Hydrolysisof Glutathioneby Human Liver `y
... role of ‘y-glutamyltransferase. The pH optima with these substrates is 8.25 (9, 14) and initial velocity rates are maximal only with high concentrations of the dipeptide glycylglycine (14). In a recent detailed kinetic study, we have shown that ‘y-glutamyltransferase does not catalyze the hydrolysis ...
... role of ‘y-glutamyltransferase. The pH optima with these substrates is 8.25 (9, 14) and initial velocity rates are maximal only with high concentrations of the dipeptide glycylglycine (14). In a recent detailed kinetic study, we have shown that ‘y-glutamyltransferase does not catalyze the hydrolysis ...
Purification and Biochemical Characterization of Digestive Lipase in
... Abstract Penaeus vannamei lipase was purified from midgut gland of whiteleg shrimp. Pure lipase (E.C. 3.1.1.3) was obtained after Superdex 200 gel filtration and Resource Q anionic exchange. The pure lipase, which is a glycosylated molecule, is a monomer having a molecular mass of about 44.8 kDa, as ...
... Abstract Penaeus vannamei lipase was purified from midgut gland of whiteleg shrimp. Pure lipase (E.C. 3.1.1.3) was obtained after Superdex 200 gel filtration and Resource Q anionic exchange. The pure lipase, which is a glycosylated molecule, is a monomer having a molecular mass of about 44.8 kDa, as ...
Marine Biotecnology
... Abstract Penaeus vannamei lipase was purified from midgut gland of whiteleg shrimp. Pure lipase (E.C. 3.1.1.3) was obtained after Superdex 200 gel filtration and Resource Q anionic exchange. The pure lipase, which is a glycosylated molecule, is a monomer having a molecular mass of about 44.8 kDa, as ...
... Abstract Penaeus vannamei lipase was purified from midgut gland of whiteleg shrimp. Pure lipase (E.C. 3.1.1.3) was obtained after Superdex 200 gel filtration and Resource Q anionic exchange. The pure lipase, which is a glycosylated molecule, is a monomer having a molecular mass of about 44.8 kDa, as ...
Mutations lowering the phosphatase activity of HPr kinase
... such as glycolysis or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (StuÈlke and Hillen, 2000; Deutscher et al., 2001). To carry out these functions, P-Ser-HPr interacts with the catabolite control protein A (CcpA) (Deutscher et al., 1995; Jones et al., 1997), a member of the LacI/GalR repressor family (Henkin ...
... such as glycolysis or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (StuÈlke and Hillen, 2000; Deutscher et al., 2001). To carry out these functions, P-Ser-HPr interacts with the catabolite control protein A (CcpA) (Deutscher et al., 1995; Jones et al., 1997), a member of the LacI/GalR repressor family (Henkin ...
LIPID MOBILIZATION
... As fatty acids get longer they tend to be less water soluble so it is beneficial for the enzymes to be a complex Fatty acid synthase can synthesize only saturated fatty acyl chains of up to 16-C chain length ...
... As fatty acids get longer they tend to be less water soluble so it is beneficial for the enzymes to be a complex Fatty acid synthase can synthesize only saturated fatty acyl chains of up to 16-C chain length ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... A.The end products of carbohydrate digestion are monosaccharides: glucose, galactose and fructose. They are absorbed from the jejunum to portal veins to the liver, where fructose and galactose are transformed into glucose. B.Two mechanisms are responsible for absorption of monosaccharides: active tr ...
... A.The end products of carbohydrate digestion are monosaccharides: glucose, galactose and fructose. They are absorbed from the jejunum to portal veins to the liver, where fructose and galactose are transformed into glucose. B.Two mechanisms are responsible for absorption of monosaccharides: active tr ...
and PITTARD
... by low concentrations of exogenous tyrosine and by high conceiitrations of phenylalanine or tryptophan. In these experiments the possibility of multivalent repression of DAHP synthetase could not be directly tested. The present paper reports similar repression properties for wild-type E. coli K12. I ...
... by low concentrations of exogenous tyrosine and by high conceiitrations of phenylalanine or tryptophan. In these experiments the possibility of multivalent repression of DAHP synthetase could not be directly tested. The present paper reports similar repression properties for wild-type E. coli K12. I ...
2.2. Garrido-Franco, M. Structure E. coli
... monomers remains unclear, since all monomers display similar crystal contacts and overall folds (235 Cα atoms were aligned with an average rmsd of 0.34 Å). One remarkable difference is the binding of a phosphate ion in the active site of monomer A. The average B factor of the Pi (54.1 Å2) is slightl ...
... monomers remains unclear, since all monomers display similar crystal contacts and overall folds (235 Cα atoms were aligned with an average rmsd of 0.34 Å). One remarkable difference is the binding of a phosphate ion in the active site of monomer A. The average B factor of the Pi (54.1 Å2) is slightl ...
DESIGNING OF A POTENT ANALOG AGAINST DRUG RESISTANT HIV-1 PROTEASE:... STUDY Research Article
... crystal structure of HIV protease3 (Fig.1).HIV protease has two identical 99 amino acid chains (chain A and chain B) with each chain containing the characteristics D-T-G active site sequence at position 25 to 274.HIV protease is an aspartyl protease which functions as a homodimer with only one activ ...
... crystal structure of HIV protease3 (Fig.1).HIV protease has two identical 99 amino acid chains (chain A and chain B) with each chain containing the characteristics D-T-G active site sequence at position 25 to 274.HIV protease is an aspartyl protease which functions as a homodimer with only one activ ...
Vitamins B, E, K
... The role of vitamin K is as a cofactor for a carboxylase that adds CO2 to certain glutamate residues of blood clotting proteins, such as thrombin (“Factor II”) and several others. The resultant residue (upper right) is gammacarboxyglutamate or Gla (in 3-letter code). Gla residues can bind Ca2+, and ...
... The role of vitamin K is as a cofactor for a carboxylase that adds CO2 to certain glutamate residues of blood clotting proteins, such as thrombin (“Factor II”) and several others. The resultant residue (upper right) is gammacarboxyglutamate or Gla (in 3-letter code). Gla residues can bind Ca2+, and ...
Respiration and Lipid Metabolism - Roberto Cezar | Fisiologista
... At the end of the glycolytic sequence, plants have alternative pathways for metabolizing PEP. In one pathway PEP is carboxylated by the ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme PEP carboxylase to form the organic acid oxaloacetate (OAA). The OAA is then reduced to malate by the action of malate dehydrogenase, wh ...
... At the end of the glycolytic sequence, plants have alternative pathways for metabolizing PEP. In one pathway PEP is carboxylated by the ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme PEP carboxylase to form the organic acid oxaloacetate (OAA). The OAA is then reduced to malate by the action of malate dehydrogenase, wh ...
Oxidation and biosynthesis of fatty acids
... mammary glands during lactation • Occurs in cytoplasm ...
... mammary glands during lactation • Occurs in cytoplasm ...
The promiscuous primase
... with Pol b. It is a template-independent DNA and RNA polymerase that has a key role in the generation of antibody diversity by the V(D)J recombination process. In pre-T-cell extracts, TdT associates with Ku, a heterodimeric protein required for V(D)J recombination and for nonhomologous end joining ( ...
... with Pol b. It is a template-independent DNA and RNA polymerase that has a key role in the generation of antibody diversity by the V(D)J recombination process. In pre-T-cell extracts, TdT associates with Ku, a heterodimeric protein required for V(D)J recombination and for nonhomologous end joining ( ...
Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine
... the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.[1] ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is produced by photophosphorylation and cellular respiration and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, ...
... the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.[1] ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is produced by photophosphorylation and cellular respiration and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, ...
Mitochondrial trans-2-Enoyl-CoA Reductase of Wax Ester
... anaerobic conditions. Using NADH, the recombinant enzyme accepted crotonyl-CoA (km ⴝ 68 M) and trans-2hexenoyl-CoA (km ⴝ 91 M). In the crotonyl-CoA-dependent reaction, both NADH (km ⴝ 109 M) or NADPH (km ⴝ 119 M) were accepted, with 2–3-fold higher specific activities for NADH relative to NADPH. ...
... anaerobic conditions. Using NADH, the recombinant enzyme accepted crotonyl-CoA (km ⴝ 68 M) and trans-2hexenoyl-CoA (km ⴝ 91 M). In the crotonyl-CoA-dependent reaction, both NADH (km ⴝ 109 M) or NADPH (km ⴝ 119 M) were accepted, with 2–3-fold higher specific activities for NADH relative to NADPH. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... o Occurs predominantly in the liver cells Also present in kidney and maybe intestine cells Kidney is back up plan for gluconeogenesis Enzymes of gluconeogenesis o 3 key enzymes from glycolysis that need to be bypassed in gluconeogenesis Need to be reversed because they use ATP Reversed with ...
... o Occurs predominantly in the liver cells Also present in kidney and maybe intestine cells Kidney is back up plan for gluconeogenesis Enzymes of gluconeogenesis o 3 key enzymes from glycolysis that need to be bypassed in gluconeogenesis Need to be reversed because they use ATP Reversed with ...
Electrone transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
... Biochemical reactions in cell are organized into multistep sequences called pathways. In a pathway, the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction. These are collectively called metabolism, which is the sum of all the chemical changes occurring in a cell, a tissue, or ...
... Biochemical reactions in cell are organized into multistep sequences called pathways. In a pathway, the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction. These are collectively called metabolism, which is the sum of all the chemical changes occurring in a cell, a tissue, or ...
M.Sc. (Semester - III) BIOCHEMISTRY BCH
... a) Elaborate on primary and secondary lymphoid organs and their significance with neat diagram. b) List out different classes of antibodies and give their features. c) Classify immunodiffusion techniques and elaborate on the procedure of any one such technique. d) Explain the principle procedure and ...
... a) Elaborate on primary and secondary lymphoid organs and their significance with neat diagram. b) List out different classes of antibodies and give their features. c) Classify immunodiffusion techniques and elaborate on the procedure of any one such technique. d) Explain the principle procedure and ...
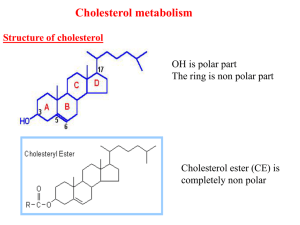
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity activated by high CHO and fat diet and inhibited in starvation. 4- Hormonal re ...
... simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity activated by high CHO and fat diet and inhibited in starvation. 4- Hormonal re ...
... The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of the transition state (+1 pt) Enzymes lower the energy of the transition state by: (3 pts) a) pre-ordering functional groups so there is no decrease in entropy in going from (ES) to (EP) b) forming energetic interactions with just the transitio ...
Off-the-Vine Ripening of Tomato Fruit Causes Alteration
... significant increase in red fruits ripened on-the-vine but not off-the-vine. Deaminating GDH decreased sharply under both ripening conditions, and the GDH aminating to deaminating activity ratio increased as well. The SSADH activity decreased during ripening although the level was similar under both ...
... significant increase in red fruits ripened on-the-vine but not off-the-vine. Deaminating GDH decreased sharply under both ripening conditions, and the GDH aminating to deaminating activity ratio increased as well. The SSADH activity decreased during ripening although the level was similar under both ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.