Student Exploration: Digestive System
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. 5. Observe: Now look at t ...
... Fat molecules can be difficult to break down because large fat droplets do not mix well with water-based enzymes such as lipase. For lipase to work, it helps if the fat is emulsified into tiny droplets. This is done with the help of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. 5. Observe: Now look at t ...
Unit 2 ~ Learning Guide Name
... Hydrogen of one amino acid and an Oxygen further down the chain. An alpha helix contains 3.6 amino acids per spiral. There are other secondary structures, but the alpha helix is the most common and the one you will need to know for this course. Protein Structure - Tertiary and Quaternary Structures ...
... Hydrogen of one amino acid and an Oxygen further down the chain. An alpha helix contains 3.6 amino acids per spiral. There are other secondary structures, but the alpha helix is the most common and the one you will need to know for this course. Protein Structure - Tertiary and Quaternary Structures ...
Lecture 31
... In mammals, found in the liver and small intestine mucosa XO is a homodimer with FAD, two [2Fe-2S] clusters and a molybdopterin complex (Mo-pt) that cycles between Mol (VI) and Mol (IV) oxidation states. Final electron acceptor is O2 which is converted to H2O2 XO is cleaved into 3 segments. The uncl ...
... In mammals, found in the liver and small intestine mucosa XO is a homodimer with FAD, two [2Fe-2S] clusters and a molybdopterin complex (Mo-pt) that cycles between Mol (VI) and Mol (IV) oxidation states. Final electron acceptor is O2 which is converted to H2O2 XO is cleaved into 3 segments. The uncl ...
No Slide Title
... Problem 15.5 Consider a hypothetical regulatory scheme in which citrulline induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase act ...
... Problem 15.5 Consider a hypothetical regulatory scheme in which citrulline induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase act ...
Identification of two amino acid residues which - Wiley-VCH
... a crystallized enzyme-substrate complex of the related enzyme chitobiase. The model contains a central hydrophilic region referred to as the “substrate cavity”. Figure 2 shows only this portion of the proposed structure. The three residues implicated in active site function cluster on the “left” sid ...
... a crystallized enzyme-substrate complex of the related enzyme chitobiase. The model contains a central hydrophilic region referred to as the “substrate cavity”. Figure 2 shows only this portion of the proposed structure. The three residues implicated in active site function cluster on the “left” sid ...
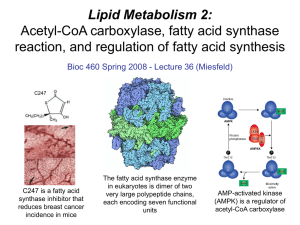
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... convert excess acetyl CoA that builds up in the mitochondrial matrix when glucose levels are high into fatty acids that can be stored or exported as triacylglycerols. ...
... convert excess acetyl CoA that builds up in the mitochondrial matrix when glucose levels are high into fatty acids that can be stored or exported as triacylglycerols. ...
Chapter 1--Title
... The four heme groups are shown in purple Each heme group can bind one oxygen molecule in a reversible complex ...
... The four heme groups are shown in purple Each heme group can bind one oxygen molecule in a reversible complex ...
Bulletin - Sigma
... that exhibits a 3’→5’ exonucleolytic activity. This blend increases the length of amplification products by using the proofreading polymerase to repair terminal misincorporations. This repair allows the polymerase to resume elongating the growing DNA strand. AccuTaq LA Polymerase Mix combines Sigma’ ...
... that exhibits a 3’→5’ exonucleolytic activity. This blend increases the length of amplification products by using the proofreading polymerase to repair terminal misincorporations. This repair allows the polymerase to resume elongating the growing DNA strand. AccuTaq LA Polymerase Mix combines Sigma’ ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... deficiency because pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. ...
... deficiency because pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme in NAD+ biosynthesis from tryptophan. ...
Role of NAD+-Dependent Malate Dehydrogenase in the Metabolism
... the alphaproteobacterial methanotrophs, such as Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b, assimilating carbon via the serine pathway with the formation of C2 and C3 compounds as primary intermediates; however, the activity of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase was rather low [3]. The gammaproteobacterial methanotr ...
... the alphaproteobacterial methanotrophs, such as Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b, assimilating carbon via the serine pathway with the formation of C2 and C3 compounds as primary intermediates; however, the activity of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase was rather low [3]. The gammaproteobacterial methanotr ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
physiological reviews
... Fisher et al. (19) have observed that reduced DPN prepared with sodium hyhrosulfite in the presenceof heavy water transferred only about one-half of its deuterium to acetaldehyde in the presence of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. The reaction is stereospecificsince the enzyme is capable of removing the ...
... Fisher et al. (19) have observed that reduced DPN prepared with sodium hyhrosulfite in the presenceof heavy water transferred only about one-half of its deuterium to acetaldehyde in the presence of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. The reaction is stereospecificsince the enzyme is capable of removing the ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
A: Objective type questions: Choose the correct answers Most
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
... Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits b. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates c. High ATP stimulates the enzyme, but fructose-2,6-bisphosphate inhibits d. Low ATP stimulates the enzyme, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates e. ATP ...
Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis – Structure, function, regulation
... 2400 Å2 at the enzymes surface. Substrates appear to access the active site from within this region which is consistent with their localization in plastid membranes (Lee et al., 2008). AOSs belong to an atypical cytochrome P450 subfamily, the CYP74 enzymes. Unlike other P450s, they do not require mo ...
... 2400 Å2 at the enzymes surface. Substrates appear to access the active site from within this region which is consistent with their localization in plastid membranes (Lee et al., 2008). AOSs belong to an atypical cytochrome P450 subfamily, the CYP74 enzymes. Unlike other P450s, they do not require mo ...
Chemistry of Life
... • Carbon atoms can form diverse molecules by bonding to four other atoms – Carbon has amazing ability to form molecules because: ...
... • Carbon atoms can form diverse molecules by bonding to four other atoms – Carbon has amazing ability to form molecules because: ...
IOSR Journal Of Environmental Science, Toxicology And Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... including human in which foetus is developed (Blackburn and Flemming, 2011). One of the major and pathological disorder affecting the uterus is a disease called uterine myomas, fibromyomas and leiomyomas (Okolo, 2008), which develops during the early and later reproductive years of women. About 20 t ...
... including human in which foetus is developed (Blackburn and Flemming, 2011). One of the major and pathological disorder affecting the uterus is a disease called uterine myomas, fibromyomas and leiomyomas (Okolo, 2008), which develops during the early and later reproductive years of women. About 20 t ...
cAMP-Dependent Protein Kinase, Catalytic Subunit Product
... in intracellular cAMP levels regulate cellular responses by influencing interaction between the Regulatory (R) and Catalytic (C) Subunits of PKA (6). The PKA holoenzyme exists as an inactive tetrameric complex (R2C2), which consists of a regulatory dimer (R2) associated with two Catalytic Subunits. ...
... in intracellular cAMP levels regulate cellular responses by influencing interaction between the Regulatory (R) and Catalytic (C) Subunits of PKA (6). The PKA holoenzyme exists as an inactive tetrameric complex (R2C2), which consists of a regulatory dimer (R2) associated with two Catalytic Subunits. ...
Regeneration of Cofactors for Enzyme Biocatalysis
... synthesis has been very successful for treatment of cancer and viral diseases such as HIV (Gulick 2003). There are four enzymes commonly employed in the regeneration of ATP from ADP, including the use of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in a coupled reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK), acetylphospha ...
... synthesis has been very successful for treatment of cancer and viral diseases such as HIV (Gulick 2003). There are four enzymes commonly employed in the regeneration of ATP from ADP, including the use of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in a coupled reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (PK), acetylphospha ...
Protocol in its entirety
... The modification of mammalian cells by the expression of multiple genes is a crucial technology in modern biological research. MultiLabel allows the modular assembly of independent expression units in a single plasmid which can be used for transient and stable modification of cells. In contrast to o ...
... The modification of mammalian cells by the expression of multiple genes is a crucial technology in modern biological research. MultiLabel allows the modular assembly of independent expression units in a single plasmid which can be used for transient and stable modification of cells. In contrast to o ...
The 10.8-AA structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... strands surrounded by a helices. Of the three binding sites available per subunit, two of them form the active site binding Fru 6-P and ATP, while the third, the allosteric site, binds either PEP or ADP. Essentially, the tetramers can be considered as dimers of dimers presenting small interactions b ...
... strands surrounded by a helices. Of the three binding sites available per subunit, two of them form the active site binding Fru 6-P and ATP, while the third, the allosteric site, binds either PEP or ADP. Essentially, the tetramers can be considered as dimers of dimers presenting small interactions b ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation in Homogenates of
... remains constant during phase II when inorganic phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogena ...
... remains constant during phase II when inorganic phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogena ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
... Structure of xanthan gum (glucose backbone with Man-GluA-Man trisaccharide sidechains) Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA, Fourth Edition Bernard R. Glick, Jack J. Pasternak, and Cheryl L. Patten ...
... Structure of xanthan gum (glucose backbone with Man-GluA-Man trisaccharide sidechains) Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA, Fourth Edition Bernard R. Glick, Jack J. Pasternak, and Cheryl L. Patten ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.