Pubertal Influences on Sleep
... 1. Why is it so hard for students to understand abstract ideas?…we understand new things in context of what we already know…and most of what we know is concrete. 2. Is drilling worth it?...It is virtually impossible to become proficient at mental or physical tasks without extended practice. (frees u ...
... 1. Why is it so hard for students to understand abstract ideas?…we understand new things in context of what we already know…and most of what we know is concrete. 2. Is drilling worth it?...It is virtually impossible to become proficient at mental or physical tasks without extended practice. (frees u ...
Chapter 9: Learning and Memory Multiple Choice Questions (1
... 1. Which is the best example of divided attention? a. scanning a crowd looking for a friend b. changing clothes in the dark c. watching the lip movements of a singer while listening to the song d. playing online poker while studying for a midterm 2. Which of the following is not a type of human memo ...
... 1. Which is the best example of divided attention? a. scanning a crowd looking for a friend b. changing clothes in the dark c. watching the lip movements of a singer while listening to the song d. playing online poker while studying for a midterm 2. Which of the following is not a type of human memo ...
on Memory
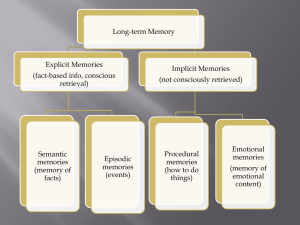
... events of our own life. • Declarative memory: stored knowledge that can be called forth consciously as needed. • Procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection. (swimming, driving, tying a tie) ...
... events of our own life. • Declarative memory: stored knowledge that can be called forth consciously as needed. • Procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection. (swimming, driving, tying a tie) ...
Memory and Law
... into a construct that can be stored within the brain for recall by short term or long term memory. This process begins with attention to the stimuli, which is increased by emotion. An engram (or memory trace) is a hypothetical biophysical/biochemical change in the neurons of the brain. (No one h ...
... into a construct that can be stored within the brain for recall by short term or long term memory. This process begins with attention to the stimuli, which is increased by emotion. An engram (or memory trace) is a hypothetical biophysical/biochemical change in the neurons of the brain. (No one h ...
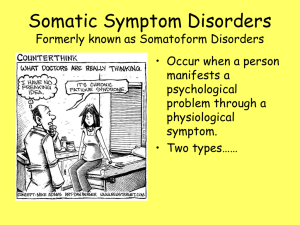
Psychological Disorders
... • It’s still critical to get treated for this – may interfere with your ability to function and increase your risk of Bipolar I or Bipolar II ...
... • It’s still critical to get treated for this – may interfere with your ability to function and increase your risk of Bipolar I or Bipolar II ...
Forgetting
... memories” were big headlines. • Individuals of all ages were claiming to suddenly remember events that had been “repressed” and forgotten for years. • Often these memories were of abuse. • Sometimes these recovered memories were corroborated with physical evidence and justice was served. • Other tim ...
... memories” were big headlines. • Individuals of all ages were claiming to suddenly remember events that had been “repressed” and forgotten for years. • Often these memories were of abuse. • Sometimes these recovered memories were corroborated with physical evidence and justice was served. • Other tim ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...
Knowledge Representation
... what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
... what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_slides
... from the mass of stimuli around us • Involves audio and/or visual senses • Information at the interface should be structured to ...
... from the mass of stimuli around us • Involves audio and/or visual senses • Information at the interface should be structured to ...
Before Milgram`s study on obedience, a team of psychiatrists
... 41. Yeşim enters the classroom and sees a sign on the wall that says, “Please turn off cell phones during class. Thank you.” Yeşim turns her phone off. This is an example of what kind of social influence? a) conformity b) obedience c) compliance d) persuasion 42. Although Kerem usually enjoys playi ...
... 41. Yeşim enters the classroom and sees a sign on the wall that says, “Please turn off cell phones during class. Thank you.” Yeşim turns her phone off. This is an example of what kind of social influence? a) conformity b) obedience c) compliance d) persuasion 42. Although Kerem usually enjoys playi ...
Speech_Presentation
... impossible because there will be no words to express it” “The purpose of Newspeak was not only to provide a medium of expression for the world-view and mental habits proper to the devotees of Ingsoc, but to make all other modes of thought impossible.” ...
... impossible because there will be no words to express it” “The purpose of Newspeak was not only to provide a medium of expression for the world-view and mental habits proper to the devotees of Ingsoc, but to make all other modes of thought impossible.” ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... of bicycles. Retrieval and use of explicit memories, which is in part a working memory or executive function, is directed by the ...
... of bicycles. Retrieval and use of explicit memories, which is in part a working memory or executive function, is directed by the ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... which explains why memories based on emotional events are remembered better. It also explains why people suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder have problems forgetting emotional memories. ...
... which explains why memories based on emotional events are remembered better. It also explains why people suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder have problems forgetting emotional memories. ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... Many of Kandel’s studies with Aplysia involved using a very thin electrode to mildly stimulate a part of the body called the siphon. The siphon is like a tail and the stimulation caused it to reflexively contract. An Aplysia would also immediately withdraw its delicate gill in case whatever shocked ...
... Many of Kandel’s studies with Aplysia involved using a very thin electrode to mildly stimulate a part of the body called the siphon. The siphon is like a tail and the stimulation caused it to reflexively contract. An Aplysia would also immediately withdraw its delicate gill in case whatever shocked ...
DISSOCIATIVE DISORDER
... Sudden onset Wander in a purposeful way Have complete amnesia for their past lives and associations Generally unaware that they have forgotten anything ...
... Sudden onset Wander in a purposeful way Have complete amnesia for their past lives and associations Generally unaware that they have forgotten anything ...
Lecture05
... Subjects studied and recalled 12 lists of 10 common unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were gi ...
... Subjects studied and recalled 12 lists of 10 common unrelated words. Then they had to recall all lists a second time cued by the first word of each list. Narrative subjects were to make a story incorporating the words in the list. Control subjects were told just to study each of the list and were gi ...
schema theory
... aspects of our world • Scripts are schemas which provide information about the sequence of events that occur in a more or less unchanging order in particular contexts such as going to a restaurant, or going to the dentist. • Self schemas organize information we have about ourselves; for example, inf ...
... aspects of our world • Scripts are schemas which provide information about the sequence of events that occur in a more or less unchanging order in particular contexts such as going to a restaurant, or going to the dentist. • Self schemas organize information we have about ourselves; for example, inf ...
Amnesia Cartoon
... • Lack of recall for biographical information from childhood through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory • able to sight-read ...
... • Lack of recall for biographical information from childhood through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory • able to sight-read ...
Clinically Relevant Functional Neuroanatomy
... The Human Amnesic Syndrome • Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay • Impaired recollection of events learned prior to onset of amnesia (retrograde amnesia), often in temporally ...
... The Human Amnesic Syndrome • Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay • Impaired recollection of events learned prior to onset of amnesia (retrograde amnesia), often in temporally ...
Information Processing and Memory
... information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neurological level, a 60 minute lecture does not allow students sufficient time to process new information. However, short-term memory is enhanced ...
... information takes ten seconds to process in order to be stored in long-term memory. The implications for lecture-based instruction are significant. On a neurological level, a 60 minute lecture does not allow students sufficient time to process new information. However, short-term memory is enhanced ...
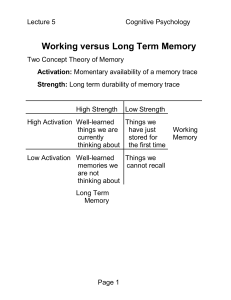
The Neuroscience of Memory - Albert Einstein College of
... Approach to Memory Short term v. long term memory Recall in milliseconds/seconds/minutes v. days/years 4 C’s of memory: Connection – cellular level of memory Cognition – memories at a psychological level. Includes behavioraism (all learning is 2/2 conditioned responses) v. congitivism (co ...
... Approach to Memory Short term v. long term memory Recall in milliseconds/seconds/minutes v. days/years 4 C’s of memory: Connection – cellular level of memory Cognition – memories at a psychological level. Includes behavioraism (all learning is 2/2 conditioned responses) v. congitivism (co ...
Module 12 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time ...
... anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time ...
Memory - Hensley
... 6. We store information in memory as libraries store their books, that is, in discrete precise locations. 7. When people learn something while intoxicated, they recall it best when they are again intoxicated. 8. The hour before sleep is good time to commit information to memory. 9. Repeatedly imagin ...
... 6. We store information in memory as libraries store their books, that is, in discrete precise locations. 7. When people learn something while intoxicated, they recall it best when they are again intoxicated. 8. The hour before sleep is good time to commit information to memory. 9. Repeatedly imagin ...
Source amnesia

Source amnesia is the inability to remember where, when or how previously learned information has been acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge. This branch of amnesia is associated with the malfunctioning of one's explicit memory. It is likely that the disconnect between having the knowledge and remembering the context in which the knowledge was acquired is due to a dissociation between semantic and episodic memory – an individual retains the semantic knowledge (the fact), but lacks the episodic knowledge to indicate the context in which the knowledge was gained.Memory representations reflect the encoding processes during acquisition. Different types of acquisition processes (e.g.: reading, thinking, listening) and different types of events (e.g.: newspaper, thoughts, conversation) will produce mental depictions that perceptually differ from one another in the brain, making it harder to retrieve where information was learned when placed in a different context of retrieval. Source monitoring involves a systematic process of slow and deliberate thought of where information was originally learned. Source monitoring can be improved by using more retrieval cues, discovering and noting relations and extended reasoning.