Chapter 5 Proteins - Liberty Public Schools
... • Each chain is called a subunit. • Subunits are not necessarily the ...
... • Each chain is called a subunit. • Subunits are not necessarily the ...
"Central Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism". In: Microbial
... to lactate. Other microorganisms that use the EMP pathway have the capacity to convert pyruvate to a wide variety of other fermentation end products. These fermentation pathways are discussed in more detail in Chapter 10. The enzymes of the glycolytic pathway and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle a ...
... to lactate. Other microorganisms that use the EMP pathway have the capacity to convert pyruvate to a wide variety of other fermentation end products. These fermentation pathways are discussed in more detail in Chapter 10. The enzymes of the glycolytic pathway and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle a ...
U5Word
... 5. in cyto: mal + NADP+ NADPH + pyr + CO2 ; (pyr goes to matrix). this rxn is catalysed by the malic enzyme 6. The NADPH is needed for FA synthesis (below) 7. The cyto ACoA is activated for joining by conversion to malonyl CoA (carboxylation): ACoA + CO2 +ATP ---> ADP + Pi + mal CoA B. FA synthase ...
... 5. in cyto: mal + NADP+ NADPH + pyr + CO2 ; (pyr goes to matrix). this rxn is catalysed by the malic enzyme 6. The NADPH is needed for FA synthesis (below) 7. The cyto ACoA is activated for joining by conversion to malonyl CoA (carboxylation): ACoA + CO2 +ATP ---> ADP + Pi + mal CoA B. FA synthase ...
Fermentative degradation of glycolic acid by defined syntrophic
... bacterium which used only glycolate as growth substrate. These cells were gram-positive, formed terminal oval spores, and did not contain cytochromes. Growth with glycolate was possible only in coculture with either a homoacetogenic bacterium or a hydrogen-utilizing methanogenic bacterium; the overa ...
... bacterium which used only glycolate as growth substrate. These cells were gram-positive, formed terminal oval spores, and did not contain cytochromes. Growth with glycolate was possible only in coculture with either a homoacetogenic bacterium or a hydrogen-utilizing methanogenic bacterium; the overa ...
Biochemistry of Sulfur
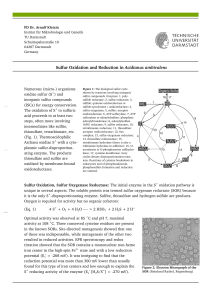
... The predicted orientation and the molecular composition of the Ac. ambivalens SR deduced from the biochemical results and the sequence analysis are similar to the W. succinogenes PSR (Fig. 7). Both enzymes consist of homologous catalytic and electron transfer subunits (SreA/PsrA and SreB/PsrB, resp ...
... The predicted orientation and the molecular composition of the Ac. ambivalens SR deduced from the biochemical results and the sequence analysis are similar to the W. succinogenes PSR (Fig. 7). Both enzymes consist of homologous catalytic and electron transfer subunits (SreA/PsrA and SreB/PsrB, resp ...
m5zn_a9c640ccbe96115
... 149) …………………..is a technique used mainly to detect the presence of antigen or antibodies in a sample . a) Immunoblot b) Estern blot . c) Isoelectric focusing d) ELISA . ...
... 149) …………………..is a technique used mainly to detect the presence of antigen or antibodies in a sample . a) Immunoblot b) Estern blot . c) Isoelectric focusing d) ELISA . ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam III - S2014 Name:________________________
... 18. (6 pts) Please do one of the following choices. Choice A: Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the TCA cycle are all regulated by “energy sensing”. Select one of the three pathways and describe: i) the step that is regulated (1 pt). ii) the compounds that regulate that step, and whether they activat ...
... 18. (6 pts) Please do one of the following choices. Choice A: Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the TCA cycle are all regulated by “energy sensing”. Select one of the three pathways and describe: i) the step that is regulated (1 pt). ii) the compounds that regulate that step, and whether they activat ...
Slides
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
... Increases the rate of chemical reaction / biological process Remains unchanged Biomolecules that catalyze chemical reactions Usually proteins ...
Mechanism Of Hormonal Action:3
... It releases Ca2+ from intracellular storage sites: Mitochondria. Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... It releases Ca2+ from intracellular storage sites: Mitochondria. Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
prepex3
... Start your studies by knowing how amino acids are prepared for metabolism. Know what is meant by a 26S proteosome, the 20S proteosome, the N-rule, reactions involved in protein ubiquination. Know the mechanism of an aminotransferase, the role of glutamate/-Kg pair in the reaction, the different for ...
... Start your studies by knowing how amino acids are prepared for metabolism. Know what is meant by a 26S proteosome, the 20S proteosome, the N-rule, reactions involved in protein ubiquination. Know the mechanism of an aminotransferase, the role of glutamate/-Kg pair in the reaction, the different for ...
4 Metabolism and Enzymes
... •Cellular Respiration: Oxidative Catabolism •Oxidation-Reduction Reactions(NAD+, FAD+ trucks) •C6H12O6 + 6O2 -->6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) •Glycolysis (6C glucose--> 2 pyruvate + 2NADH +2ATP •Krebs Cycle (2 pyruvate-->6CO2 + 8NADH +2FADH2 + 2ATP •Electron Transport Chain (Cashing in on e-) •FADH2 + ...
... •Cellular Respiration: Oxidative Catabolism •Oxidation-Reduction Reactions(NAD+, FAD+ trucks) •C6H12O6 + 6O2 -->6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) •Glycolysis (6C glucose--> 2 pyruvate + 2NADH +2ATP •Krebs Cycle (2 pyruvate-->6CO2 + 8NADH +2FADH2 + 2ATP •Electron Transport Chain (Cashing in on e-) •FADH2 + ...
ppt
... Amino acid oxidation forms many TCA cycle intermediates: • Oxidation of even-chain fatty acids and ketone body not replenish ...
... Amino acid oxidation forms many TCA cycle intermediates: • Oxidation of even-chain fatty acids and ketone body not replenish ...
Ch. 20 Tricarboxylic acid cyle Student Learning Outcomes
... Amino acid oxidation forms many TCA cycle intermediates: • Oxidation of even-chain fatty acids and ketone body not replenish ...
... Amino acid oxidation forms many TCA cycle intermediates: • Oxidation of even-chain fatty acids and ketone body not replenish ...
New Advances in Catalytic Systems for Conversion of CH4 and CO2
... widely investigated since 1990’s. Although many different kinds of mimic enzymes have the ability to activate the C-H bond in methane to a certain extent, a rule manifests that the more similar a structure it has, the higher oxidative activity it exhibits. Therefore, small molecular models of the mi ...
... widely investigated since 1990’s. Although many different kinds of mimic enzymes have the ability to activate the C-H bond in methane to a certain extent, a rule manifests that the more similar a structure it has, the higher oxidative activity it exhibits. Therefore, small molecular models of the mi ...
Bean Brew - Science Case Network
... 1. Describe a typical enzyme-substrate complex. What mechanisms do enzymes use to lower activation energy and speed up a reaction? Enzymes are proteins that contain a pocket or groove known as the active site. The active site is the area of the enzyme that binds to specific substrate molecules. When ...
... 1. Describe a typical enzyme-substrate complex. What mechanisms do enzymes use to lower activation energy and speed up a reaction? Enzymes are proteins that contain a pocket or groove known as the active site. The active site is the area of the enzyme that binds to specific substrate molecules. When ...
Teaching Active Transport At the Turn of the Twenty
... FIGURE 4 Three-dimensional image of the SR ATPase obtained by cryoelectron microscopy. One of the membrane-bound ATPase molecules shown in Fig. 1 is here presented with its threedimensional structure at 14-Å resolution (Toyoshima et al., 1993). The extramembranous cytosolic region is here shaped as ...
... FIGURE 4 Three-dimensional image of the SR ATPase obtained by cryoelectron microscopy. One of the membrane-bound ATPase molecules shown in Fig. 1 is here presented with its threedimensional structure at 14-Å resolution (Toyoshima et al., 1993). The extramembranous cytosolic region is here shaped as ...
Microsoft Word
... In the present study, effect of cosolvents, proteolytic enzymes and metal ions on -casein structure and function and stability was studied. Bovine milk -casein constitutes 65% of total casein. -Casein contains a mixture of S1 casein and S2 casein in the ratio of 4:1. This group consists of clos ...
... In the present study, effect of cosolvents, proteolytic enzymes and metal ions on -casein structure and function and stability was studied. Bovine milk -casein constitutes 65% of total casein. -Casein contains a mixture of S1 casein and S2 casein in the ratio of 4:1. This group consists of clos ...
Cloning and expression of maize-leaf pyruvate, Pi dikinase
... means for cloning the RP gene. We sought to do this by identifying those sequences that were consistent with the known properties of the RP. These included plant proteins with (i) an estimated molecular mass of between 45 and 48 kDa, (ii) a chloroplast transit peptide, (iii) a threonine/ serine prot ...
... means for cloning the RP gene. We sought to do this by identifying those sequences that were consistent with the known properties of the RP. These included plant proteins with (i) an estimated molecular mass of between 45 and 48 kDa, (ii) a chloroplast transit peptide, (iii) a threonine/ serine prot ...
Moonlighting proteins—an update
... of factors might be employed. Of the new examples, some proteins make use of the general methods seen in previously identified moonlighting proteins to switch between functions, although the details differ, for example how interacting with a different protein partner or cofactor results in a conformati ...
... of factors might be employed. Of the new examples, some proteins make use of the general methods seen in previously identified moonlighting proteins to switch between functions, although the details differ, for example how interacting with a different protein partner or cofactor results in a conformati ...
SUBJECT OUTLINE Chemistry and Biochemistry BIOB111
... of matter. This provides the foundation for the second part – Biochemistry — which examines the relationship between the structure and function of complex biomolecules. Students will study the role of enzymes, coenzymes and cofactors in energy metabolism, and metabolic pathways involving glucose, fa ...
... of matter. This provides the foundation for the second part – Biochemistry — which examines the relationship between the structure and function of complex biomolecules. Students will study the role of enzymes, coenzymes and cofactors in energy metabolism, and metabolic pathways involving glucose, fa ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.