* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of Dermis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
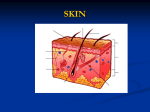
Integumentary system Min-Chuan Huang 台大醫學院解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 黃敏銓 1 Integumentary system Skin: Epidermis Dermis Skin appendages Sebaceous glands Sweat glands Mammary glands Hair Arrector pili muscles Nails Teeth 2 Development of skin: overview 4 weeks • Embryonic skin: begins from embryo of 4-5 weeks • Epidermis: surface ectoderm Dermis: mesoderm Mutual inductive mechanism for ectodermal/mesenchymal interactions (epidermal / dermal interactions) WNT, fibroblast growth factor (FGF), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), sonic hedgehog (SHH) 3 Development of epidermis: early stage 4 weeks • 4 weeks: primordial skin from surface ectoderm • 7 weeks: ● Periderm: single layer of squamous epithelium 7 weeks - Continue keratinization, desquamation - Exfoliated cells form part of vernix caseosa ● Basal layer: proliferation 4 Development of Epidermis at 11 weeks • Stratum germinativum –Epidermal ridges: begin at 10 weeks, permanently established at 19th week; genetically determined (fingerprint), Dermatoglyphics 皮紋學 • Intermediate layer: from stratum germinativum • Migration of neural crest cells to developing dermis (melanoblasts), later melanocytes (as early as 40-50 days) in stratum germinativum 11 weeks 5 Development of epidermis: 21st week forward (periderm disappears) ichthyosis: severe keratinization Newborn • Stratum corneum: originally periderm • Appearance of stratum lucidum, granulosum, spinosum Melanocytes fail to produce melanin: 1. Generalized albinism 2. Localized albinism (piebaldism) 6 Development of Dermis • Mesenchyme from mesoderm: (major) somatic layer of lateral mesoderm & (minor) dermatomes of somites • By 11 weeks: mesenchymal cells produce collagenous & elastic connective tissues fibers • Dermal ridge: with capillary loops & sensory nerve endings • Capillary-like vessels: derived from mesenchyme, begin at the end of 5th week 11 weeks 7 Week 16 Week 20 Development of sebaceous glands • Glandular buds from sides of developing epidermal root sheaths of hair follicles, branch to form primordia of alveoli & ducts • Central cells of alveoli: break down, release into hair follicle, mix with desquamated peridermal cells (vernix caseosa) • Sebaceous glands independent of hair follicles: in external genital organs 8 Development of eccrine sweat glands • Epidermal downgrowth into dermis by elongation, and coiling • End: primordium of secretory part; (1) myoepithelial cells, (2) secretory cells • Epithelial attachment: primordium of duct, central cells degenerate • weeks Begin to function after birth 20 9 Development of apocrine sweat glands • Axilla, pubic, perineal regions, areolae of the nipples • Downgrowths of stratum germinativum giving rise to hair follicles • Open into the upper part of hair follicles superficial to the openings of sebaceous glands • Secrete during puberty • Pheromone 10 Development of hair (1/2) Week 9-12 • Hair follicle: stratum germinativum into dermis • Hair bud • Hair bulb (primordium of hair root) –Germinal matrix, invaginated by mesenchymal hair papilla –Hair shaft: keratinized portion 11 Development of hair (2/2) • Epidermal root sheath: from peripheral cells of hair follicles • Dermal root sheath: from mesenchymal cells • Lanugo: the first hair, end of 12th week, replaced during perinatal period • Melanocyte in hair bulb from migrating melanoblast • Arrector pili muscles from mesenchyme, goose bumps Week 12 Week 20 12 Hypertrichosis 13 Hypertrichosis Nature. 2007 Alopecia 14 Folliculogenesis Hair cycling 15 Hair follicle stem cells in bulge region 16 Stem Cells 2005;23:150–165 Hair follicle stem cells • • • • • • • • • Hair follicles Schwann cells Neurons Glial cells Keratinocytes/sebaceous glands Smooth muscle cells Blood vessels Adipocytes Hematopoietic cells 17 We need tissue regeneration instead of scar formation Nature. 2008. 453:314-21. Myocardial infarction Spinal cord injury Liver cirrhosis Lung fibrosis Development of mammary glands • Mammary ridges: 4th week; thickened strips of ectoderm from axillary to inguinal regions • Mammary buds: downgrowth of epidermis at 6th week 19 Supernumerary nipples Supernumerary breasts 1% of the female 5.6% 20 Development of mammary glands • Mammary buds: primary bud → secondary buds → lactiferous ducts/branches: canalization by placental sex hormones • Mammary pits: depressed epidermis → nipples rise by proliferation of connective tissues (areola) 21 Flat or inverted nipples (10-20%)