heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... When an individual participates in novel and high arousal experiences, the template is at risk for being altered. High arousal experiences change the brains expectations. The brain than keeps pursuing these high arousal experiences in order to get to the same level of “pay off”. ...
... When an individual participates in novel and high arousal experiences, the template is at risk for being altered. High arousal experiences change the brains expectations. The brain than keeps pursuing these high arousal experiences in order to get to the same level of “pay off”. ...
Ch07a
... • During stressful or emotional events, the sympathetic nervous system works to boost production of the hormones cortisol and adrenaline. • This is usually accompanied by increase stimulation of the amygdala. • You are more likely to remember joyous or traumatic events than any other type of event. ...
... • During stressful or emotional events, the sympathetic nervous system works to boost production of the hormones cortisol and adrenaline. • This is usually accompanied by increase stimulation of the amygdala. • You are more likely to remember joyous or traumatic events than any other type of event. ...
Neurotransmitters and Sleep
... In the first part of this lesson we discussed the characteristics of the stages of sleep, the sleep cycle, and the functions of sleep. We will now explore sleep at the level of neurotransmitters and brain structures, beginning with the neurotransmitter that plays, perhaps, the largest role in sleep ...
... In the first part of this lesson we discussed the characteristics of the stages of sleep, the sleep cycle, and the functions of sleep. We will now explore sleep at the level of neurotransmitters and brain structures, beginning with the neurotransmitter that plays, perhaps, the largest role in sleep ...
Latest Findings in the Mechanisms of Cortical `Arousal`: `Enabling
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
Latest Findings in the Mechanisms of Cortical `Arousal`: `Enabling
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
Brain_stemCh45
... Origins from pontine reticular formation Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped ...
... Origins from pontine reticular formation Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped ...
Brain_stemCh45
... Origins from pontine reticular formation Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped ...
... Origins from pontine reticular formation Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped ...
Conformity - University of Winnipeg
... • Best action best for each individual will, if adopted by others, create a loss for all • Reflects conflicts between: • individual versus group • short-term and long-term interests ...
... • Best action best for each individual will, if adopted by others, create a loss for all • Reflects conflicts between: • individual versus group • short-term and long-term interests ...
EMOTION: Information as Subjective Feeling
... • Like any new learning does • New information affects the way that neuraltransmitters are released or processed at neural synapses • What you learn affects the way your brain works, which affects the way your mind works ...
... • Like any new learning does • New information affects the way that neuraltransmitters are released or processed at neural synapses • What you learn affects the way your brain works, which affects the way your mind works ...
Emotions Lecture Notes Page
... Both Cannon-Bard and Schachter would predict the Capilano Bridge results Further Support for Schachter’s theory • Patients were told they would receive an injection of a vitamin (actually epinephrine, which increases arousal) • Observed either an actor that was happy after the injection, or was angr ...
... Both Cannon-Bard and Schachter would predict the Capilano Bridge results Further Support for Schachter’s theory • Patients were told they would receive an injection of a vitamin (actually epinephrine, which increases arousal) • Observed either an actor that was happy after the injection, or was angr ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
Introduction to Psychology - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... High doses, withdrawal are uncomfortable Irritability, insomnia, seizures, high BP ...
... High doses, withdrawal are uncomfortable Irritability, insomnia, seizures, high BP ...
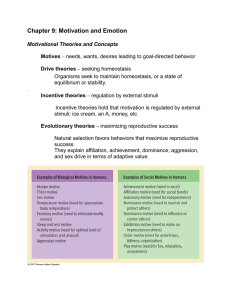
Chapter 9: Motivation and Emotion
... good to them. Quantity available: people eat more when more food is put in front of them. Variety: people eat more when there is a greater variety of foods available to them Learned preferences and habits Classical conditioning Observational learning People’s food preferences are influenced through ...
... good to them. Quantity available: people eat more when more food is put in front of them. Variety: people eat more when there is a greater variety of foods available to them Learned preferences and habits Classical conditioning Observational learning People’s food preferences are influenced through ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
Initiation of the arousal response
... there is a progressive breakdown in the establishment of long-term memory. Retrieval of memory, or performance, requires a lower level of arousal, with only moderate activation of GR. At the neural level, this relationship is seen in the hippocampal processes which mediate long term memory storage, ...
... there is a progressive breakdown in the establishment of long-term memory. Retrieval of memory, or performance, requires a lower level of arousal, with only moderate activation of GR. At the neural level, this relationship is seen in the hippocampal processes which mediate long term memory storage, ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... • In the PNS – helps with muscle contraction • In the CNS – sensory perception • Related to learning, memory, movement • If a person is having difficulty moving, it may be due to a blockage of acetylcholine ...
... • In the PNS – helps with muscle contraction • In the CNS – sensory perception • Related to learning, memory, movement • If a person is having difficulty moving, it may be due to a blockage of acetylcholine ...
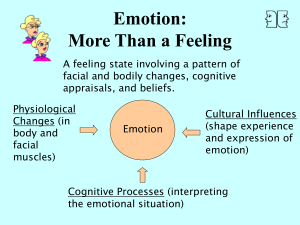
Emotion: More Than a Feeling
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
9 Functions of the Middle Prefrontal Cortex
... Emotional Balance in this context is defined as being able to balance between rigidity and chaos/arousal. In other words, being able to keep from being overwhelmed or becoming inflexible in one’s emotional response. The ability to feel fear, sadness and anger and change it to ease and peace. Also gi ...
... Emotional Balance in this context is defined as being able to balance between rigidity and chaos/arousal. In other words, being able to keep from being overwhelmed or becoming inflexible in one’s emotional response. The ability to feel fear, sadness and anger and change it to ease and peace. Also gi ...
Arousal Systems
... PPT/LDT nuclei leads to cortical activation and arousal) • LC activation associated with heightened arousal, LC lesions, associated with hypersomnolence, • Lesions of midbrain dopaminergic nuclei associated with akinetic state (failure to arouse) • Serotonergic neurons during sleep, firing rate drops ...
... PPT/LDT nuclei leads to cortical activation and arousal) • LC activation associated with heightened arousal, LC lesions, associated with hypersomnolence, • Lesions of midbrain dopaminergic nuclei associated with akinetic state (failure to arouse) • Serotonergic neurons during sleep, firing rate drops ...
emotion_08
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
... • "My theory ... is that the bodily changes follow directly the perception of the exciting fact, and that our feeling of the same changes as they occur is the emotion. Common sense says, we lose our fortune, are sorry and weep; we meet a bear, are frightened and run; we are insulted by a rival, and ...
Personality and Physiology
... out interactions with others and more susceptible to positive emotions. – Highly BAS individuals appear to work faster and are more accurate when rewards are used while BIS individuals appear to work faster and improve performance under punishment conditions. ...
... out interactions with others and more susceptible to positive emotions. – Highly BAS individuals appear to work faster and are more accurate when rewards are used while BIS individuals appear to work faster and improve performance under punishment conditions. ...
The Frustration of Learning Monopoly
... out. This in turn causes Susan to have to attend to this incident, further creating tension. As the tension grows, we can see a corresponding increase in arousal. Incident 2: Integrating A Novice Player and a Spoilsport After reading the directions, Susan’s family takes turns rolling the die and mov ...
... out. This in turn causes Susan to have to attend to this incident, further creating tension. As the tension grows, we can see a corresponding increase in arousal. Incident 2: Integrating A Novice Player and a Spoilsport After reading the directions, Susan’s family takes turns rolling the die and mov ...
Type A Personality
... – Studies suggest that the left hemisphere is more active than the right when an individual is experience unpleasant emotions and visa versa – May reflect an underlying biological disposition or trait – May also be related to the release of hormones like ...
... – Studies suggest that the left hemisphere is more active than the right when an individual is experience unpleasant emotions and visa versa – May reflect an underlying biological disposition or trait – May also be related to the release of hormones like ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... Controlled by several centers in the cerebrum and brainstem Reticular formation: neurons that pass through the brainstem – Reticular activating system--regulates sleep and arousal – Increased input to cortex, increases alertness ...
... Controlled by several centers in the cerebrum and brainstem Reticular formation: neurons that pass through the brainstem – Reticular activating system--regulates sleep and arousal – Increased input to cortex, increases alertness ...
Sleep and Arousal
... • Waking: Alpha (10 Hz) and beta/gamma waves (40 Hz). • Slow-Wave sleep: From alpha to spindles (14 Hz) and delta (1-4 Hz). • REM sleep: Cortical arousal and muscular atonia. Also called paradoxical or dream sleep. • Triggered in pontine reticular formation. ...
... • Waking: Alpha (10 Hz) and beta/gamma waves (40 Hz). • Slow-Wave sleep: From alpha to spindles (14 Hz) and delta (1-4 Hz). • REM sleep: Cortical arousal and muscular atonia. Also called paradoxical or dream sleep. • Triggered in pontine reticular formation. ...