Paranasal Sinuses: Anatomy and Function
... Function of Paranasal Sinuses Humidifying and warming inspired air Regulation of intranasal pressure Increasing surface area for olfaction Lightening the skull Resonance Absorbing shock Contribute to facial growth ...
... Function of Paranasal Sinuses Humidifying and warming inspired air Regulation of intranasal pressure Increasing surface area for olfaction Lightening the skull Resonance Absorbing shock Contribute to facial growth ...
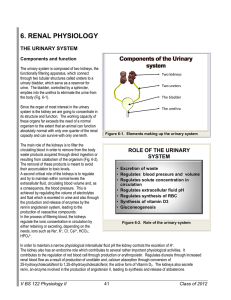
6. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... The main role of the kidneys is to filter the circulating blood in order to remove from the body waste products acquired through direct ingestion or resulting from catabolism of the organism (Fig. 6-2). The removal of these products is meant to avoid their accumulation to toxic levels. A second crit ...
... The main role of the kidneys is to filter the circulating blood in order to remove from the body waste products acquired through direct ingestion or resulting from catabolism of the organism (Fig. 6-2). The removal of these products is meant to avoid their accumulation to toxic levels. A second crit ...
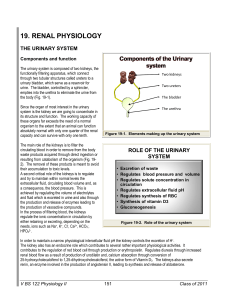
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... The main role of the kidneys is to filter the circulating blood in order to remove from the body waste products acquired through direct ingestion or resulting from catabolism of the organism (Fig. 192). The removal of these products is meant to avoid their accumulation to toxic levels. A second crit ...
... The main role of the kidneys is to filter the circulating blood in order to remove from the body waste products acquired through direct ingestion or resulting from catabolism of the organism (Fig. 192). The removal of these products is meant to avoid their accumulation to toxic levels. A second crit ...
Anatomy Exam 1 - UTCOM 2012 Wiki
... Multipolar – many processes; motor neurons Pseudounipolar - primary sensory neurons Peripheral process - „dendrite‟ Central process – „axon‟ ○ Definitions Nucleus – collection of neuronal cell bodies within the CNS (collected because they do the same thing) Ganglion – collection of neuro ...
... Multipolar – many processes; motor neurons Pseudounipolar - primary sensory neurons Peripheral process - „dendrite‟ Central process – „axon‟ ○ Definitions Nucleus – collection of neuronal cell bodies within the CNS (collected because they do the same thing) Ganglion – collection of neuro ...
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma - The Medical Post | Trusting
... Stage IV: Tumor invading cavernous sinus or optic chiasma or pituitary fossa ...
... Stage IV: Tumor invading cavernous sinus or optic chiasma or pituitary fossa ...
Organs from the mesoderm
... efferent vessel has as yet appeared. No vessels are present at this time in the fourth branchial arch. The dorsal aorta is represented by ,1 paired vessel in the dorso-pharyngeal region. Opposite the hyoid arch each branch of the dorsal aorta divides into a dorsal and into a ventral braneh. The dors ...
... efferent vessel has as yet appeared. No vessels are present at this time in the fourth branchial arch. The dorsal aorta is represented by ,1 paired vessel in the dorso-pharyngeal region. Opposite the hyoid arch each branch of the dorsal aorta divides into a dorsal and into a ventral braneh. The dors ...
dr.mohamed farouk Cervical cancer
... MRI findings in normal cervix: MRI anatomy of the cervix is best delineated on T2W image as four major zones of cervix From center to periphery, these are high signal intensity endocervical canal, intermediate signal intensity plicae palmatae, low signal intensity fibrous stroma, and intermediate s ...
... MRI findings in normal cervix: MRI anatomy of the cervix is best delineated on T2W image as four major zones of cervix From center to periphery, these are high signal intensity endocervical canal, intermediate signal intensity plicae palmatae, low signal intensity fibrous stroma, and intermediate s ...
File
... remaining in lung after normal expiration, cannot be measured by spirometry because it includes residual volume:ERV + RV = 2400 ml • VITAL CAPACITY (VC): Volume of maximal inspiration and expiration:IRV + TV + ERV = IC + ERV = 4800 ml • TOTAL LUNG CAPACITY (TLC): The volume of the lung after maximal ...
... remaining in lung after normal expiration, cannot be measured by spirometry because it includes residual volume:ERV + RV = 2400 ml • VITAL CAPACITY (VC): Volume of maximal inspiration and expiration:IRV + TV + ERV = IC + ERV = 4800 ml • TOTAL LUNG CAPACITY (TLC): The volume of the lung after maximal ...
The Embryology of Patella1
... Fig. 1, while the inner surface is smooth. *) The larger pits are simply indentations in the outer surface of the chorion and are not connected with or extended into fine lines or tubes. None of these dots nor the fine lines connected with them have anything in the nature of a micropyle, which is si ...
... Fig. 1, while the inner surface is smooth. *) The larger pits are simply indentations in the outer surface of the chorion and are not connected with or extended into fine lines or tubes. None of these dots nor the fine lines connected with them have anything in the nature of a micropyle, which is si ...
DEVELOPMENTOF FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM
... 7th week. They begin to differentiate in the 9th week. They are fully differentiated by the 12th week. ...
... 7th week. They begin to differentiate in the 9th week. They are fully differentiated by the 12th week. ...
LYMPHOID SYSTEM,LYMPHATIC VESSELS,LYMPH NODES
... The functions of the thymus are the "schooling" of Tlymphocytes (T cells), which are critical cells of the adaptive immune system, and the production and secretion of thymosins, hormones which control Tlymphocyte activities and various other aspects of the immune system. thoracic duct It is the ...
... The functions of the thymus are the "schooling" of Tlymphocytes (T cells), which are critical cells of the adaptive immune system, and the production and secretion of thymosins, hormones which control Tlymphocyte activities and various other aspects of the immune system. thoracic duct It is the ...
Neuroanatomy Laboratory
... The relatively acellular molecular layer lies just beneath the pial surface. The two types of neuron found in this layer are (1) the stellate cells (small neurons located in the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer), and (2) the basket cells, which are located near the Purkinje cell bodies. The d ...
... The relatively acellular molecular layer lies just beneath the pial surface. The two types of neuron found in this layer are (1) the stellate cells (small neurons located in the outer two-thirds of the molecular layer), and (2) the basket cells, which are located near the Purkinje cell bodies. The d ...
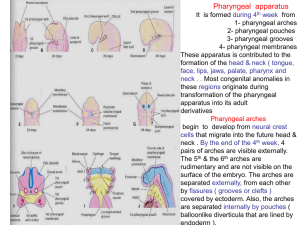
03-pharyngeal arches ,pouchs
... Histogenesis of the thyroid gland The thyroid primordium consists of a solid mass of endodermal cells Later, this cellular aggregation breaks up into a network of epithelial cords . This is due to its invasion by the surrounding vascular mesenchyme. By the 10th week , the cords have divided into sm ...
... Histogenesis of the thyroid gland The thyroid primordium consists of a solid mass of endodermal cells Later, this cellular aggregation breaks up into a network of epithelial cords . This is due to its invasion by the surrounding vascular mesenchyme. By the 10th week , the cords have divided into sm ...
the leaf structure of some nepenthes danser
... In cross section, the tendril shows a circular shape, with 7-8 ribs at N. maxima (Fig. 6). Small cells, covered by a thick cuticle, form the epidermis. Here an there, hydathodes, short, sometimes branched tector hairs and stomata prominig above the epidermis are present. The cortical parenchyma is f ...
... In cross section, the tendril shows a circular shape, with 7-8 ribs at N. maxima (Fig. 6). Small cells, covered by a thick cuticle, form the epidermis. Here an there, hydathodes, short, sometimes branched tector hairs and stomata prominig above the epidermis are present. The cortical parenchyma is f ...
Differential Diagnosis of Temporal Bone and Skull Base
... Glomus jugulare tumors arise in the jugular fossa and are usually large before patients become symptomatic. Compression of neurovascular structures in the jugular fossa and extension along the skull base to the hypoglossal canal can lead to cranial neuropathies. Erosion of the jugular fossa anterior ...
... Glomus jugulare tumors arise in the jugular fossa and are usually large before patients become symptomatic. Compression of neurovascular structures in the jugular fossa and extension along the skull base to the hypoglossal canal can lead to cranial neuropathies. Erosion of the jugular fossa anterior ...
Bovine mammary glands
... directly into the teat cistern. The cisterns function for milk storage (holds ~100400 ml). The gland cistern varies greatly in size and shape. There are often pockets formed in the cistern at the end of the larger ducts. The major ducts which empty into the gland cistern sometimes are called ...
... directly into the teat cistern. The cisterns function for milk storage (holds ~100400 ml). The gland cistern varies greatly in size and shape. There are often pockets formed in the cistern at the end of the larger ducts. The major ducts which empty into the gland cistern sometimes are called ...
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
... vein to a second capillary network, and then it will drain into the venous circulation, so the portal vein is always located between two capillary networks. In the hypophyseal portal system the arteries that supply the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe) will receive the blood supply from the Superior h ...
... vein to a second capillary network, and then it will drain into the venous circulation, so the portal vein is always located between two capillary networks. In the hypophyseal portal system the arteries that supply the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe) will receive the blood supply from the Superior h ...
Auditory system
... Conductive hearing loss - various problems in the middle ear which can reduce conduction of vibrations by the chain of ossicles from the tympanic membrane to the oval window Sensorineural hearing loss – is due to defects in any structure or cell from the cochlea to auditory centers of the brain, but ...
... Conductive hearing loss - various problems in the middle ear which can reduce conduction of vibrations by the chain of ossicles from the tympanic membrane to the oval window Sensorineural hearing loss – is due to defects in any structure or cell from the cochlea to auditory centers of the brain, but ...
Portland Community College, Sylvania Campus
... 5. For your safety, please restrain long hair, loose fitting clothing and dangling jewelry. Hair ties are available, ask your instructor. Hats and bare midriffs are not acceptable in the laboratory. Shoes, not sandals, must be worn at all times in laboratory. You may wear a laboratory apron or lab c ...
... 5. For your safety, please restrain long hair, loose fitting clothing and dangling jewelry. Hair ties are available, ask your instructor. Hats and bare midriffs are not acceptable in the laboratory. Shoes, not sandals, must be worn at all times in laboratory. You may wear a laboratory apron or lab c ...
Anatomy and Histology of the Pancreas
... The pancreas is a compound, finely nodular gland that is grossly similar to but less compact than the salivary glands. It is surrounded by fine connective tissue but does not have a fibrous tissue capsule. The lobules are visible on gross examination and are connected by connective tissue septa that ...
... The pancreas is a compound, finely nodular gland that is grossly similar to but less compact than the salivary glands. It is surrounded by fine connective tissue but does not have a fibrous tissue capsule. The lobules are visible on gross examination and are connected by connective tissue septa that ...
THE NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION Ralph F
... medulla and pons and contributes to the roof of the fourth ventricle. It constitutes about 10% of the weight of the brain. It consists of a midline vermis and two lateral hemispheres. From the dorsal side of the cerebellum, it is not possible to observe these distinctions, but they are obvious from ...
... medulla and pons and contributes to the roof of the fourth ventricle. It constitutes about 10% of the weight of the brain. It consists of a midline vermis and two lateral hemispheres. From the dorsal side of the cerebellum, it is not possible to observe these distinctions, but they are obvious from ...
Chapter 1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE
... extend from the dorsal root entry zone, envelop the dorsal rootlets and then follow the rootlets laterally. This attachment continues into the root sleeve, where it may distinguish the dorsal rootlets from the ventral rootlets, the latter having no arachnoid covering. The dorsolateral septae are mos ...
... extend from the dorsal root entry zone, envelop the dorsal rootlets and then follow the rootlets laterally. This attachment continues into the root sleeve, where it may distinguish the dorsal rootlets from the ventral rootlets, the latter having no arachnoid covering. The dorsolateral septae are mos ...
Organs from the endoderm
... eircular blastopore is reduced to an elongated slit-like opening; but there seems to be some variation in the details of the method of its later reduction. The medullary folds arch over only the anterior end of the elongated blastopore, leaving free the posterior end. The anterior end becomes the ne ...
... eircular blastopore is reduced to an elongated slit-like opening; but there seems to be some variation in the details of the method of its later reduction. The medullary folds arch over only the anterior end of the elongated blastopore, leaving free the posterior end. The anterior end becomes the ne ...
Rabbit RX Uterine Adenocarcinoma in Rabbits with Dr. Jay E. Hreiz
... the incidence of uterine cancer to be higher in certain breeds. They include the Tan, Havana, and Dutch. The incidence in uterine cancer in these breeds over the age of four can be as high as 5080%. Despite these breeds that may be overrepresented, age is the number one factor when considering wheth ...
... the incidence of uterine cancer to be higher in certain breeds. They include the Tan, Havana, and Dutch. The incidence in uterine cancer in these breeds over the age of four can be as high as 5080%. Despite these breeds that may be overrepresented, age is the number one factor when considering wheth ...
Biology_218_Lecture_Outline_24_Respration
... a capillary network; the blood capillaries consist of a single layer of endothelial cells and a basement membrane. The exchange of respiratory gases between the air spaces in the lungs and the blood occurs by diffusion across the respiratory membrane; this membrane consists of four layers: 1. a laye ...
... a capillary network; the blood capillaries consist of a single layer of endothelial cells and a basement membrane. The exchange of respiratory gases between the air spaces in the lungs and the blood occurs by diffusion across the respiratory membrane; this membrane consists of four layers: 1. a laye ...
Circulating tumor cell
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cells that have shed into the vasculature from a primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. CTCs thus constitute seeds for subsequent growth of additional tumors (metastasis) in vital distant organs, triggering a mechanism that is responsible for the vast majority of cancer-related deaths.CTCs were observed for the first time in 1869 in the blood of a man with metastatic cancer by Thomas Ashworth, who postulated that “cells identical with those of the cancer itself being seen in the blood may tend to throw some light upon the mode of origin of multiple tumours existing in the same person”. A thorough comparison of the morphology of the circulating cells to tumor cells from different lesions led Ashworth to conclude that “One thing is certain, that if they [CTC] came from an existing cancer structure, they must have passed through the greater part of the circulatory system to have arrived at the internal saphena vein of the sound leg”.The importance of CTC's in modern cancer research began in the mid 1990's with the demonstration [J. Uhr, UT-Dallas, L. Terstappen and P. Liberti, Immunicon, Philadelphia] that CTC's exist early on in the course of the disease. Those results were made possible by exquisitely sensitive magnetic separation technology employing Ferrofluids (colloidal magnetic nanoparticles) and high gradient magnetic separators invented by Liberti at Immunicon and motivated by theoretical calculations by Liberti and Terstappen that indicated very small tumors shedding cells at less than 1.0 % per day should result in detectable cells in blood. A variety of other technologies have been applied to CTC enumeration and identification since that time.Modern cancer research has demonstrated that CTCs derive from clones in the primary tumor, validating Ashworth's remarks. The significant efforts put into understanding the CTCs biological properties have demonstrated the critical role circulating tumor cells play in the metastatic spread of carcinoma.Furthermore, highly sensitive, single-cell analysis demonstrated a high level of heterogeneity seen at the single cell level for both protein expression and protein localization and the CTCs reflected both the primary biopsy and the changes seen in the metastatic sites. Tissue biopsies are poor diagnostic procedures: they are invasive, cannot be used repeatedly, and are ineffective in understanding metastatic risk, disease progression, and treatment effectiveness. CTCs thus could be considered a “liquid biopsy” which reveals metastasis in action, providing live information about the patient’s disease status. Analysis of blood samples found a propensity for increased CTC detection as the disease progressed in individual patients. Blood tests are easy and safe to perform and multiple samples can be taken over time. By contrast, analysis of solid tumors necessitates invasive procedures that might limit patient compliance. The ability to monitor disease progression over time could facilitate appropriate modification to a patient's therapy, potentially improving their prognosis and quality of life.To this end, technologies with the requisite sensitivity and reproducibility to detect CTCs in patients with metastatic disease have recently been developed.