... Diformyldeuteroporphyrin DTBE was deesterified in dry methylene chloride saturated with anhydrous HCl for 8 h. The solvent was removed in a vacuum and the free acid crystallized from pyridineacetic acid. The iron complex of the free acid (12) was synthesized by the method of Adler et al. (32) using ...
lecture6
... fatty acids are so simple. The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon atoms yield a propionyl CoA at the final thiolysis step that must be converted into an easily usable form by additional enzyme reactions ...
... fatty acids are so simple. The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon atoms yield a propionyl CoA at the final thiolysis step that must be converted into an easily usable form by additional enzyme reactions ...
The Complete Oxidation of Palmitate Yields 106 Molecules of ATP
... l -3-Hydroxyacyl CoA + NAD+ ↔ 3- keto acyl CoA + NADH+ H+ 3-ketoacyl CoA + CoA ↔acetyl CoA + acyl CoA (shortened by C2) ...
... l -3-Hydroxyacyl CoA + NAD+ ↔ 3- keto acyl CoA + NADH+ H+ 3-ketoacyl CoA + CoA ↔acetyl CoA + acyl CoA (shortened by C2) ...
On the origin of biochemistry at an alkaline hydrothermal vent
... methanogenesis were the ancestral forms of energy metabolism among the first free-living eubacteria and archaebacteria, respectively, stands in the foreground. The synthesis of formyl pterins, which are essential intermediates of the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway and purine biosynthesis, is found to confro ...
... methanogenesis were the ancestral forms of energy metabolism among the first free-living eubacteria and archaebacteria, respectively, stands in the foreground. The synthesis of formyl pterins, which are essential intermediates of the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway and purine biosynthesis, is found to confro ...
THE MULTIFARIOUS AND DYNAMIC REGULATION OF THE LIVING CELL Karen van Eunen
... 1.2.1 Mechanisms of flux regulation The flux through a pathway or an enzyme can be changed by many different regulatory mechanisms. Speaking in the terms introduced above, many buttons are available in the cell. In this section I will describe the various levels of regulation briefly. The regulatory ...
... 1.2.1 Mechanisms of flux regulation The flux through a pathway or an enzyme can be changed by many different regulatory mechanisms. Speaking in the terms introduced above, many buttons are available in the cell. In this section I will describe the various levels of regulation briefly. The regulatory ...
Direction of Krebs cycle Which way does the citric acid cycle turn
... "Several of the criticisms arise solely from a misinterpretation of the theory. Thomas as well as Breusch draw incorrect conclusions from the theory and argue against the theory when these conclusions are not confirmed by their experiments. This applies, for instance, to Thomas's statement that the ...
... "Several of the criticisms arise solely from a misinterpretation of the theory. Thomas as well as Breusch draw incorrect conclusions from the theory and argue against the theory when these conclusions are not confirmed by their experiments. This applies, for instance, to Thomas's statement that the ...
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5
... ( the thing we want to measure ) – A standard curve can be constructed with known antigen concentrations giving the following general results • High concentrations of patient antigen means that more of the antibody-antigen complexes are untagged • Low concentrations of patient antigen means that mor ...
... ( the thing we want to measure ) – A standard curve can be constructed with known antigen concentrations giving the following general results • High concentrations of patient antigen means that more of the antibody-antigen complexes are untagged • Low concentrations of patient antigen means that mor ...
- BioMedSearch
... that may have been formed from ADP in the presence of contaminating adenylate kinase (Figure 3). Only about 40% of the PEPS was inactivated which suggested that less than 50% of the PEPS was catalytically phosphorylated during pre-incubation with PEP. This result was investigated further and it was ...
... that may have been formed from ADP in the presence of contaminating adenylate kinase (Figure 3). Only about 40% of the PEPS was inactivated which suggested that less than 50% of the PEPS was catalytically phosphorylated during pre-incubation with PEP. This result was investigated further and it was ...
Proteins - The Open University
... In this course, we will consider aspects of the structure of proteins and illustrate how, through their interactions with other cellular components, they can function as dynamic molecular machines. We will begin by exploring the three-dimensional nature of proteins, reviewing some of their biochemis ...
... In this course, we will consider aspects of the structure of proteins and illustrate how, through their interactions with other cellular components, they can function as dynamic molecular machines. We will begin by exploring the three-dimensional nature of proteins, reviewing some of their biochemis ...
lecture6
... l -3-Hydroxyacyl CoA + NAD+ ↔ 3- keto acyl CoA + NADH+ H+ 3-ketoacyl CoA + CoA ↔acetyl CoA + acyl CoA (shortened by C2) ...
... l -3-Hydroxyacyl CoA + NAD+ ↔ 3- keto acyl CoA + NADH+ H+ 3-ketoacyl CoA + CoA ↔acetyl CoA + acyl CoA (shortened by C2) ...
Chapter 9: Pathways that Harvest Chemical
... chemical fuel is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6). Other molecules, including other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, can also supply energy. However, to release their energy they must be converted into glucose or intermediate compounds that can enter into the various pathways of glucose metabolism. In ...
... chemical fuel is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6). Other molecules, including other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, can also supply energy. However, to release their energy they must be converted into glucose or intermediate compounds that can enter into the various pathways of glucose metabolism. In ...
Induced-fit of the peptidyl-transferase center of the
... nature of the P-site donor. The most efficient (A-Phe) and the least active (A-Gly, A-(D)Phe) acceptors are however the same in all three donor configurations tested in (Rychlík et al. 1970). Because the acceptor activity comprises Km and kcat, catalytic rate constants cannot be extrapolated from th ...
... nature of the P-site donor. The most efficient (A-Phe) and the least active (A-Gly, A-(D)Phe) acceptors are however the same in all three donor configurations tested in (Rychlík et al. 1970). Because the acceptor activity comprises Km and kcat, catalytic rate constants cannot be extrapolated from th ...
New Functions for Parts of the Krebs Cycle in Procyclic
... Metabolic Pathways in the Presence of Glucose (10 mM), Glycerol (13 mM), Proline (5 mM), and Threonine (3 mM)—The incubations performed with [6-14C]glucose demonstrated that acetate and succinate were the main excreted end products of glucose metabolism (Fig. 1A), which is in agreement with previous ...
... Metabolic Pathways in the Presence of Glucose (10 mM), Glycerol (13 mM), Proline (5 mM), and Threonine (3 mM)—The incubations performed with [6-14C]glucose demonstrated that acetate and succinate were the main excreted end products of glucose metabolism (Fig. 1A), which is in agreement with previous ...
TRANSLATION OF mRNA - E-Learning/An
... O-acetylhomoserine, cystathionine, homocysteine, or methionine. Based on their growth properties, the mutant strains that had been originally identified as requiring methionine for growth could be placed into four groups designated strains 1, 2, 3, and 4 in this figure. A strain 1 mutant was missing ...
... O-acetylhomoserine, cystathionine, homocysteine, or methionine. Based on their growth properties, the mutant strains that had been originally identified as requiring methionine for growth could be placed into four groups designated strains 1, 2, 3, and 4 in this figure. A strain 1 mutant was missing ...
Specificity of the Organic Acid Activation of
... McIntosh, 1993). The activity of AOX is controlled by the oxidation or reduction of sulfhydryl groups, which form enzyme dimers (Umbach and Siedow, 1993), and this can be regulated in intact mitochondria by the redox poise of the NADP(H) pool in the mitochondrial matrix (Vanlerberghe et al., 1995). ...
... McIntosh, 1993). The activity of AOX is controlled by the oxidation or reduction of sulfhydryl groups, which form enzyme dimers (Umbach and Siedow, 1993), and this can be regulated in intact mitochondria by the redox poise of the NADP(H) pool in the mitochondrial matrix (Vanlerberghe et al., 1995). ...
Nature inspired platforms for production of acetyl
... fertilizers, and pesticides, which burden the environment2. Ethanol has the additional problems of containing ~70% of the energy content of gasoline and is miscible with water, making it difficult to distill from fermentation broth and corrosive to storage and distribution infrastructures3. Advanced ...
... fertilizers, and pesticides, which burden the environment2. Ethanol has the additional problems of containing ~70% of the energy content of gasoline and is miscible with water, making it difficult to distill from fermentation broth and corrosive to storage and distribution infrastructures3. Advanced ...
Fulltext PDF
... anticodon. In the first step the amino acid is activated by ATP to form tRNA synthetase (amino acid-AMP) which in the second step is loaded on tRNA to form aminoacyl tRNA (aa-tRNA). One may wonder as to how this specificity is maintained. Nobel Laureate Chrisitan de Devu commented that the second ge ...
... anticodon. In the first step the amino acid is activated by ATP to form tRNA synthetase (amino acid-AMP) which in the second step is loaded on tRNA to form aminoacyl tRNA (aa-tRNA). One may wonder as to how this specificity is maintained. Nobel Laureate Chrisitan de Devu commented that the second ge ...
13synthesis
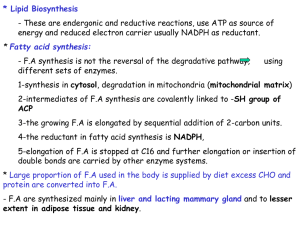
... - Palmitoyl CoA : -ve feed back in the biosynthesis, it inhibits the carboxylase enzyme. - When mitochondrial acetyl CoA + ATP increase increase production of citrate which transfers out of mitochondria increase cystolic citrate. 1- citrate is an allosteric activator for this carboxylase. 2- citrate ...
... - Palmitoyl CoA : -ve feed back in the biosynthesis, it inhibits the carboxylase enzyme. - When mitochondrial acetyl CoA + ATP increase increase production of citrate which transfers out of mitochondria increase cystolic citrate. 1- citrate is an allosteric activator for this carboxylase. 2- citrate ...
Diversity and origins of anaerobic metabolism in mitochondria and
... Mitochondria and related organelles are ubiquitous among eukaryotes. The last half-century of cellular and molecular evolutionary research has conclusively shown that mitochondria are descended from an a-proteobacterial endosymbiont that took up residence within a host cell prior to the last eukaryo ...
... Mitochondria and related organelles are ubiquitous among eukaryotes. The last half-century of cellular and molecular evolutionary research has conclusively shown that mitochondria are descended from an a-proteobacterial endosymbiont that took up residence within a host cell prior to the last eukaryo ...
Report Organelles in Blastocystis that Blur the
... C-terminal domain homologous to flavodoxins, a unique domain arrangement for this protein family of [FeFe] hydrogenases. Flavodoxins can be functionally interchangeable with ferredoxins and may be used as an alternative redox partner [12]. The flavodoxin domain may, thus, substitute for ferredoxin i ...
... C-terminal domain homologous to flavodoxins, a unique domain arrangement for this protein family of [FeFe] hydrogenases. Flavodoxins can be functionally interchangeable with ferredoxins and may be used as an alternative redox partner [12]. The flavodoxin domain may, thus, substitute for ferredoxin i ...
MOL WS 2016 Handout T3 Metabolism RNA world
... Studies suggest that ancient ribosomes constructed solely of rRNA could have developed the ability to synthesize peptide bonds. In addition, evidence strongly points to ancient ribosomes as self-replicating complexes, where the rRNA in the ribosomes had informational, structural, and catalytic purpo ...
... Studies suggest that ancient ribosomes constructed solely of rRNA could have developed the ability to synthesize peptide bonds. In addition, evidence strongly points to ancient ribosomes as self-replicating complexes, where the rRNA in the ribosomes had informational, structural, and catalytic purpo ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.