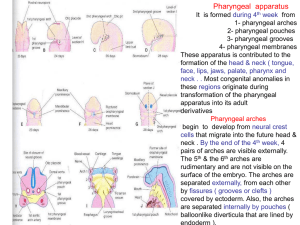
02-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... internally open into the tonsillar sinus & externally in the side of the neck. It results from persistence of parts of the 2nd groove & 2nd pouch. It passes between the internal and ...
... internally open into the tonsillar sinus & externally in the side of the neck. It results from persistence of parts of the 2nd groove & 2nd pouch. It passes between the internal and ...
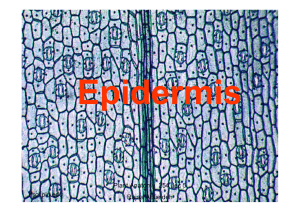
Epidermis
... leaf and on different leaves on same plant. It is affected by environmental conditions • In leaves it may occur on both sides or only on one side which is usually the lower one. • Vary depending on their position relative to epidermis could be : -even with other epidermal cells - raised above - belo ...
... leaf and on different leaves on same plant. It is affected by environmental conditions • In leaves it may occur on both sides or only on one side which is usually the lower one. • Vary depending on their position relative to epidermis could be : -even with other epidermal cells - raised above - belo ...
Development of the Mesodermal Organs in Vertebrates
... blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much later in development. The blood vessels are originally laid down as a network. Those blood vessels through which the most blood is channeled develop into arteries & veins. ...
... blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much later in development. The blood vessels are originally laid down as a network. Those blood vessels through which the most blood is channeled develop into arteries & veins. ...
Female Anatomy & Physiology
... stimulus, the uterus can not maintain its thick lining, so this falls off and is shed as menstruation. If fertilization and pregnancy occur, the placenta of the embryo secretes a hormone called chorionic gonadotropin, which stimulates the corpus luteum to keep secreting progesterone, which in turn k ...
... stimulus, the uterus can not maintain its thick lining, so this falls off and is shed as menstruation. If fertilization and pregnancy occur, the placenta of the embryo secretes a hormone called chorionic gonadotropin, which stimulates the corpus luteum to keep secreting progesterone, which in turn k ...
BIOL1151L - Clayton State University
... Epithelial Tissues ID Sheet Epithelial Tissues For this lab we will only be looking at one type of tissue. Epithelial tissues are found lining or covering various organs in the body. They can be recognized by the presence of a free surface, where the cells are in contact with spaces inside the body ...
... Epithelial Tissues ID Sheet Epithelial Tissues For this lab we will only be looking at one type of tissue. Epithelial tissues are found lining or covering various organs in the body. They can be recognized by the presence of a free surface, where the cells are in contact with spaces inside the body ...
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
... and the frontal sinus, by “deflating” the cells. This is best done by passing the ball probe well above their domes and gently lateralizing them. ...
... and the frontal sinus, by “deflating” the cells. This is best done by passing the ball probe well above their domes and gently lateralizing them. ...
Anatomy - Exam 1 Lab
... ○ Right and Left Internal thoracic arteries – on inside of thoracic wall Feeds anterior intercostal arteries ○ Anterior intercostal artery and vein – same as posterior, just in the anterior area ○ Posterior intercostal artery and vein – in the rib groove between internal and innermost intercostal ...
... ○ Right and Left Internal thoracic arteries – on inside of thoracic wall Feeds anterior intercostal arteries ○ Anterior intercostal artery and vein – same as posterior, just in the anterior area ○ Posterior intercostal artery and vein – in the rib groove between internal and innermost intercostal ...
EMBRYOLOGY
... ventral mesentery that also encloses the liver. When the stomach first appears, its concave border faces ventrally, and its convex border faces dorsally. Two concomitant positional shifts bring the stomach to its adult configuration. The first is an approximately 90-degree rotation about its cranioc ...
... ventral mesentery that also encloses the liver. When the stomach first appears, its concave border faces ventrally, and its convex border faces dorsally. Two concomitant positional shifts bring the stomach to its adult configuration. The first is an approximately 90-degree rotation about its cranioc ...
42. Lungs, pleura
... Two lungs are soft, spongy and elastic In the child, they are pink, but with age, they become dark and mottled because of the inhalation of dust particles These particles are trapped in the phagocytes of the lung The lungs are situated so that one lies on each side of the mediastinum ...
... Two lungs are soft, spongy and elastic In the child, they are pink, but with age, they become dark and mottled because of the inhalation of dust particles These particles are trapped in the phagocytes of the lung The lungs are situated so that one lies on each side of the mediastinum ...
Embryology02-BodyPlanFetalMembranes
... FGF signaling from the node drives proliferation; Retinoic acid from adjacent mesoderm drives differentiation. Because the node is caudal to the forming somites, there is a head-to-tail gradient of differentiation. Proliferating cells express a ligand (called ephrin B1). As cells differentiate, they ...
... FGF signaling from the node drives proliferation; Retinoic acid from adjacent mesoderm drives differentiation. Because the node is caudal to the forming somites, there is a head-to-tail gradient of differentiation. Proliferating cells express a ligand (called ephrin B1). As cells differentiate, they ...
anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
... Pars Intermedia. The pars intermedia surrounds a series of small cystic cavities that represent the residual lumen of Rathke’s pouch fig.(2). The parenchymal cells of the pars intermedia surround colloid-filled follicles. The cells lining these follicles appear to be derived either from folliculo-st ...
... Pars Intermedia. The pars intermedia surrounds a series of small cystic cavities that represent the residual lumen of Rathke’s pouch fig.(2). The parenchymal cells of the pars intermedia surround colloid-filled follicles. The cells lining these follicles appear to be derived either from folliculo-st ...
Gastrulation COO
... Cells that move through Hensen’s node migrate anteriorly. They form the “anlage” of the foregut, head-mesoderm and the notochord. Cells that move through the primitive streak form the majority of the endoderm and mesoderm. The presumptive endodermal cells move deeper than the presumptive mesodermal ...
... Cells that move through Hensen’s node migrate anteriorly. They form the “anlage” of the foregut, head-mesoderm and the notochord. Cells that move through the primitive streak form the majority of the endoderm and mesoderm. The presumptive endodermal cells move deeper than the presumptive mesodermal ...
The Eye File
... 8. Layer of optic nerve fibres. The axons of the ganglion cells travel in this layer towards the optic disc. Towards the optic disc, the thickness of this layer increases as more and more axons are added to it. ...
... 8. Layer of optic nerve fibres. The axons of the ganglion cells travel in this layer towards the optic disc. Towards the optic disc, the thickness of this layer increases as more and more axons are added to it. ...
Gustatory and Olfactory Systems - Dr. Costanzo
... thought to be the site for transduction of odor molecules. The basal end of the receptor cells give rise to a thin unmyelinated fiber which passes out of the epithelium and travels centrally to the olfactory bulb. These olfactory nerve fibers are unique for two reasons. First, they are among the sma ...
... thought to be the site for transduction of odor molecules. The basal end of the receptor cells give rise to a thin unmyelinated fiber which passes out of the epithelium and travels centrally to the olfactory bulb. These olfactory nerve fibers are unique for two reasons. First, they are among the sma ...
3_Bilaminar Embryo_(week2)
... o Symptoms: vaginal bleeding twds end of 1st trimester o Diagnostic: excessive hCG (made by trophoblast cells) levels early in pregnancy; confirm with ultrasound to show absence of fetus o Invasive mole – uterine tissue invaded, incl. myometrium Choriocarcinoma – malignant transformation of tropho ...
... o Symptoms: vaginal bleeding twds end of 1st trimester o Diagnostic: excessive hCG (made by trophoblast cells) levels early in pregnancy; confirm with ultrasound to show absence of fetus o Invasive mole – uterine tissue invaded, incl. myometrium Choriocarcinoma – malignant transformation of tropho ...
Accessory Organs of the Small Intestine
... These ducts will eventually coalesce to form the Main Pancreatic Duct and the Accessory Pancreatic Duct (if present) which will drain into the lumen of the duodenum via the Hepatopancreatic Ampulla. Although the pancreas is retroperitoneal, there is a peritoneal component covering a portion of the p ...
... These ducts will eventually coalesce to form the Main Pancreatic Duct and the Accessory Pancreatic Duct (if present) which will drain into the lumen of the duodenum via the Hepatopancreatic Ampulla. Although the pancreas is retroperitoneal, there is a peritoneal component covering a portion of the p ...
Document
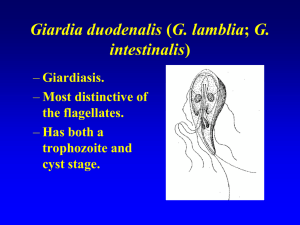
... • At least 3 exams (one every other day) before judge negative. • ELISA tests: detect soluble antigen. • PCR ...
... • At least 3 exams (one every other day) before judge negative. • ELISA tests: detect soluble antigen. • PCR ...
females
... – Stores and transports sperm during ejaculation – Runs from epididymis to ejaculatory duct • ED then runs within the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra ...
... – Stores and transports sperm during ejaculation – Runs from epididymis to ejaculatory duct • ED then runs within the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra ...
Document
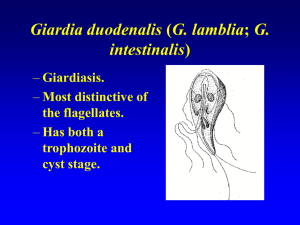
... • At least 3 exams (one every other day) before judge negative. • ELISA tests: detect soluble antigen. ...
... • At least 3 exams (one every other day) before judge negative. • ELISA tests: detect soluble antigen. ...
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM (I)
... the midzone. They are referred to as intermediate cells when exfoliated. They do not divide. The superficial zone contains the most mature cell population. Are glycogen-rich. ...
... the midzone. They are referred to as intermediate cells when exfoliated. They do not divide. The superficial zone contains the most mature cell population. Are glycogen-rich. ...
Lecture 12
... • Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens) – Stores and transports sperm during ejaculation – Runs from epididymis to ejaculatory duct • ED then runs within the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra ...
... • Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens) – Stores and transports sperm during ejaculation – Runs from epididymis to ejaculatory duct • ED then runs within the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra ...
Circulating tumor cell
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cells that have shed into the vasculature from a primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. CTCs thus constitute seeds for subsequent growth of additional tumors (metastasis) in vital distant organs, triggering a mechanism that is responsible for the vast majority of cancer-related deaths.CTCs were observed for the first time in 1869 in the blood of a man with metastatic cancer by Thomas Ashworth, who postulated that “cells identical with those of the cancer itself being seen in the blood may tend to throw some light upon the mode of origin of multiple tumours existing in the same person”. A thorough comparison of the morphology of the circulating cells to tumor cells from different lesions led Ashworth to conclude that “One thing is certain, that if they [CTC] came from an existing cancer structure, they must have passed through the greater part of the circulatory system to have arrived at the internal saphena vein of the sound leg”.The importance of CTC's in modern cancer research began in the mid 1990's with the demonstration [J. Uhr, UT-Dallas, L. Terstappen and P. Liberti, Immunicon, Philadelphia] that CTC's exist early on in the course of the disease. Those results were made possible by exquisitely sensitive magnetic separation technology employing Ferrofluids (colloidal magnetic nanoparticles) and high gradient magnetic separators invented by Liberti at Immunicon and motivated by theoretical calculations by Liberti and Terstappen that indicated very small tumors shedding cells at less than 1.0 % per day should result in detectable cells in blood. A variety of other technologies have been applied to CTC enumeration and identification since that time.Modern cancer research has demonstrated that CTCs derive from clones in the primary tumor, validating Ashworth's remarks. The significant efforts put into understanding the CTCs biological properties have demonstrated the critical role circulating tumor cells play in the metastatic spread of carcinoma.Furthermore, highly sensitive, single-cell analysis demonstrated a high level of heterogeneity seen at the single cell level for both protein expression and protein localization and the CTCs reflected both the primary biopsy and the changes seen in the metastatic sites. Tissue biopsies are poor diagnostic procedures: they are invasive, cannot be used repeatedly, and are ineffective in understanding metastatic risk, disease progression, and treatment effectiveness. CTCs thus could be considered a “liquid biopsy” which reveals metastasis in action, providing live information about the patient’s disease status. Analysis of blood samples found a propensity for increased CTC detection as the disease progressed in individual patients. Blood tests are easy and safe to perform and multiple samples can be taken over time. By contrast, analysis of solid tumors necessitates invasive procedures that might limit patient compliance. The ability to monitor disease progression over time could facilitate appropriate modification to a patient's therapy, potentially improving their prognosis and quality of life.To this end, technologies with the requisite sensitivity and reproducibility to detect CTCs in patients with metastatic disease have recently been developed.