How ribosomes make peptide bonds
... formation by positioning substrates, reorganizing water in the active site and providing an electrostatic network that stabilizes reaction intermediates. Proton transfer during the reaction seems to be promoted by a concerted shuttle mechanism that involves ribose hydroxyl groups on the tRNA substra ...
... formation by positioning substrates, reorganizing water in the active site and providing an electrostatic network that stabilizes reaction intermediates. Proton transfer during the reaction seems to be promoted by a concerted shuttle mechanism that involves ribose hydroxyl groups on the tRNA substra ...
The origin of the RNA world: Co-evolution of genes and metabolism
... S.D. Copley et al. / Bioorganic Chemistry 35 (2007) 430–443 ...
... S.D. Copley et al. / Bioorganic Chemistry 35 (2007) 430–443 ...
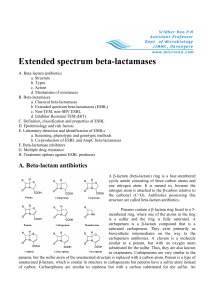
Extended spectrum beta-lactamases - Micro-Rao
... that most of the plasmid mediated beta-lactamases may have their origin in bacterial chromosomes. Genes coding for beta-lactamases are also present on transposons or insertion sequences, resulting in their dissemination among different plasmids. The Ω-loop, which is a conserved structural feature o ...
... that most of the plasmid mediated beta-lactamases may have their origin in bacterial chromosomes. Genes coding for beta-lactamases are also present on transposons or insertion sequences, resulting in their dissemination among different plasmids. The Ω-loop, which is a conserved structural feature o ...
Exam 2
... (a) (4 pts) Which blood group carbohydrate-containing structure is the smallest and not antigenic? An individual homozygous for this blood group antigen can accept blood from what other types? (b) (2 pts) A b-specific nuclease catalyzes the hydrolysis of pApGpCpTp between the C and T residues. Write ...
... (a) (4 pts) Which blood group carbohydrate-containing structure is the smallest and not antigenic? An individual homozygous for this blood group antigen can accept blood from what other types? (b) (2 pts) A b-specific nuclease catalyzes the hydrolysis of pApGpCpTp between the C and T residues. Write ...
Procedure and Troubleshooting
... bases 5′-tail to the primers containing DNA sequences that are homologous to the sequences flanking the site of insertion into the MultiLabel vector. The described primers bind to the 3’ end of the CMV promoter (RF-CMV-for) and to the5’ end of the poly A signal (RF-PolyA-back, Fig 2C). This method h ...
... bases 5′-tail to the primers containing DNA sequences that are homologous to the sequences flanking the site of insertion into the MultiLabel vector. The described primers bind to the 3’ end of the CMV promoter (RF-CMV-for) and to the5’ end of the poly A signal (RF-PolyA-back, Fig 2C). This method h ...
AFFINITY OF WARFARIN WITH CYP2C9 BY MOLECULAR DOCKING STUDY Original Article
... Systematic name: 4-Hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-chromen2-one, its Anticoagulant effect bycyclic conversion of vitamin K and vitamin K epoxide.3months anticoagulants therapy is required in VTE it includes- Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary Embolism (PE)& also used in treatment of Rheumati ...
... Systematic name: 4-Hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-chromen2-one, its Anticoagulant effect bycyclic conversion of vitamin K and vitamin K epoxide.3months anticoagulants therapy is required in VTE it includes- Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT), Pulmonary Embolism (PE)& also used in treatment of Rheumati ...
printed handout sheet
... in turn promotes the release of glucose and free fatty acids into the bloodstream. 2. Short-term mechanisms based on catecholamine messengers and the autonomic nervous system are essential for the metabolic adaptation to physical exercise. Direct delivery of neurotransmitters to particular target ti ...
... in turn promotes the release of glucose and free fatty acids into the bloodstream. 2. Short-term mechanisms based on catecholamine messengers and the autonomic nervous system are essential for the metabolic adaptation to physical exercise. Direct delivery of neurotransmitters to particular target ti ...
Isoenzymes in Clinical Diagnosis
... detected by their different pH optima and called "acid" and "alkaline" phosphatase. Further "isoenzymes" of phosphatase were differentiated by susceptibility to inhibition by tartrate and other chemicals.'6 Different pepsins were separated by differences in solubility.17 Since these early examples, ...
... detected by their different pH optima and called "acid" and "alkaline" phosphatase. Further "isoenzymes" of phosphatase were differentiated by susceptibility to inhibition by tartrate and other chemicals.'6 Different pepsins were separated by differences in solubility.17 Since these early examples, ...
C9 Cellular Respiration (Video)
... 3. Coenzyme A is attached to the acetate by unstable bond that makes the acetyl group very reactive. (Now acetyl CoA). Krebs cycle – Hans Krebs, 1930’s. 8 steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme in the mitochondrial matrix. CO2 given off in steps 3 and 4. Most energy conserved as NADH. For each a ...
... 3. Coenzyme A is attached to the acetate by unstable bond that makes the acetyl group very reactive. (Now acetyl CoA). Krebs cycle – Hans Krebs, 1930’s. 8 steps, each catalyzed by a specific enzyme in the mitochondrial matrix. CO2 given off in steps 3 and 4. Most energy conserved as NADH. For each a ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... Proteins constantly undergo turnover. Amino acids are also used to synthesize some non-protein metabolites. No protein stores, so essential amino acids must come from diet. ...
... Proteins constantly undergo turnover. Amino acids are also used to synthesize some non-protein metabolites. No protein stores, so essential amino acids must come from diet. ...
150-06 (8-10-96) RNA world begins to add up
... proteins to its repertoire, are therefore seeking to create self-replicating RNA molecules to mirror those with which life on Earth might have originated. To self-replicate, an RNA strand would need to string together nucleotides, its subunits. In modern organisms, this job is handled by proteins ca ...
... proteins to its repertoire, are therefore seeking to create self-replicating RNA molecules to mirror those with which life on Earth might have originated. To self-replicate, an RNA strand would need to string together nucleotides, its subunits. In modern organisms, this job is handled by proteins ca ...
Glycosaminoglycans and Ocular Structures
... GAGs pile up in the joints and internal organs, there is a distorted facial appearance, deformed and stiff joints with an enlarged liver and spleen. In the eyes, the cornea becomes cloudy and the optic nerve degenerates. Also glaucoma may occur. The disease is usually fatal within a few years due to ...
... GAGs pile up in the joints and internal organs, there is a distorted facial appearance, deformed and stiff joints with an enlarged liver and spleen. In the eyes, the cornea becomes cloudy and the optic nerve degenerates. Also glaucoma may occur. The disease is usually fatal within a few years due to ...
Cellular Respiration www.AssignmentPoint.com Cellular respiration
... combustion reaction, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a living cell due to slow release of energy from the series of reactions. ...
... combustion reaction, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a living cell due to slow release of energy from the series of reactions. ...
Plant Physiology 66:
... of amino and amide group transfer in the metabolism of young seedcoats is presented in Figure 7. At this stage, the seedcoats have their maximal content of free amino acids (Figs. I and 2), and they are net exporters of homoserine, glutamine, alanine, and certain other amino acids (6), citric acid a ...
... of amino and amide group transfer in the metabolism of young seedcoats is presented in Figure 7. At this stage, the seedcoats have their maximal content of free amino acids (Figs. I and 2), and they are net exporters of homoserine, glutamine, alanine, and certain other amino acids (6), citric acid a ...
Relationship between the structure and function of proteins
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
1 - Free
... 27. list what you should measure to determine the specific activity of lactate dehydrogenase in a muscle homogenate. ...
... 27. list what you should measure to determine the specific activity of lactate dehydrogenase in a muscle homogenate. ...
Conversion of trypsin to a functional threonine protease
... greater than that of the S195T single variant against the highly activated Sbzl ester substrate (kcat increased by >100-fold), supporting the assertion that removal of the disulfide bridge formed by Cys 42 and Cys 58 allows the hydroxyl group of threonine at position 195 to substitute and function i ...
... greater than that of the S195T single variant against the highly activated Sbzl ester substrate (kcat increased by >100-fold), supporting the assertion that removal of the disulfide bridge formed by Cys 42 and Cys 58 allows the hydroxyl group of threonine at position 195 to substitute and function i ...
Macromolecules Review 1. What is the function of starch and
... a) lower the activation energy (b) can be used in many different chemical reactions (c) involved in but not changed by the reaction (d) allow chemical reactions to occur at moderate temperatures 3. An enzyme reduces the _____ of a chemical reaction. 4 Explain how changing the pH and/or salt concentr ...
... a) lower the activation energy (b) can be used in many different chemical reactions (c) involved in but not changed by the reaction (d) allow chemical reactions to occur at moderate temperatures 3. An enzyme reduces the _____ of a chemical reaction. 4 Explain how changing the pH and/or salt concentr ...
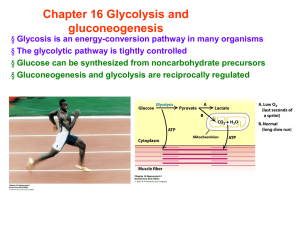
CHAP NUM="9" ID="CH
... Figure 9.10 Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the junction between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate is a charged molecule, so in eukaryotic cells it must enter the mitochondrion via active transport, with the help of a transport protein. Next, a complex of several enzymes (the py ...
... Figure 9.10 Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the junction between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate is a charged molecule, so in eukaryotic cells it must enter the mitochondrion via active transport, with the help of a transport protein. Next, a complex of several enzymes (the py ...
Text S1.
... the reaction would not be reversible (the equilibrium reaction is close to 1 based on data from [2]), attempts to measure phosphoketolase activity in the reverse direction, using in vitro assays, failed to demonstrate activity [3]. It may be that the enzyme has been kinetically optimized by evolutio ...
... the reaction would not be reversible (the equilibrium reaction is close to 1 based on data from [2]), attempts to measure phosphoketolase activity in the reverse direction, using in vitro assays, failed to demonstrate activity [3]. It may be that the enzyme has been kinetically optimized by evolutio ...
Biology 20 Final Review Package
... a) lower the activation energy (b) can be used in many different chemical reactions (c) involved in but not changed by the reaction (d) allow chemical reactions to occur at moderate temperatures 3. An enzyme reduces the _____ of a chemical reaction. 4 Explain how changing the pH and/or salt concentr ...
... a) lower the activation energy (b) can be used in many different chemical reactions (c) involved in but not changed by the reaction (d) allow chemical reactions to occur at moderate temperatures 3. An enzyme reduces the _____ of a chemical reaction. 4 Explain how changing the pH and/or salt concentr ...
Electron Transport Chain
... Each new acceptor requires that the electron be at a slightly lower energy state Energy is siphoned off of the electrons in small increments The energy is used by the acceptor molecules to change conformation All are proteins except Q (ubiquinone) is lipid ...
... Each new acceptor requires that the electron be at a slightly lower energy state Energy is siphoned off of the electrons in small increments The energy is used by the acceptor molecules to change conformation All are proteins except Q (ubiquinone) is lipid ...
Developmental Analysis of a Putative ATP/ADP Carrier Protein
... for ped mutants with defects in the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle (Hayashi et al. 1998, Hayashi et al. 2000). Since 2,4dichlorophenoxybutyric acid (2,4-DB) is metabolized to produce a herbicide, 2,4-D, by the action of the fatty acid >oxidation cycle in higher plants, wild-type plants cannot germinat ...
... for ped mutants with defects in the fatty acid >-oxidation cycle (Hayashi et al. 1998, Hayashi et al. 2000). Since 2,4dichlorophenoxybutyric acid (2,4-DB) is metabolized to produce a herbicide, 2,4-D, by the action of the fatty acid >oxidation cycle in higher plants, wild-type plants cannot germinat ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.