Presentation
... Tertiary structure is determined by interactions of R-groups: • Disulfide bonds • Aggregation of hydrophobic side chains • van der Waals forces • Ionic bonds • Hydrogen bonds ...
... Tertiary structure is determined by interactions of R-groups: • Disulfide bonds • Aggregation of hydrophobic side chains • van der Waals forces • Ionic bonds • Hydrogen bonds ...
Partial purification of fatty acid synthetase from Streptomyces
... Thus the synthetase migrated as a single species during these Filamentous bacteria of the genus Streptomyces are extremely procedures (with a consistent recovery of over 80%), and its versatile in making antibiotics, many of which are phenolic activity presumably resides in multifunctional polypepti ...
... Thus the synthetase migrated as a single species during these Filamentous bacteria of the genus Streptomyces are extremely procedures (with a consistent recovery of over 80%), and its versatile in making antibiotics, many of which are phenolic activity presumably resides in multifunctional polypepti ...
Chem 499 Final Exam Name
... alpha carbon to become a good leaving group. Use mechanism arrows. Explain how it allows each of these eliminations to occur so easy? What structural feature on an enzyme could orientate the specified leaving group to be in the correct position for elimination? The example structure(s) have been sim ...
... alpha carbon to become a good leaving group. Use mechanism arrows. Explain how it allows each of these eliminations to occur so easy? What structural feature on an enzyme could orientate the specified leaving group to be in the correct position for elimination? The example structure(s) have been sim ...
The Specificity of Enzymes Adding Amino Acids in the
... fractions were collected at 45 to 55 %, 55 to 65 % and 65 to 75 % of saturation. These are referred to as C. insidiosurn fractions I, I1 and 111, respectively. Preparation of substrates. Cultures of TOF33 accumulate nucleotide precursors of wall peptidoglycan when grown at 30 "C. UDP-MurNAc is the m ...
... fractions were collected at 45 to 55 %, 55 to 65 % and 65 to 75 % of saturation. These are referred to as C. insidiosurn fractions I, I1 and 111, respectively. Preparation of substrates. Cultures of TOF33 accumulate nucleotide precursors of wall peptidoglycan when grown at 30 "C. UDP-MurNAc is the m ...
Practical part
... 8. Objective of biochemical investigations: the whole organism and its organs, tissues, cells, homogenates, subcellular organelles, extracts and molecular biocomplexes. 9. Clinical and diagnostic significance of biochemical investigation. 10. Biological material used in biochemical investigations. 1 ...
... 8. Objective of biochemical investigations: the whole organism and its organs, tissues, cells, homogenates, subcellular organelles, extracts and molecular biocomplexes. 9. Clinical and diagnostic significance of biochemical investigation. 10. Biological material used in biochemical investigations. 1 ...
Fate of pyruvate
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes & five coenzymes ...
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes & five coenzymes ...
Bio 2 – Vocabulary--Biological Molecules
... The reactive group on amino acids. R groups can range from a single hydrogen atom, to complicated rings. It is the different R groups that make the differences between the twenty odd amino acids ...
... The reactive group on amino acids. R groups can range from a single hydrogen atom, to complicated rings. It is the different R groups that make the differences between the twenty odd amino acids ...
Homeostatic Control of Metabolism
... – Energy output = work + heat – 3 categories of work: • Transport work – moving molecules from one side of membrane to the other • Mechanical work – movement • Chemical work – synthesis and storage of molecules – Short-term energy storage – ATP – Long-term energy storage – glycogen, fat ...
... – Energy output = work + heat – 3 categories of work: • Transport work – moving molecules from one side of membrane to the other • Mechanical work – movement • Chemical work – synthesis and storage of molecules – Short-term energy storage – ATP – Long-term energy storage – glycogen, fat ...
Multiple choice questions
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
The Cell, 5e
... Superoxide anion Produced by ETC and other sites; does not diffuse far, generates other ROS, such as by reaction with H2O2 in Haber-Weiss reaction ...
... Superoxide anion Produced by ETC and other sites; does not diffuse far, generates other ROS, such as by reaction with H2O2 in Haber-Weiss reaction ...
Chem ppt for lecture, part 2 File
... Characteristics of Enzymes Often named for the reaction they catalyze; usually end in -ase (e.g., hydrolases, oxidases) Some functional enzymes (holoenzymes) consist of: • Apoenzyme (protein) • Cofactor (metal ion) or coenzyme (a vitamin) ...
... Characteristics of Enzymes Often named for the reaction they catalyze; usually end in -ase (e.g., hydrolases, oxidases) Some functional enzymes (holoenzymes) consist of: • Apoenzyme (protein) • Cofactor (metal ion) or coenzyme (a vitamin) ...
Bacterial Death Results from Mutations Made in the Translocation Peptide... tRNA Synthetase
... interactions with tRNA. However, based on the structures of LeuRS and the positions of F382 and N383, these residues most likely play vital secondary structural roles in helping to provide the correct orientation of the translocation peptide so that it may interact with the tRNA. F382 and N383 are p ...
... interactions with tRNA. However, based on the structures of LeuRS and the positions of F382 and N383, these residues most likely play vital secondary structural roles in helping to provide the correct orientation of the translocation peptide so that it may interact with the tRNA. F382 and N383 are p ...
Metazoan Remaining Genes for Essential Amino Acid Biosynthesis
... in their genomes, characterizing the Essential Amino Acid (EAA) phenotype. There is no consensus over the exact number of essential amino acids, but it is normally accepted that His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp and Val belong to this group. Although this phenotype was discovered in 1932, it wa ...
... in their genomes, characterizing the Essential Amino Acid (EAA) phenotype. There is no consensus over the exact number of essential amino acids, but it is normally accepted that His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp and Val belong to this group. Although this phenotype was discovered in 1932, it wa ...
chapter 11
... enantiomers, the L- form and the D-form. • Since one of the pair usually does not have biological activity, the racemic mixture is likely to have reduced potency. • These are usually designated by indicating both forms, such as D/L. • In many cases, the enantiomer without biological activity display ...
... enantiomers, the L- form and the D-form. • Since one of the pair usually does not have biological activity, the racemic mixture is likely to have reduced potency. • These are usually designated by indicating both forms, such as D/L. • In many cases, the enantiomer without biological activity display ...
P8100Datasheet-Lot0041208
... Buffer. 1 µl of the above reaction (50 ng) was mixed with 1 µl of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix solution, air-dried and subjected to MALDI-TOF MS analysis on an ABI Voyager DE MALDI-TOF MS. Peptide Digestion: ACTH (1–17) peptide is subjected to digestion by GluC at a ratio of 20:1 respective ...
... Buffer. 1 µl of the above reaction (50 ng) was mixed with 1 µl of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix solution, air-dried and subjected to MALDI-TOF MS analysis on an ABI Voyager DE MALDI-TOF MS. Peptide Digestion: ACTH (1–17) peptide is subjected to digestion by GluC at a ratio of 20:1 respective ...
Step 1 Biochemistry Review
... hypovolemic shock as a result of blood loss. He is conscious and his respiratory rate is elevated. Which of the following biochemical processes is most likely increased in this patient? xA anion gap B. electron transport chain C. Na+/K+ATPase D.citric acid cycle activity E. oxidative phosphorylation ...
... hypovolemic shock as a result of blood loss. He is conscious and his respiratory rate is elevated. Which of the following biochemical processes is most likely increased in this patient? xA anion gap B. electron transport chain C. Na+/K+ATPase D.citric acid cycle activity E. oxidative phosphorylation ...
Teitler-Koo - Collegiate Quiz Bowl Packet
... 13. These organisms possess pores for gas exchange known as cyphellae. Usnic acid may be secreted by their cortex, which is sometimes covered by a layer called the tomentum. Warty growths known as cephalodia can allow these organisms to fix nitrogen in addition to performing photosynthesis. They can ...
... 13. These organisms possess pores for gas exchange known as cyphellae. Usnic acid may be secreted by their cortex, which is sometimes covered by a layer called the tomentum. Warty growths known as cephalodia can allow these organisms to fix nitrogen in addition to performing photosynthesis. They can ...
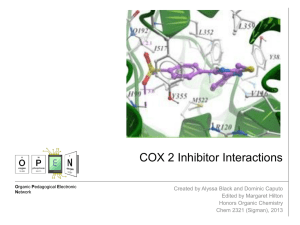
COX 2 Inhibitor Interactions - Center for Selective C–H
... Acetylation of COX-2 Active Site by Aspirin Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue ...
... Acetylation of COX-2 Active Site by Aspirin Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue ...
Slide 1
... Amino-acids that are degraded to pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, succinyl coA, fumarate or oxaloacetate are termed glucogenic amino-acids. Net synthesis of glucose is possible because TCA cycle intermediates and Pyruvate can be be converted to phosphoenolpyruvate and then into Glucoce (Gluconeogenesis) ...
... Amino-acids that are degraded to pyruvate, α-ketoglutarate, succinyl coA, fumarate or oxaloacetate are termed glucogenic amino-acids. Net synthesis of glucose is possible because TCA cycle intermediates and Pyruvate can be be converted to phosphoenolpyruvate and then into Glucoce (Gluconeogenesis) ...
Protein synthesis File
... unzipping of DNA by helicase complementary mRNA synthesised using an RNA polymerase mRNA leaves nucleus and goes to ribosome spaces for two codons complementary base pairing between codon and anticodon of tRNA peptide bond inserted between amino acids peptide grows by one amino acid at ...
... unzipping of DNA by helicase complementary mRNA synthesised using an RNA polymerase mRNA leaves nucleus and goes to ribosome spaces for two codons complementary base pairing between codon and anticodon of tRNA peptide bond inserted between amino acids peptide grows by one amino acid at ...
The effect of endurance-training on the maximum activities of
... The l l - w e e k endurance-training programme used in this study did not cause any change in the activities of the enzymes of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle in cardiac muscle (Table 1). This suggests that the maximum capacities of both anaerobic and aerobic processes in cardiac muscle are unaffected ...
... The l l - w e e k endurance-training programme used in this study did not cause any change in the activities of the enzymes of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle in cardiac muscle (Table 1). This suggests that the maximum capacities of both anaerobic and aerobic processes in cardiac muscle are unaffected ...
Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme and the Changes
... intestinal brush border.43 In the choroid plexus where ACE faces the cerebrospinal fluid and in the subfornical organ, ACE may facilitate the production of angiotensin II, which is a potent dipsogen. In addition the choroid plexus may be the source of ACE in cerebrospinal fluid. The very wide distri ...
... intestinal brush border.43 In the choroid plexus where ACE faces the cerebrospinal fluid and in the subfornical organ, ACE may facilitate the production of angiotensin II, which is a potent dipsogen. In addition the choroid plexus may be the source of ACE in cerebrospinal fluid. The very wide distri ...
Lecture 4 - Biological Molecules Part II
... • Enzymes are a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix “-ase” ...
... • Enzymes are a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix “-ase” ...
Free radicals and antioxidants
... • Markers of oxidative stress • Disorders Associated with Oxidative stress ...
... • Markers of oxidative stress • Disorders Associated with Oxidative stress ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.