Plasma
... Classification of lipoprotein They are classified according to their density as highdensity lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and verylow-density lipoproteins. Health care workers are interested in the concentration of the different types of lipoproteins in the blood because it has implic ...
... Classification of lipoprotein They are classified according to their density as highdensity lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and verylow-density lipoproteins. Health care workers are interested in the concentration of the different types of lipoproteins in the blood because it has implic ...
Epsilon glutathione transferases possess a unique class
... the quaternary structure as well as have a role in subunit communication between active sites [18]. The structural contributions of the clasp motif in the Delta GST also have an impact on catalytic specificity and the efficiency of the enzyme. In the Epsilon DmGSTE6, a second histidine in each subun ...
... the quaternary structure as well as have a role in subunit communication between active sites [18]. The structural contributions of the clasp motif in the Delta GST also have an impact on catalytic specificity and the efficiency of the enzyme. In the Epsilon DmGSTE6, a second histidine in each subun ...
Activation by Exercise of Human Skeletal Muscle Pyruvate
... preparations of heart and skeletal muscle, both Mgz+ and CaZ+are important activators of the enzyme [41, among other metabolites [21. The energy required for the regeneration of ATP during heavy exercise is largely derived from muscle glycogen, with only a minor proportion coming from fats and amino ...
... preparations of heart and skeletal muscle, both Mgz+ and CaZ+are important activators of the enzyme [41, among other metabolites [21. The energy required for the regeneration of ATP during heavy exercise is largely derived from muscle glycogen, with only a minor proportion coming from fats and amino ...
as a PDF - PubAg
... pulling the terminal abdomen segments with another forceps. Salivary glands or guts were transferred to microcentrifuge tubes and held on ice. After dissection, the SGC and guts were stored at ⫺80 °C until needed. Enzyme extracts were prepared using a method similar to that described by Oppert et al ...
... pulling the terminal abdomen segments with another forceps. Salivary glands or guts were transferred to microcentrifuge tubes and held on ice. After dissection, the SGC and guts were stored at ⫺80 °C until needed. Enzyme extracts were prepared using a method similar to that described by Oppert et al ...
Phosphoketolase pathway dominates in
... PEP, normally only observed when cells are starved, was evident here (data not shown) despite the fact that the cultures were harvested when high extracellular glucose levels still remained in the media. A duplicate sample from a different culture gave identical results. Growth could be greatly impr ...
... PEP, normally only observed when cells are starved, was evident here (data not shown) despite the fact that the cultures were harvested when high extracellular glucose levels still remained in the media. A duplicate sample from a different culture gave identical results. Growth could be greatly impr ...
BiochemicalSociety A nnualSymposium No.79
... CYP46A1 is one of the four key P450s involved in cholesterol homoeostasis and catalyses the first step in cholesterol elimination from the brain, producing (24S)hydroxycholesterol, which controls cholesterol turnover in the central nervous system. This membrane-permeable form of cholesterol can diff ...
... CYP46A1 is one of the four key P450s involved in cholesterol homoeostasis and catalyses the first step in cholesterol elimination from the brain, producing (24S)hydroxycholesterol, which controls cholesterol turnover in the central nervous system. This membrane-permeable form of cholesterol can diff ...
Metal ion reconstitution studies of yeast copper
... gel electrophoresis. We conclude that yeast apo CuZnSOD, unlike the bovine and human apoproteins, cannot be reconstituted fully with metal ions under the same conditions. Instead, only one subunit of the homodimer, the “normal” subunit, can be remetalled in a fashion reminiscent of the well-characte ...
... gel electrophoresis. We conclude that yeast apo CuZnSOD, unlike the bovine and human apoproteins, cannot be reconstituted fully with metal ions under the same conditions. Instead, only one subunit of the homodimer, the “normal” subunit, can be remetalled in a fashion reminiscent of the well-characte ...
Chapter 18 Glycolysis
... Glycerol is produced in the decomposition of triacylglycerols. It can be converted to glycerol-3-P by glycerol kinase. Glycerol-3-P is then oxidized to dehydroxyacetone phosphate by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase ...
... Glycerol is produced in the decomposition of triacylglycerols. It can be converted to glycerol-3-P by glycerol kinase. Glycerol-3-P is then oxidized to dehydroxyacetone phosphate by the action of glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase ...
39 Synthesis and Degradation of Amino Acids
... required for certain reactions involving the carbon skeleton of amino acids. Tetrahydrofolate (FH4) is a coenzyme used to transfer one-carbon groups at various oxidation states. FH4 is used both in amino acid degradation (e.g., serine and histidine) and biosynthesis (e.g,, glycine). Tetrahydrobiopte ...
... required for certain reactions involving the carbon skeleton of amino acids. Tetrahydrofolate (FH4) is a coenzyme used to transfer one-carbon groups at various oxidation states. FH4 is used both in amino acid degradation (e.g., serine and histidine) and biosynthesis (e.g,, glycine). Tetrahydrobiopte ...
RNA 3`-terminal phosphate cyclases and cyclase
... Formation of RNAs terminating with 2’,3’-cyclic phosphate is a common phenomenon. Many endoribonucleases produce 2’,3’-cyclic phosphate-terminated RNAs as intermediates or final products of the cleavage reaction. These are proteinaceous (often referred to as cyclasing or metal-independent nucleases) ...
... Formation of RNAs terminating with 2’,3’-cyclic phosphate is a common phenomenon. Many endoribonucleases produce 2’,3’-cyclic phosphate-terminated RNAs as intermediates or final products of the cleavage reaction. These are proteinaceous (often referred to as cyclasing or metal-independent nucleases) ...
Substrate recognition by nonribosomal peptide
... signature sequence. In this case particularly, but also in the two other cases, it would be useful to know if the catalytic efficiency of the mutant domain is comparable to the catalytic efficiency of wild-type A domains activating the same substrate. The engineered changes in substrate selectivity ...
... signature sequence. In this case particularly, but also in the two other cases, it would be useful to know if the catalytic efficiency of the mutant domain is comparable to the catalytic efficiency of wild-type A domains activating the same substrate. The engineered changes in substrate selectivity ...
Amino Acid Catabolism: N
... In addition to equilibrating amino groups among available a-keto acids, transaminases funnel amino groups from excess dietary amino acids to those amino acids (e.g., glutamate) that can be deaminated. Carbon skeletons of deaminated amino acids can be catabolized for energy, or used to synthesize gl ...
... In addition to equilibrating amino groups among available a-keto acids, transaminases funnel amino groups from excess dietary amino acids to those amino acids (e.g., glutamate) that can be deaminated. Carbon skeletons of deaminated amino acids can be catabolized for energy, or used to synthesize gl ...
The extraction of collagen protein from pigskin
... separation the solution of collagen protein is obtained. The dechroming fraction of alkali method is higher than that of acid method, but it has some disadvantages as well. For example, the hydrolysis level of the obtained collagen protein is high; the molecular weight is small; ash content and chro ...
... separation the solution of collagen protein is obtained. The dechroming fraction of alkali method is higher than that of acid method, but it has some disadvantages as well. For example, the hydrolysis level of the obtained collagen protein is high; the molecular weight is small; ash content and chro ...
Enzymatic Activities for the Synthesis of Chlorophyll in Pigment
... coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin IX. Almost no formation of porphyrin was detected in the absence of PBG (Table 1). However, upon the addition of 0.2 mM PBG, significant amounts of porphyrin intermediates were formed. The most abundant intermediate was uroporphyrin. Since the extracts had no ferroc ...
... coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin IX. Almost no formation of porphyrin was detected in the absence of PBG (Table 1). However, upon the addition of 0.2 mM PBG, significant amounts of porphyrin intermediates were formed. The most abundant intermediate was uroporphyrin. Since the extracts had no ferroc ...
PDF w - Amazon Web Services
... building blocks could have produced complex life forms over eons of natural selection and evolution. The challenge, however, is to explain how sufficiently complex proteins or ribozymes could have been produced in the lipid membranes necessary for the metabolism of their own catalysis and reproducti ...
... building blocks could have produced complex life forms over eons of natural selection and evolution. The challenge, however, is to explain how sufficiently complex proteins or ribozymes could have been produced in the lipid membranes necessary for the metabolism of their own catalysis and reproducti ...
Synthesis of higher alcohols during alcoholic fermentation of rye
... acids that are further decarboxylated to higher alcohols. They are products of either transamination of corresponding amino acids or intermediates in their synthesis. The sequence of these reactions is shown in Fig. 5 [12]. Pyruvate which is a product of glycolysis is further converted to correspond ...
... acids that are further decarboxylated to higher alcohols. They are products of either transamination of corresponding amino acids or intermediates in their synthesis. The sequence of these reactions is shown in Fig. 5 [12]. Pyruvate which is a product of glycolysis is further converted to correspond ...
Glycolysis
... and acetaldehyde and the latter is reduced by NADH to ethanol and NAD+ is regenerated (alcoholic fermentation). ...
... and acetaldehyde and the latter is reduced by NADH to ethanol and NAD+ is regenerated (alcoholic fermentation). ...
amino-acids - ChemConnections
... bonds eg. ARDV:Ala.Arg.Asp.Val. 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
... bonds eg. ARDV:Ala.Arg.Asp.Val. 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
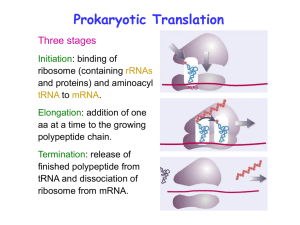
Class I tRNA
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
... Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis in Protozoan Parasites: Unusual Pathways and
... From a functional perspective, however, grouping these evolutionarily diverse organisms together can be informative. All share similar environments, being intimately associated with their human hosts. The access these parasites have to the products of host metabolism has led to striking similarities ...
... From a functional perspective, however, grouping these evolutionarily diverse organisms together can be informative. All share similar environments, being intimately associated with their human hosts. The access these parasites have to the products of host metabolism has led to striking similarities ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.