0 to a final value v over a time interval. We can relate Newton’s second law to speed by way of (4.23), v 2 = 2as + v 02 , as follows. First, because of (4.26) and because F = ma, we can write W = Fs = mas. Note that both (4.23) and the above equation contain the term ...
Ch. 6 Section 6.1 Powerpoint
... destroyed, but can be converted between forms. •The First Law of Thermodynamics: The total energy content of the universe is constant. ...
... destroyed, but can be converted between forms. •The First Law of Thermodynamics: The total energy content of the universe is constant. ...
A note on the variation of specific heats in ideal gases Most diatomic
... of one of the specific heats with T. We shall talk about cv in this note. In the following discussion all energies are mass specific, i.e. expressed per unit mass, and denoted by lower case quantities. Energies per mole are obtained by multiplying mass specific by the molar mass. In equations that c ...
... of one of the specific heats with T. We shall talk about cv in this note. In the following discussion all energies are mass specific, i.e. expressed per unit mass, and denoted by lower case quantities. Energies per mole are obtained by multiplying mass specific by the molar mass. In equations that c ...
2-Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
... Definition Science that deals with heat and work and the changes they can produce. e.g. change of temperature (T), pressure (P) etc. Basis is experimental observations written down as laws. e.g. 1st law of thermodynamics: Energy can change from one form to another but the total amount remains consta ...
... Definition Science that deals with heat and work and the changes they can produce. e.g. change of temperature (T), pressure (P) etc. Basis is experimental observations written down as laws. e.g. 1st law of thermodynamics: Energy can change from one form to another but the total amount remains consta ...
Matching: 1. Independent variable 2. Physical science 3. Control 4
... 16. Heat and temperature are the same in that: a. They both deal with potential energy b. They both are warm c. They both rely on particle motion d. They both start with “T” 17. Thermal energy differs from mechanical energy because: a. Thermal energy deals with temperature b. Mechanical energy deals ...
... 16. Heat and temperature are the same in that: a. They both deal with potential energy b. They both are warm c. They both rely on particle motion d. They both start with “T” 17. Thermal energy differs from mechanical energy because: a. Thermal energy deals with temperature b. Mechanical energy deals ...
7-1,2,3
... No exception to this has ever been found. Think of the many types of energy as being numbers representing money in many types of bank accounts. Rules have been made about what such money numbers mean and how they can be changed. You can transfer money numbers from one account to another or from one ...
... No exception to this has ever been found. Think of the many types of energy as being numbers representing money in many types of bank accounts. Rules have been made about what such money numbers mean and how they can be changed. You can transfer money numbers from one account to another or from one ...
Freezing Point of Water
... 2. From which part of the atom do radioactive emissions originate? nucleus 3. What effect does the emission of an alpha particle have on the mass number and the atomic number of the original isotope? Mass drops by four, proton number by 2 4. What effect does the emission of a beta particle have on t ...
... 2. From which part of the atom do radioactive emissions originate? nucleus 3. What effect does the emission of an alpha particle have on the mass number and the atomic number of the original isotope? Mass drops by four, proton number by 2 4. What effect does the emission of a beta particle have on t ...
t 0 - PhysicsEducation.net
... either into or out of the system. (Your answer to #7 should have decided whether it’s into or out of, or if instead x is really just 0 joules. Which is it?) Experiment B. Suppose that again we have 2 liters of each reactant solution. Now, though, let’s suppose that the concentration of each solution ...
... either into or out of the system. (Your answer to #7 should have decided whether it’s into or out of, or if instead x is really just 0 joules. Which is it?) Experiment B. Suppose that again we have 2 liters of each reactant solution. Now, though, let’s suppose that the concentration of each solution ...
CCC HOH FUK TONG COLLEGE
... (3) R and W form an action-and-reaction pair according to Newton's third law. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (2) only D (2) and (3) only C ...
... (3) R and W form an action-and-reaction pair according to Newton's third law. A (1) only B (2) only C (1) and (2) only D (2) and (3) only C ...
Geography - aps mhow
... A in opposite directions with a speed of 54 km/h each. At a certain instant, when the distance AB is equal to AC, both being 1km, B decides to overtake A before C does. What minimum acceleration of car B is required to avoid an accident? ...
... A in opposite directions with a speed of 54 km/h each. At a certain instant, when the distance AB is equal to AC, both being 1km, B decides to overtake A before C does. What minimum acceleration of car B is required to avoid an accident? ...
Introduction To Weather Dynamics
... Types of Energy Transfer Conduction • Requires contact between atoms; more energetic atoms collide with more energetic atoms and energy is transferred (solids with solids) • Example: Warming a pot on a stove ...
... Types of Energy Transfer Conduction • Requires contact between atoms; more energetic atoms collide with more energetic atoms and energy is transferred (solids with solids) • Example: Warming a pot on a stove ...
$doc.title
... consisting of the object, Earth and atmosphere continues to decrease. Which of the following best describes why this is not a violation of the conservation of energy for the system consisting of the ...
... consisting of the object, Earth and atmosphere continues to decrease. Which of the following best describes why this is not a violation of the conservation of energy for the system consisting of the ...
Temperature
... This statement can easily be proved experimentally and is very important because it enables us to define temperature. We can think of temperature as the property that determines whether an object is in thermal equilibrium with other objects. Two objects in thermal equilibrium with each other are at ...
... This statement can easily be proved experimentally and is very important because it enables us to define temperature. We can think of temperature as the property that determines whether an object is in thermal equilibrium with other objects. Two objects in thermal equilibrium with each other are at ...
Problem 1. An unstable Pu-‐240 nucleus (mass
... consisting of the object, Earth and atmosphere continues to decrease. Which of the following best describes why this is not a violation of the conservation of energy for the system consisting of the ...
... consisting of the object, Earth and atmosphere continues to decrease. Which of the following best describes why this is not a violation of the conservation of energy for the system consisting of the ...
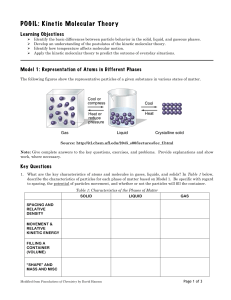
POGIL: Kinetic Molecular Theory
... Gases consist of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). These particles are so small compared with the distance between them that the volume (size) of the individual particles can be assumed to be negligible (zero). The particles are in constant random motion, colliding with the walls of the container ...
... Gases consist of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). These particles are so small compared with the distance between them that the volume (size) of the individual particles can be assumed to be negligible (zero). The particles are in constant random motion, colliding with the walls of the container ...