RED BLOOD CELLS - Little Miami Schools
... blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh positive (Rh+). If your blood does not contain the protein, your blo ...
... blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh positive (Rh+). If your blood does not contain the protein, your blo ...
2017 Human A and P Pacing Guide
... understanding of the growth and development of the skeletal system (e.g., bone growth and remodeling). 4b. Obtain and communicate information to demonstrate understanding of the pathology of the skeletal system (e.g., types of bone fractures and their treatment, osteoporosis, rickets, other bone dis ...
... understanding of the growth and development of the skeletal system (e.g., bone growth and remodeling). 4b. Obtain and communicate information to demonstrate understanding of the pathology of the skeletal system (e.g., types of bone fractures and their treatment, osteoporosis, rickets, other bone dis ...
CH 16 Sense Organs A aand P 2016
... make basilar membrane less or more flexible – this allows hair cells to be more sensitive – and allows brain to – to better differentiate between frequencies also pons sends efferents – to IHC – to inhibit some cells – so areas of most and least sensitivity can be differentiated ...
... make basilar membrane less or more flexible – this allows hair cells to be more sensitive – and allows brain to – to better differentiate between frequencies also pons sends efferents – to IHC – to inhibit some cells – so areas of most and least sensitivity can be differentiated ...
CH 16 Sense Organs A aand P 2017
... make basilar membrane less or more flexible – this allows hair cells to be more sensitive – and allows brain to – better differentiate between frequencies also pons sends efferents – to IHC – to inhibit some cells – so areas of most and least sensitivity can be differentiated ...
... make basilar membrane less or more flexible – this allows hair cells to be more sensitive – and allows brain to – better differentiate between frequencies also pons sends efferents – to IHC – to inhibit some cells – so areas of most and least sensitivity can be differentiated ...
Slajd 1 - Naslovnica - Web Stomatološkog fakulteta
... Fluids constitute over half of an adult’s weight under normal conditions These fluids are vital in the transport of nutrients to all cells ...
... Fluids constitute over half of an adult’s weight under normal conditions These fluids are vital in the transport of nutrients to all cells ...
m5zn_a2ee964dc9b908b
... • This leads to sloughing of the surface epithelial cells and then they undergo physiologic cell death (apoptotic cell death) to expose basal epithelial cells. • These basal cells have an extra cellular surface substances particularly glycopoteins that enhance adhesion between the shelf edges as wel ...
... • This leads to sloughing of the surface epithelial cells and then they undergo physiologic cell death (apoptotic cell death) to expose basal epithelial cells. • These basal cells have an extra cellular surface substances particularly glycopoteins that enhance adhesion between the shelf edges as wel ...
Meningioamele parasagitale
... can occur during dissection, and the surgeon must be prepared for a venous reconstruction to avoid a devastating venous hemorrhagic stroke in eloquent cortex in cases that require SSS wall reconstruction, an endto-end venous graft to the stump of the bridging vein can be performed ...
... can occur during dissection, and the surgeon must be prepared for a venous reconstruction to avoid a devastating venous hemorrhagic stroke in eloquent cortex in cases that require SSS wall reconstruction, an endto-end venous graft to the stump of the bridging vein can be performed ...
The Digestive Tract of the Cod Eleutheroembryo ("Yolk
... Eletitheroambryo. 3-5mm. Peak-hatch to 5 nr 6 days This phase is the last part of the embryonic period, during which the embryo is free-living (eleutheros=free), but still depends mainly on its yolk-sac for food, and lasts from hatching to the start of exogenous feeding. No mouth is present just aft ...
... Eletitheroambryo. 3-5mm. Peak-hatch to 5 nr 6 days This phase is the last part of the embryonic period, during which the embryo is free-living (eleutheros=free), but still depends mainly on its yolk-sac for food, and lasts from hatching to the start of exogenous feeding. No mouth is present just aft ...
ANATOMY OF INNER EAR
... • Inner phalangeal cells & border cells enclose inner hair cells • Deiters’ cells enclose outer hair cells & send phalangeal processes to the adjacent cells • Hensen’s cells & Claudius’ cells are present on the outer edge of basilar membrane ...
... • Inner phalangeal cells & border cells enclose inner hair cells • Deiters’ cells enclose outer hair cells & send phalangeal processes to the adjacent cells • Hensen’s cells & Claudius’ cells are present on the outer edge of basilar membrane ...
gray matter
... the nerve cells or neurons and special supporting cells called neuroglia neurons - cells in which two properties of protoplasm are developed to a great degree: irritability (the capacity for response to physical and chemical agents with the initiation of an impulse), conductivity (the ability to tra ...
... the nerve cells or neurons and special supporting cells called neuroglia neurons - cells in which two properties of protoplasm are developed to a great degree: irritability (the capacity for response to physical and chemical agents with the initiation of an impulse), conductivity (the ability to tra ...
Cardiovascular
... The sciatic nerve supplies muscles of the calf, & back of thigh, skin & lower thigh & upper surface of the foot. ...
... The sciatic nerve supplies muscles of the calf, & back of thigh, skin & lower thigh & upper surface of the foot. ...
Development of Dermis
... Development of sebaceous glands • Glandular buds from sides of developing epidermal root sheaths of hair follicles, branch to form primordia of alveoli & ducts • Central cells of alveoli: break down, release into hair follicle, mix with desquamated peridermal cells (vernix caseosa) • Sebaceous gland ...
... Development of sebaceous glands • Glandular buds from sides of developing epidermal root sheaths of hair follicles, branch to form primordia of alveoli & ducts • Central cells of alveoli: break down, release into hair follicle, mix with desquamated peridermal cells (vernix caseosa) • Sebaceous gland ...
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline A. gustation
... bipolar cells - superficial to photoreceptors, connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells ganglion cells - surface of nervous layer; axons form cranial nerve II (optic nerve) anterior margin of nervous layer = ora serrata macula lutea - spot in exact center of back of eyeball fovea centralis - indenta ...
... bipolar cells - superficial to photoreceptors, connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells ganglion cells - surface of nervous layer; axons form cranial nerve II (optic nerve) anterior margin of nervous layer = ora serrata macula lutea - spot in exact center of back of eyeball fovea centralis - indenta ...
KEY CHAPTER 23 OBJECTIVES: PREGNANCY, GROWTH, AND
... will form the outer covering (i.e. epidermis and its derivatives) and nervous system organs in the adult. Endoderm is the layer of ICM epithelial cells that border the blastocoele. a. considered the innermost germ layer b. will form the inner lining (mucosa) of the adult (i.e. digestive, respiratory ...
... will form the outer covering (i.e. epidermis and its derivatives) and nervous system organs in the adult. Endoderm is the layer of ICM epithelial cells that border the blastocoele. a. considered the innermost germ layer b. will form the inner lining (mucosa) of the adult (i.e. digestive, respiratory ...
Pathology
... Using sophisticated microscopes and a trained eye, they examine tissues and cells removed from patients in the clinic or at operation. By examining tissue sections which have been stained to reveal the microscopic structure, a histopathologist decides whether disease is present and, if so, what effe ...
... Using sophisticated microscopes and a trained eye, they examine tissues and cells removed from patients in the clinic or at operation. By examining tissue sections which have been stained to reveal the microscopic structure, a histopathologist decides whether disease is present and, if so, what effe ...
Chapter 35. - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
... tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
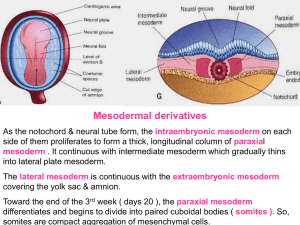
07 - mesodermal
... mesoderm between the pericardial part of I.E.C. and the roof of the secondary yolk sac ( cardiogenic area ). So, the heart tubes are paired longitudinal endothelial lined channels. These tubes fused to form a primordial heart tube. The tubular heart joins with blood vessels in the embryo; connecting ...
... mesoderm between the pericardial part of I.E.C. and the roof of the secondary yolk sac ( cardiogenic area ). So, the heart tubes are paired longitudinal endothelial lined channels. These tubes fused to form a primordial heart tube. The tubular heart joins with blood vessels in the embryo; connecting ...
File
... Antigen: any foreign substance or cell in the body that reacts with antibodies Cell-surface protein: proteins embedded in the cell membrane Red blood cells: donut-shaped cells that carry oxygen throughout the body White Blood Cells: cells that police the body by destroying foreign materials ...
... Antigen: any foreign substance or cell in the body that reacts with antibodies Cell-surface protein: proteins embedded in the cell membrane Red blood cells: donut-shaped cells that carry oxygen throughout the body White Blood Cells: cells that police the body by destroying foreign materials ...
Introduction - Biology Courses Server
... MITOSIS / MEIOSIS (circle one), eventually becoming a ____________ when it reaches 12 cells. A fluid-filled cavity forms, at which point the ball of cells is called a _________________. The outer cell mass is called the __________________ and the inner cell mass is called the ________________. Every ...
... MITOSIS / MEIOSIS (circle one), eventually becoming a ____________ when it reaches 12 cells. A fluid-filled cavity forms, at which point the ball of cells is called a _________________. The outer cell mass is called the __________________ and the inner cell mass is called the ________________. Every ...
IB 3 Liver - susanpittinaro
... Cirrhosis – build up scar tissue left in areas of liver destroyed by prolonged alcohol exposure ...
... Cirrhosis – build up scar tissue left in areas of liver destroyed by prolonged alcohol exposure ...
Anatomy 101: The Colon and Rectum
... remove them during a colonoscopy. In most cases, benign polyps do not come back after they are removed. Their cells do not spread to tissues around them or to other parts of the body. Malignant polyps are cancer. They are usually more serious and, if not removed, may be life-threatening. Cancer cell ...
... remove them during a colonoscopy. In most cases, benign polyps do not come back after they are removed. Their cells do not spread to tissues around them or to other parts of the body. Malignant polyps are cancer. They are usually more serious and, if not removed, may be life-threatening. Cancer cell ...
Lab #15 - Sensory Structures
... e. suspensory ligaments (ciliary zonule) f. iris*: spinctor pupillae m., dilator pupillae m. g. pupil* 3. sensory tunic/retina* a. ora serrata retinae b. macula lutea c. fovea centralis d. optic disc* ...
... e. suspensory ligaments (ciliary zonule) f. iris*: spinctor pupillae m., dilator pupillae m. g. pupil* 3. sensory tunic/retina* a. ora serrata retinae b. macula lutea c. fovea centralis d. optic disc* ...
Ch 4 study guide page 1
... 2. Fat in the ________________ tissue layer beneath the dermis helps to insulate the body. 3. The waterproofing protein found in the epidermal cells is called _______________________. 4. A vitamin that is manufactured in the skin is _______________________. 5. A localized concentration of melanin is ...
... 2. Fat in the ________________ tissue layer beneath the dermis helps to insulate the body. 3. The waterproofing protein found in the epidermal cells is called _______________________. 4. A vitamin that is manufactured in the skin is _______________________. 5. A localized concentration of melanin is ...
Chapter 4: Tissue Level of Organization
... Tissues: collections of specialized cells and cell products that perform a limited number of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
... Tissues: collections of specialized cells and cell products that perform a limited number of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
Circulating tumor cell
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cells that have shed into the vasculature from a primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. CTCs thus constitute seeds for subsequent growth of additional tumors (metastasis) in vital distant organs, triggering a mechanism that is responsible for the vast majority of cancer-related deaths.CTCs were observed for the first time in 1869 in the blood of a man with metastatic cancer by Thomas Ashworth, who postulated that “cells identical with those of the cancer itself being seen in the blood may tend to throw some light upon the mode of origin of multiple tumours existing in the same person”. A thorough comparison of the morphology of the circulating cells to tumor cells from different lesions led Ashworth to conclude that “One thing is certain, that if they [CTC] came from an existing cancer structure, they must have passed through the greater part of the circulatory system to have arrived at the internal saphena vein of the sound leg”.The importance of CTC's in modern cancer research began in the mid 1990's with the demonstration [J. Uhr, UT-Dallas, L. Terstappen and P. Liberti, Immunicon, Philadelphia] that CTC's exist early on in the course of the disease. Those results were made possible by exquisitely sensitive magnetic separation technology employing Ferrofluids (colloidal magnetic nanoparticles) and high gradient magnetic separators invented by Liberti at Immunicon and motivated by theoretical calculations by Liberti and Terstappen that indicated very small tumors shedding cells at less than 1.0 % per day should result in detectable cells in blood. A variety of other technologies have been applied to CTC enumeration and identification since that time.Modern cancer research has demonstrated that CTCs derive from clones in the primary tumor, validating Ashworth's remarks. The significant efforts put into understanding the CTCs biological properties have demonstrated the critical role circulating tumor cells play in the metastatic spread of carcinoma.Furthermore, highly sensitive, single-cell analysis demonstrated a high level of heterogeneity seen at the single cell level for both protein expression and protein localization and the CTCs reflected both the primary biopsy and the changes seen in the metastatic sites. Tissue biopsies are poor diagnostic procedures: they are invasive, cannot be used repeatedly, and are ineffective in understanding metastatic risk, disease progression, and treatment effectiveness. CTCs thus could be considered a “liquid biopsy” which reveals metastasis in action, providing live information about the patient’s disease status. Analysis of blood samples found a propensity for increased CTC detection as the disease progressed in individual patients. Blood tests are easy and safe to perform and multiple samples can be taken over time. By contrast, analysis of solid tumors necessitates invasive procedures that might limit patient compliance. The ability to monitor disease progression over time could facilitate appropriate modification to a patient's therapy, potentially improving their prognosis and quality of life.To this end, technologies with the requisite sensitivity and reproducibility to detect CTCs in patients with metastatic disease have recently been developed.