lnternal morphology and histology of the fish mite
... (Michael, 190!.), and C. mycophagits (Rhode and Oemick, 1967; Kuo and Nesbitt, 1970.) are suggestive that the oesophageal wall of the Acaridiae has no epithelium. But as evidenced by the present study, there is an epithelial layer though narrow, and formed of short, flattened cells, beneath the chit ...
... (Michael, 190!.), and C. mycophagits (Rhode and Oemick, 1967; Kuo and Nesbitt, 1970.) are suggestive that the oesophageal wall of the Acaridiae has no epithelium. But as evidenced by the present study, there is an epithelial layer though narrow, and formed of short, flattened cells, beneath the chit ...
PPT - UCLA Health
... • Stereotactic radiation therapy demonstrates good shortterm control for many benign cranial base tumors • Short-term quality of life outcomes favor stereotactic radiation therapy over conventional surgical ...
... • Stereotactic radiation therapy demonstrates good shortterm control for many benign cranial base tumors • Short-term quality of life outcomes favor stereotactic radiation therapy over conventional surgical ...
Acoustic Neuroma & Glomus Tympanicum
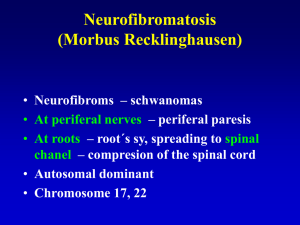
... involves 5th, 7th, 9th, 10th, 11th cranial nerves displacement of brainstem & cerebellum ...
... involves 5th, 7th, 9th, 10th, 11th cranial nerves displacement of brainstem & cerebellum ...
heparin added to cardioplegic solution inhibits tnf
... ischemia and on left ventricular performances during 30 minutes of postischemic reperfusion was investigated. Results: Significant amounts of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in myocardial tissue (1149±33.7 pg/g) and effluent (951.8±27.3 pg/ml) from the coronary sinus were detected after global cardiople ...
... ischemia and on left ventricular performances during 30 minutes of postischemic reperfusion was investigated. Results: Significant amounts of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in myocardial tissue (1149±33.7 pg/g) and effluent (951.8±27.3 pg/ml) from the coronary sinus were detected after global cardiople ...
Human Life Cycle
... Explain why the changes occurring in the endometrium are important for implantation Describe how the endometrium is maintained if pregnancy ensues ...
... Explain why the changes occurring in the endometrium are important for implantation Describe how the endometrium is maintained if pregnancy ensues ...
Reproduction
... finite number of egg cells. During early fetal development germ cells migrate into the ovaries and differentiate into oogonia ...
... finite number of egg cells. During early fetal development germ cells migrate into the ovaries and differentiate into oogonia ...
Anatomy Pre-Course Quiz
... A) Trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchiole, bronchus, alveoli B) Pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchiole, alveoli C) Trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchus, bronchiole, alveoli D) Pharynx, trachea, larynx, bronchiole, bronchus, alveoli ...
... A) Trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchiole, bronchus, alveoli B) Pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchiole, alveoli C) Trachea, pharynx, larynx, bronchus, bronchiole, alveoli D) Pharynx, trachea, larynx, bronchiole, bronchus, alveoli ...
Anterior - Mr. Morrison's Biology Class
... • Thus, one inherits either A or B antigens (group A or B), both A and B antigens (group AB), or neither antigen (group O). • Conversely, a person develops a natural immunity, or antibody, in their plasma to the ABO antigens that are absent on their own red cells. • Thus, a group A person has anti-B ...
... • Thus, one inherits either A or B antigens (group A or B), both A and B antigens (group AB), or neither antigen (group O). • Conversely, a person develops a natural immunity, or antibody, in their plasma to the ABO antigens that are absent on their own red cells. • Thus, a group A person has anti-B ...
Cell and Embryology Textbook: Wolpert L, Beddington R, Jessell T
... the embryo does not enlarge during this period but simply partitions the cytoplasm of the zygote into many smaller cells, called blastomeres and each with its own nucleus ...
... the embryo does not enlarge during this period but simply partitions the cytoplasm of the zygote into many smaller cells, called blastomeres and each with its own nucleus ...
Histology - take homes from lectures 2012
... NK cells release perforins and granzymes to kill target cells Lymphocytes mature in bone marrow, GALT (tonsils, adenoids, appendix, etc.), and thymus (antigen independent environment) Antigen-dependent activation of antigen recognition – lymphocytes make effector lymphocytes and memory cells (about ...
... NK cells release perforins and granzymes to kill target cells Lymphocytes mature in bone marrow, GALT (tonsils, adenoids, appendix, etc.), and thymus (antigen independent environment) Antigen-dependent activation of antigen recognition – lymphocytes make effector lymphocytes and memory cells (about ...
1 CLASS 1X BIOLOGY PLANT TISSUES Definition of tissue Tissues
... 1. Epidermis: forms one cell thick outermost layer of the organs of plants, such as, leaves, flowers, stems and roots. This layer of cells is covered from the outside by the cuticle. 2. Cork: is made up of dead cells with thick walls, with no intercellular spaces, found in older stems and roots of d ...
... 1. Epidermis: forms one cell thick outermost layer of the organs of plants, such as, leaves, flowers, stems and roots. This layer of cells is covered from the outside by the cuticle. 2. Cork: is made up of dead cells with thick walls, with no intercellular spaces, found in older stems and roots of d ...
Suprarenal Glands
... • The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. The medulla remains relatively small until after birth. • The suprarenal glands rapidly be ...
... • The suprarenal gland of the fetus is 10-20 times larger than the adult glands relative to the body weight, and are large compared with the kidneys. This is because of the extensive size of the fetal cortex. The medulla remains relatively small until after birth. • The suprarenal glands rapidly be ...
Rat Dissection Guide
... 1. Liver: The liver does many more things than making bile. It collects almost all of the blood circulated through the intestines and processes many of the chemicals picked up there (such as alcohol, which your liver detoxifies). Waste products from protein metabolism are processed into the less-tox ...
... 1. Liver: The liver does many more things than making bile. It collects almost all of the blood circulated through the intestines and processes many of the chemicals picked up there (such as alcohol, which your liver detoxifies). Waste products from protein metabolism are processed into the less-tox ...
VDB Learning Objectives - V14-Study
... Chapter 18: Development of the Structures of Head and Neck - Part 3 1. True/ False- Ectodermal cells of the embryo form the periderm. (After neurulation, ectodermal cells proliferate to form the periderm, a new outer squamous cell layer on top of the original basal cell layer) 2. True/ False- Neural ...
... Chapter 18: Development of the Structures of Head and Neck - Part 3 1. True/ False- Ectodermal cells of the embryo form the periderm. (After neurulation, ectodermal cells proliferate to form the periderm, a new outer squamous cell layer on top of the original basal cell layer) 2. True/ False- Neural ...
paraganglioma Displacing IVC: a Surgical Challenge
... in the sympathetic ganglia [1, 3]. These tumors comprise approximately 10% to 15% of all cases of pheochromocytoma [8]. A large series from the Mayo clinic reported the head and neck region to be the most common site for benign paragangliomas. Within the abdomen, the majority of these lesions are lo ...
... in the sympathetic ganglia [1, 3]. These tumors comprise approximately 10% to 15% of all cases of pheochromocytoma [8]. A large series from the Mayo clinic reported the head and neck region to be the most common site for benign paragangliomas. Within the abdomen, the majority of these lesions are lo ...
Thumb side = thenar - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... In fetus, blood bypasses the liver sinusoid through the ductus venosus What part of humerus articulates with radius? -capitulum (“Want to put a cap on the head of radius.”) ...
... In fetus, blood bypasses the liver sinusoid through the ductus venosus What part of humerus articulates with radius? -capitulum (“Want to put a cap on the head of radius.”) ...
Lecture 1
... Impaired uteroplacental blood flow: This leads to fetal starvation caused by small chorionic or umbilical vessels impairment, severe hypotension or renal disease. Genetic factors: growth retardation Diagnostic Amniocentesis: Typically 20-30 ml’s of fluid is removed and analyzed. A needle is inserted ...
... Impaired uteroplacental blood flow: This leads to fetal starvation caused by small chorionic or umbilical vessels impairment, severe hypotension or renal disease. Genetic factors: growth retardation Diagnostic Amniocentesis: Typically 20-30 ml’s of fluid is removed and analyzed. A needle is inserted ...
Cardiovascular System_Lecture III - Medical
... Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels, measuring 5-10 μm. They connect arteries and veins, and most closely interact with tissues. Capillaries have walls composed of a single layer of cells, the endothelium. This layer is so thin that molecules such as oxygen, water and lipids can p ...
... Capillaries are the smallest of a body's blood vessels, measuring 5-10 μm. They connect arteries and veins, and most closely interact with tissues. Capillaries have walls composed of a single layer of cells, the endothelium. This layer is so thin that molecules such as oxygen, water and lipids can p ...
Phlebotomist - ExploreHealthCareers.org
... The phlebotomist then locates a vein and inserts a needle, a process called “venipuncture.” Phlebotomists can also sample blood through skin puncture, such as pricking a finger to test a patient’s blood sugar or determine blood type. The phlebotomist must ensure that all equipment is properly saniti ...
... The phlebotomist then locates a vein and inserts a needle, a process called “venipuncture.” Phlebotomists can also sample blood through skin puncture, such as pricking a finger to test a patient’s blood sugar or determine blood type. The phlebotomist must ensure that all equipment is properly saniti ...
unit 8 - blood / lymphatic / cardiovascular systems
... 14. What problems might you have if you had no platelets in your blood? Your blood would not be able to clot. 15. As you increase altitude, there is less oxygen in the air. How might this affect your blood? Your body would produce more red blood cells to be able to carry enough oxygen for your body’ ...
... 14. What problems might you have if you had no platelets in your blood? Your blood would not be able to clot. 15. As you increase altitude, there is less oxygen in the air. How might this affect your blood? Your body would produce more red blood cells to be able to carry enough oxygen for your body’ ...
Biology 233
... zona pellucida – clear, glycoprotein layer around oocyte thecal cells – CT surrounding follicle; nourishes follicle and helps it produce hormones secondary follicles – a few primary follicles mature to this stage pockets of secretions from granulosa cells surround primary oocyte tertiary follicle – ...
... zona pellucida – clear, glycoprotein layer around oocyte thecal cells – CT surrounding follicle; nourishes follicle and helps it produce hormones secondary follicles – a few primary follicles mature to this stage pockets of secretions from granulosa cells surround primary oocyte tertiary follicle – ...
Anatomy introduction11
... of the body; some transport or store materials.e.g. Blood, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue . 3. Muscle tissues:specialized for contraction, which brings about movement. Our skeletal muscles and the heart are examples . 4. Nerve tissue:specialized to generate and transmit electrochemical impulses ...
... of the body; some transport or store materials.e.g. Blood, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue . 3. Muscle tissues:specialized for contraction, which brings about movement. Our skeletal muscles and the heart are examples . 4. Nerve tissue:specialized to generate and transmit electrochemical impulses ...
Vrodené a perinatálne získané ochorenia mozgu
... • Pat.-anat. – degeneration of Purkyne cells and granular cells • Gen ATM also risk of cancer ...
... • Pat.-anat. – degeneration of Purkyne cells and granular cells • Gen ATM also risk of cancer ...
... Rod cells consist of: THE PERIPHERAL PART - serves as photoreceptive apparatus; it has two segments - the outer and the inner ones, that are separated each other by a constriction containing an atypical kinocilium the outer segment contains 600 to 1000 flattened membranous disks piled up like a stac ...
Circulating tumor cell
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cells that have shed into the vasculature from a primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. CTCs thus constitute seeds for subsequent growth of additional tumors (metastasis) in vital distant organs, triggering a mechanism that is responsible for the vast majority of cancer-related deaths.CTCs were observed for the first time in 1869 in the blood of a man with metastatic cancer by Thomas Ashworth, who postulated that “cells identical with those of the cancer itself being seen in the blood may tend to throw some light upon the mode of origin of multiple tumours existing in the same person”. A thorough comparison of the morphology of the circulating cells to tumor cells from different lesions led Ashworth to conclude that “One thing is certain, that if they [CTC] came from an existing cancer structure, they must have passed through the greater part of the circulatory system to have arrived at the internal saphena vein of the sound leg”.The importance of CTC's in modern cancer research began in the mid 1990's with the demonstration [J. Uhr, UT-Dallas, L. Terstappen and P. Liberti, Immunicon, Philadelphia] that CTC's exist early on in the course of the disease. Those results were made possible by exquisitely sensitive magnetic separation technology employing Ferrofluids (colloidal magnetic nanoparticles) and high gradient magnetic separators invented by Liberti at Immunicon and motivated by theoretical calculations by Liberti and Terstappen that indicated very small tumors shedding cells at less than 1.0 % per day should result in detectable cells in blood. A variety of other technologies have been applied to CTC enumeration and identification since that time.Modern cancer research has demonstrated that CTCs derive from clones in the primary tumor, validating Ashworth's remarks. The significant efforts put into understanding the CTCs biological properties have demonstrated the critical role circulating tumor cells play in the metastatic spread of carcinoma.Furthermore, highly sensitive, single-cell analysis demonstrated a high level of heterogeneity seen at the single cell level for both protein expression and protein localization and the CTCs reflected both the primary biopsy and the changes seen in the metastatic sites. Tissue biopsies are poor diagnostic procedures: they are invasive, cannot be used repeatedly, and are ineffective in understanding metastatic risk, disease progression, and treatment effectiveness. CTCs thus could be considered a “liquid biopsy” which reveals metastasis in action, providing live information about the patient’s disease status. Analysis of blood samples found a propensity for increased CTC detection as the disease progressed in individual patients. Blood tests are easy and safe to perform and multiple samples can be taken over time. By contrast, analysis of solid tumors necessitates invasive procedures that might limit patient compliance. The ability to monitor disease progression over time could facilitate appropriate modification to a patient's therapy, potentially improving their prognosis and quality of life.To this end, technologies with the requisite sensitivity and reproducibility to detect CTCs in patients with metastatic disease have recently been developed.