Metabolic processes of Methanococcus maripaludis and potential
... like Escherichia coli and S. cerevisiae for fundamental and experimental biotechnology studies. More than 100 experimental studies have explored different specific aspects of the biochemistry and genetics of CO2 and N2 fixation by M. maripaludis. Its genome-scale metabolic model (iMM518) also exists ...
... like Escherichia coli and S. cerevisiae for fundamental and experimental biotechnology studies. More than 100 experimental studies have explored different specific aspects of the biochemistry and genetics of CO2 and N2 fixation by M. maripaludis. Its genome-scale metabolic model (iMM518) also exists ...
PROTEIN PHOSPHORYLATION AND CELLULAR REGULATION, I by
... graduate student in Geneva, Ed had worked on potato phosphorylase, and we thus shared a common interest in this particular enzyme. We discussed some of the puzzling features of phosphorylase and were particularly intrigued by the still unsolved nature of th e 5’-AMP effect, i.e. how 5’AMP activates ...
... graduate student in Geneva, Ed had worked on potato phosphorylase, and we thus shared a common interest in this particular enzyme. We discussed some of the puzzling features of phosphorylase and were particularly intrigued by the still unsolved nature of th e 5’-AMP effect, i.e. how 5’AMP activates ...
The experiments provide ne~~~den~~~~t the r&rate clewage pathway... of carbon for the synthesis of $tty ack& k‘l...
... Scheme 1. Fischer prujeotion formulas of the absolute co~~~~ur~~i~n of tile stereoisomersof hjrdroxyqiaate iti relation to the absolute ctinRpurarionof citrate, cis-aconit+e and. g-isocitrate, In a, the carbon aroma fro.% the, ucetyl group of acetyl-CoA which becorn@citrate in the citrate synthasere ...
... Scheme 1. Fischer prujeotion formulas of the absolute co~~~~ur~~i~n of tile stereoisomersof hjrdroxyqiaate iti relation to the absolute ctinRpurarionof citrate, cis-aconit+e and. g-isocitrate, In a, the carbon aroma fro.% the, ucetyl group of acetyl-CoA which becorn@citrate in the citrate synthasere ...
Dynamics in the Active Site of -Secretase: A Network Analysis of
... given by Zi = ∑ jcij, i.e., the number of times the node i is visited, where cij, the edge capacity from node j to node i, is proportional to the number of direct transitions from j to i observed along a trajectory. Detailed balance is not imposed, and a comparison of networks with and without detai ...
... given by Zi = ∑ jcij, i.e., the number of times the node i is visited, where cij, the edge capacity from node j to node i, is proportional to the number of direct transitions from j to i observed along a trajectory. Detailed balance is not imposed, and a comparison of networks with and without detai ...
Lecture 2- G6PD_Deficiency
... ~400 different mutations affect G6PD gene, but only some can cause clinical hemolytic anemia G6PD deficient patients have increased resistance to infestation by falciparum malaria ...
... ~400 different mutations affect G6PD gene, but only some can cause clinical hemolytic anemia G6PD deficient patients have increased resistance to infestation by falciparum malaria ...
Identification and expression of GH
... addition, amino acid sequence alignment showed that their putative catalytic residues, Glu122 and Glu309 (proton donor and an activator of water molecule, respectively), are conserved in GH-8 chitosanases, but not in any other GH families. To compare the evolutionary relationships among the glycosyl ...
... addition, amino acid sequence alignment showed that their putative catalytic residues, Glu122 and Glu309 (proton donor and an activator of water molecule, respectively), are conserved in GH-8 chitosanases, but not in any other GH families. To compare the evolutionary relationships among the glycosyl ...
Early days of tRNA research: Discovery, function, purification and
... fraction to an RNA. At the same time, Holley (1957) showed that the pH 5 enzyme catalyzed alanine-dependent ATP-AMP exchange that was sensitive to ribonuclease. This result also supported the notion of amino acid transfer to RNA although the ribonuclease sensitive ATP-AMP exchange was observed only ...
... fraction to an RNA. At the same time, Holley (1957) showed that the pH 5 enzyme catalyzed alanine-dependent ATP-AMP exchange that was sensitive to ribonuclease. This result also supported the notion of amino acid transfer to RNA although the ribonuclease sensitive ATP-AMP exchange was observed only ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Base Compositions and Nucleotide
... nucleotides has been determined for seven pedomicrobia (10). Genome sizes are known for only two strains, Hyphomicrobium sp. strain B-522 (Mr,3.1 X lo9) (34) and Rhodomicrobiurn vannielii RM5 (Mr, 2.1 X lo9) (40). DNADNA base sequence homologies have been reported for a number of Hyphomicrobium stra ...
... nucleotides has been determined for seven pedomicrobia (10). Genome sizes are known for only two strains, Hyphomicrobium sp. strain B-522 (Mr,3.1 X lo9) (34) and Rhodomicrobiurn vannielii RM5 (Mr, 2.1 X lo9) (40). DNADNA base sequence homologies have been reported for a number of Hyphomicrobium stra ...
Fatty Acid Oxid
... coenzyme Q). Thus from reoxidation of NADH and FADH2 a total of _______ ~ bonds of ATP are produced per 12-C fatty acid. Add to this the ~P bonds of GTP produced in Krebs Cycle (one GTP per acetyl80 ~P bonds produced. CoA) for a total of _______ ...
... coenzyme Q). Thus from reoxidation of NADH and FADH2 a total of _______ ~ bonds of ATP are produced per 12-C fatty acid. Add to this the ~P bonds of GTP produced in Krebs Cycle (one GTP per acetyl80 ~P bonds produced. CoA) for a total of _______ ...
Amino acids
... amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells ...
... amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells ...
regulation of fatty acid synthesis
... been clarified that dicots and most monocots have both forms of ACCase, a >200-kDa homodimeric ACCase (probably localized in the cytosol) and a heteromeric ACCase with at least four subunits in the plastid (2, 48, 80). It is the heteromeric plastid form of the ACCase that provides malonyl-CoA for fa ...
... been clarified that dicots and most monocots have both forms of ACCase, a >200-kDa homodimeric ACCase (probably localized in the cytosol) and a heteromeric ACCase with at least four subunits in the plastid (2, 48, 80). It is the heteromeric plastid form of the ACCase that provides malonyl-CoA for fa ...
Design, Synthesis, and Antibacterial Properties of Dual
... An urgent demand for the development of new antibiotics has been created by the increase in clinical cases involving drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. A novel target for antibacterial development is acetyl-CoA carboxylase, a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in fatty a ...
... An urgent demand for the development of new antibiotics has been created by the increase in clinical cases involving drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. A novel target for antibacterial development is acetyl-CoA carboxylase, a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in fatty a ...
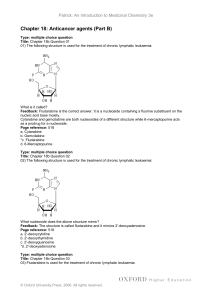
patrick_tb_ch18b
... Which of the following disadvantages apply to the above structure? Feedback: There are a variety of mechanisms by which tumour cells can gain resistance to drugs. For example, resistance to paclitaxel can arise due to mutation of tubulin resulting in a weakened binding interaction with paclitaxel. R ...
... Which of the following disadvantages apply to the above structure? Feedback: There are a variety of mechanisms by which tumour cells can gain resistance to drugs. For example, resistance to paclitaxel can arise due to mutation of tubulin resulting in a weakened binding interaction with paclitaxel. R ...
Amino acids
... amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells ...
... amino acids, of a specific protein, is determined by the sequence of the bases in the gene that encodes that protein. • The chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. • Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells ...
... Choice C: The concentration of potassium outside the cell is 1 mM and the concentration inside is 1 mM. The voltage potential across the membrane is +0.1V, with the inside positive. What direction will potassium flow, into the cell, or out of the cell? Justify your answer using (but not necessarily ...
REDESIGN OF CARNITINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE SPECIFICITY BY PROTEIN ENGINEERING UNIVERSIDAD DE BARCELONA
... was found to be 1:10,000 (Fig. 3, lane 1). At this dilution, a strong, defined, and specific band of 71 kDa (determined by comparison with comigrating size markers) was observed. Lower dilutions of the primary antibody (1:3,000 and 1:6,000) resulted in a stronger signal, but at the same time produce ...
... was found to be 1:10,000 (Fig. 3, lane 1). At this dilution, a strong, defined, and specific band of 71 kDa (determined by comparison with comigrating size markers) was observed. Lower dilutions of the primary antibody (1:3,000 and 1:6,000) resulted in a stronger signal, but at the same time produce ...
Regulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine
... hyperbolic with K , values of 0.31 r n M for chorismate and 0.015 mM for prephenate, respectively. The substrate saturation curve of the complexed prephenate dehydratase I was sigmoid; a Km value of 0-18 mM was calculated for prephenate. Chorismate mutase, prephenate dehydratase and prephenate dehyd ...
... hyperbolic with K , values of 0.31 r n M for chorismate and 0.015 mM for prephenate, respectively. The substrate saturation curve of the complexed prephenate dehydratase I was sigmoid; a Km value of 0-18 mM was calculated for prephenate. Chorismate mutase, prephenate dehydratase and prephenate dehyd ...
Structure and function of the eukaryotic ADP
... is well studied in extremophilic archaea, where ADPGK is part of a set of glycolytic enzymes that use ADP instead of ATP for the phosphorylation of various sugars. However, ADPGK has also been found in the genomes of mesophilic species and higher eukaryotes, suggesting that the enzyme is not necessa ...
... is well studied in extremophilic archaea, where ADPGK is part of a set of glycolytic enzymes that use ADP instead of ATP for the phosphorylation of various sugars. However, ADPGK has also been found in the genomes of mesophilic species and higher eukaryotes, suggesting that the enzyme is not necessa ...
A tribute to sulfur - Wiley Online Library
... desulfurases, C-DES does not have an active-site Cys of its own, but uses a cysteine residue of its substrate, cystine, to form the cysteine-hydrogen disulfide in a reductive cleavage reaction. It seems possible that for some Fe±S proteins in single-cell organisms synthesis may proceed spontaneously ...
... desulfurases, C-DES does not have an active-site Cys of its own, but uses a cysteine residue of its substrate, cystine, to form the cysteine-hydrogen disulfide in a reductive cleavage reaction. It seems possible that for some Fe±S proteins in single-cell organisms synthesis may proceed spontaneously ...
A low-molecular-mass protein from Methylococcus
... and the modifin indicate that they are unique proteins and show no similarity to alcohol or aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes isolated from methylotrophic bacteria. Substrate specificity studies demonstrated that FDH oxidized formaldehyde exclusively in the presence of the modifin; a diverse range of a ...
... and the modifin indicate that they are unique proteins and show no similarity to alcohol or aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes isolated from methylotrophic bacteria. Substrate specificity studies demonstrated that FDH oxidized formaldehyde exclusively in the presence of the modifin; a diverse range of a ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... Carnitine can be obtained from the diet, where it is found primarily in meat products. Carnitine can also be synthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine by an enzymatic pathway found in the liver and kidney but not in skeletal or heart muscle. Therefore, these tissues are totally de ...
... Carnitine can be obtained from the diet, where it is found primarily in meat products. Carnitine can also be synthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine by an enzymatic pathway found in the liver and kidney but not in skeletal or heart muscle. Therefore, these tissues are totally de ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.