Short-term memories
... through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory: good retrograde and anterograde memory • able to sight-read and to play the cell ...
... through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory: good retrograde and anterograde memory • able to sight-read and to play the cell ...
File - Wk 1-2
... “sense” of when it happened) o Episodic – Personal experiences, stored dated (you know when these personal experiences happened) Non Declarative – Also known as “Procedural Memory”. Actions, motor skills, conditioned behaviour and emotional memories. Subconscious memory expressed through actions or ...
... “sense” of when it happened) o Episodic – Personal experiences, stored dated (you know when these personal experiences happened) Non Declarative – Also known as “Procedural Memory”. Actions, motor skills, conditioned behaviour and emotional memories. Subconscious memory expressed through actions or ...
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Automaticity: the tendency for cognitive processes to occur nonintentionally, unconsciously, and with little effort after extensive practice ...
... Automaticity: the tendency for cognitive processes to occur nonintentionally, unconsciously, and with little effort after extensive practice ...
Syllabus
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: Psychology is a regular level class for students who are interested in an introduction to the science of Psychology. This course will study major topics in Psychology through lectures, group projects, discussions, and independent research. Students will be expected to demonstrate ...
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: Psychology is a regular level class for students who are interested in an introduction to the science of Psychology. This course will study major topics in Psychology through lectures, group projects, discussions, and independent research. Students will be expected to demonstrate ...
Conflicting Views on Inter-Identity Amnesia in Patients
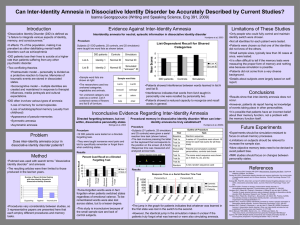
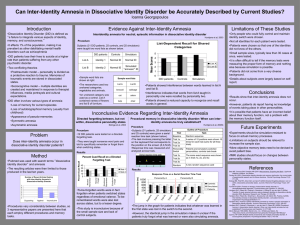
... •Patients were chosen so that one of the identities did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patien ...
... •Patients were chosen so that one of the identities did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patien ...
Can Inter-Identity Amnesia in Dissociative Identity
... •Patients were chosen so that one of the identities did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patien ...
... •Patients were chosen so that one of the identities did not know of the others. •Small sample sizes, typically less than 30 cases at once, were tested. •It is often difficult to tell if the memory tests were measuring the proper form of memory and nothing else because simulation is possible. •Patien ...
Module_12vs9_Final
... that may occur after a blow or damage to the brain or after disease, general anesthesia, certain drugs, or severe psychological trauma – Distortion • misremembering something due to memory distortions caused by bias or suggestibility ...
... that may occur after a blow or damage to the brain or after disease, general anesthesia, certain drugs, or severe psychological trauma – Distortion • misremembering something due to memory distortions caused by bias or suggestibility ...
Mental Imagery
... we store interpretations of events, whether they be verbal or visual, rather than the imaginal components. – Anderson and Bower explain that concrete concepts are coded by a rich set of predicates that bind concepts together. ..."the only difference between the internal representation for a linguist ...
... we store interpretations of events, whether they be verbal or visual, rather than the imaginal components. – Anderson and Bower explain that concrete concepts are coded by a rich set of predicates that bind concepts together. ..."the only difference between the internal representation for a linguist ...
DISSOCIATIVE AMNESIA
... ideas of the patient about how parts of the body or mind malfunction or fail to function; ...
... ideas of the patient about how parts of the body or mind malfunction or fail to function; ...
Consciousness, Thought, and Memory
... Memory is the storage and retrieval of information. The two stages of memory are short term (STM) and long term (LTM). STM is the first step, and is limited to seven or eight chunks of information. Some 5% of sensory input is transferred to the STM. The LTM is of limitless capacity, but its ability ...
... Memory is the storage and retrieval of information. The two stages of memory are short term (STM) and long term (LTM). STM is the first step, and is limited to seven or eight chunks of information. Some 5% of sensory input is transferred to the STM. The LTM is of limitless capacity, but its ability ...
Readings
... Carefully design information to be remembered. Meaningful to the individual and semantically associated with other information. o Concrete rather than abstract words when possible o Distinctive concepts to reduce interference o Well-organized sets of information (groups) o Able to be guessed based ...
... Carefully design information to be remembered. Meaningful to the individual and semantically associated with other information. o Concrete rather than abstract words when possible o Distinctive concepts to reduce interference o Well-organized sets of information (groups) o Able to be guessed based ...
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language: 18: Memory and language
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...
... and rehearsal, where rehearsal is equivalent (but not identical with) subvocal rehearsal Left posterior parietal cortex is implicated in storage ...
1 - U-System
... channels become leaky resulting in higher than normal resting levels of calcium within neurons calcium that enters during a train of stimuli (tetanus) produces less effect than in younger individuals 5. Important structures for learning and memory abilities - limbic system plays a role in deciding ...
... channels become leaky resulting in higher than normal resting levels of calcium within neurons calcium that enters during a train of stimuli (tetanus) produces less effect than in younger individuals 5. Important structures for learning and memory abilities - limbic system plays a role in deciding ...
Dissociative Disorders
... out a period of time after psychogenic cause (e.g. stress / trauma) Memory loss is often selective Relative indifference to loss of memory Remain well oriented to time and place ...
... out a period of time after psychogenic cause (e.g. stress / trauma) Memory loss is often selective Relative indifference to loss of memory Remain well oriented to time and place ...
Midterm Review Project
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
No Slide Title
... aspect of the temporal lobe causes amnesia, where immediate memory is intact, but the person cannot remember events of more than a few minutes ago. Medial temporal lobe is a sort of “gateway” to memory of facts and events. Motor memory does not depend on the medial temporal lobe. ...
... aspect of the temporal lobe causes amnesia, where immediate memory is intact, but the person cannot remember events of more than a few minutes ago. Medial temporal lobe is a sort of “gateway” to memory of facts and events. Motor memory does not depend on the medial temporal lobe. ...
Spatial Working Memory
... associated with prefrontal cortex, especially lateral prefrontal cortex. Dorso-lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive c ...
... associated with prefrontal cortex, especially lateral prefrontal cortex. Dorso-lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive c ...
File - Dr. Jeffrey Nicol`s Courses
... • DemenIa: a loss of intellectual funcIon that is severe enough to impair a person’s everyday life • Prevalence of demenIa is about 2% in people that are 65 years of age, and is about 50% in people that are over the age of 85 (Apostolova & Cummings, 2008) • At this point roughly three-quarters ...
... • DemenIa: a loss of intellectual funcIon that is severe enough to impair a person’s everyday life • Prevalence of demenIa is about 2% in people that are 65 years of age, and is about 50% in people that are over the age of 85 (Apostolova & Cummings, 2008) • At this point roughly three-quarters ...
December 3
... Procedural memory – memory for how to do things, skills. Declarative memory – memory for abstract knowledge, facts and events of one’s life. Only memory for events of one’s life is affected by amnesia – not procedural memory or memory for facts. ...
... Procedural memory – memory for how to do things, skills. Declarative memory – memory for abstract knowledge, facts and events of one’s life. Only memory for events of one’s life is affected by amnesia – not procedural memory or memory for facts. ...
Memory_Ch7_all - Arizona State University
... People were, at first. But then a bunch of new tasks were tried and a people discovered a circularity in the argument What makes a level “deep”? It leads to better memory. And why care about “depth”? It can predict memory. ...
... People were, at first. But then a bunch of new tasks were tried and a people discovered a circularity in the argument What makes a level “deep”? It leads to better memory. And why care about “depth”? It can predict memory. ...
Source amnesia

Source amnesia is the inability to remember where, when or how previously learned information has been acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge. This branch of amnesia is associated with the malfunctioning of one's explicit memory. It is likely that the disconnect between having the knowledge and remembering the context in which the knowledge was acquired is due to a dissociation between semantic and episodic memory – an individual retains the semantic knowledge (the fact), but lacks the episodic knowledge to indicate the context in which the knowledge was gained.Memory representations reflect the encoding processes during acquisition. Different types of acquisition processes (e.g.: reading, thinking, listening) and different types of events (e.g.: newspaper, thoughts, conversation) will produce mental depictions that perceptually differ from one another in the brain, making it harder to retrieve where information was learned when placed in a different context of retrieval. Source monitoring involves a systematic process of slow and deliberate thought of where information was originally learned. Source monitoring can be improved by using more retrieval cues, discovering and noting relations and extended reasoning.