THE STUDY OF INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM OF
... 2. Another procedure is based on the fact that some catalysts may under certain experimental conditions labilize carbon-bound hydrogen atoms. Many compounds when treated with hot concentrated DzSO4 exchange otherwise stable hydrogen atoms (59). A number of deuterium-containing fatty acids and amino ...
... 2. Another procedure is based on the fact that some catalysts may under certain experimental conditions labilize carbon-bound hydrogen atoms. Many compounds when treated with hot concentrated DzSO4 exchange otherwise stable hydrogen atoms (59). A number of deuterium-containing fatty acids and amino ...
Cell Energy - Kuliah FTSL
... keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP. ...
... keep only a small amount of ATP on hand. Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy stored in foods like glucose. • The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is released by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP. ...
fiiformis1 - Plant Physiology
... The Xa"thophycean alp Bumilkropsis filiformis possesses peroxisomes which on electron micrographs show a mostly spherical or ovoid shape with a diameter in the range of 03 micrometer. Their granular matrix is usually of moderate electron density and in a very few cases contains amorphous inclusions. ...
... The Xa"thophycean alp Bumilkropsis filiformis possesses peroxisomes which on electron micrographs show a mostly spherical or ovoid shape with a diameter in the range of 03 micrometer. Their granular matrix is usually of moderate electron density and in a very few cases contains amorphous inclusions. ...
FMOC The solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) was first
... group, and asparagines, glutamine, cysteine and histidine are protected by trityl group, and arginine is protected by the pbf group. A wide range of protecting groups are also available for different applications such as Hmb group used as an amide protecting group to alleviate aggregation during SPP ...
... group, and asparagines, glutamine, cysteine and histidine are protected by trityl group, and arginine is protected by the pbf group. A wide range of protecting groups are also available for different applications such as Hmb group used as an amide protecting group to alleviate aggregation during SPP ...
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
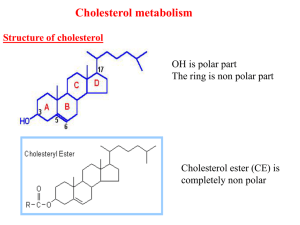
... • Most dietary cholesterol is present in free form (not estrified) with 10-15% present as cholesterol ester (CE, fatty acid attached to OH at C3). Since free cholesterol is more absorbable (can penetrate the water layer surrounding the enterocytes ), so all CE should be converted into free cholester ...
... • Most dietary cholesterol is present in free form (not estrified) with 10-15% present as cholesterol ester (CE, fatty acid attached to OH at C3). Since free cholesterol is more absorbable (can penetrate the water layer surrounding the enterocytes ), so all CE should be converted into free cholester ...
Drosophila Sirt2/mammalian SIRT3 deacetylates ATP synthase and
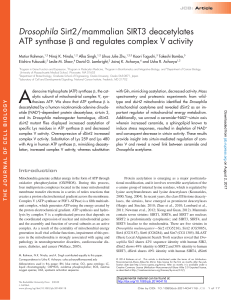
... Figure 1. Increase in ceramide levels results in depletion of NAD+ and decrease in sirtuin activity leading to hyperacetylation of proteins in different cellular compartments. (A) dcerk1 fly extracts show 65% reduction in NAD+ level compared with w1118 control. n = 3. (B) NAD synthesis and salvage ...
... Figure 1. Increase in ceramide levels results in depletion of NAD+ and decrease in sirtuin activity leading to hyperacetylation of proteins in different cellular compartments. (A) dcerk1 fly extracts show 65% reduction in NAD+ level compared with w1118 control. n = 3. (B) NAD synthesis and salvage ...
Biochemical Thermodynamics
... However, if the 129 letters making up this quotation were allowed to fall into a completely random, chaotic pattern, as shown in the following box, they would have no meaning whatsoever. In this form the 129 letters contain little or no information, but they are very rich m entropy S because of rand ...
... However, if the 129 letters making up this quotation were allowed to fall into a completely random, chaotic pattern, as shown in the following box, they would have no meaning whatsoever. In this form the 129 letters contain little or no information, but they are very rich m entropy S because of rand ...
Analysis of structural robustness of metabolic
... producing ATP drops out and when a mode producing NADPH is eliminated. For some applications, it is certainly of interest to distinguish between different products. To cope with such situations, we propose two further definitions. We consider the sub-network consisting of all elementary modes produc ...
... producing ATP drops out and when a mode producing NADPH is eliminated. For some applications, it is certainly of interest to distinguish between different products. To cope with such situations, we propose two further definitions. We consider the sub-network consisting of all elementary modes produc ...
Enzymes - Philadelphia University Jordan
... A. Recommended name Enzyme names have the suffix “-ase” attached to the substrate of the reaction (example, glucosidase and urease) or description the reaction (example, lactate dehydrogenase). [Note: no hint of the enzymic reaction, for example trypsin and pepsin.] ...
... A. Recommended name Enzyme names have the suffix “-ase” attached to the substrate of the reaction (example, glucosidase and urease) or description the reaction (example, lactate dehydrogenase). [Note: no hint of the enzymic reaction, for example trypsin and pepsin.] ...
amino acids
... compound that allows the fruit ripening. So the role of this amino acid is key for the plant growth since it is needed for the production of ethylene, but it is also important for the general metabolism of the plant since transmethylation is a very common and important reaction in the plant. ...
... compound that allows the fruit ripening. So the role of this amino acid is key for the plant growth since it is needed for the production of ethylene, but it is also important for the general metabolism of the plant since transmethylation is a very common and important reaction in the plant. ...
Browning reaction
... sugar are the basis of the Maillard reaction, which takes place in thermally processed food (Carabasa-Giribet and Ibarz-Ribas, 2000). The formation of a complex series of compounds called, Maillard reaction products (MRPs), is associated with the development of brown pigments (Mastrocola and Munari, ...
... sugar are the basis of the Maillard reaction, which takes place in thermally processed food (Carabasa-Giribet and Ibarz-Ribas, 2000). The formation of a complex series of compounds called, Maillard reaction products (MRPs), is associated with the development of brown pigments (Mastrocola and Munari, ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... two are inverted. For example, a mutation from U to C (or vice versa), is a Y mutation, since they are both pyrimidines. This will have the effect of reversing the W/S, as well as the K/M, identities. A Y/R mutation preserves the value of the first bit, and flips the second from 0 to 1, or from 0 to ...
... two are inverted. For example, a mutation from U to C (or vice versa), is a Y mutation, since they are both pyrimidines. This will have the effect of reversing the W/S, as well as the K/M, identities. A Y/R mutation preserves the value of the first bit, and flips the second from 0 to 1, or from 0 to ...
29 Pathways of Sugar Metabolism: Pentose
... also called the hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP shunt). It shunts hexoses from glycolysis, forming pentoses, which may be reconverted to glycolytic intermediates. ...
... also called the hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP shunt). It shunts hexoses from glycolysis, forming pentoses, which may be reconverted to glycolytic intermediates. ...
6b How to ID an Unk organism
... turn a rust or red color (Gram negatives tend to do this). Therefore, red is a positive result, colorless or brown is negative. CITRATE TEST (Control: positive = Enterobacter aerogenes) Citrate is a salt of citric acid. It is a part of the Kreb’s cycle. In this medium, citrate is the sole carbon sou ...
... turn a rust or red color (Gram negatives tend to do this). Therefore, red is a positive result, colorless or brown is negative. CITRATE TEST (Control: positive = Enterobacter aerogenes) Citrate is a salt of citric acid. It is a part of the Kreb’s cycle. In this medium, citrate is the sole carbon sou ...
THE USE OF TBE ETHANOL PATHWAY IN GOLDFISH CARASSIUS
... rates and the blood glucose is oxidation to carbon dioxide or conversion to lactate. The primary adaptive strategy supporting anaerobiosis in fish is profound depression of metabolic rate, lowering ATP requirements to a level that can be supported over an extended period by less efficient fermentati ...
... rates and the blood glucose is oxidation to carbon dioxide or conversion to lactate. The primary adaptive strategy supporting anaerobiosis in fish is profound depression of metabolic rate, lowering ATP requirements to a level that can be supported over an extended period by less efficient fermentati ...
Prevention of Tryptophan Oxidation During Iodination of Tyrosyl
... A s n - T r p - L e u - L e u - O H was obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of the corresponding Na-benzyloxycarbonyl derivative, an interm ediate of the Gastric ...
... A s n - T r p - L e u - L e u - O H was obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of the corresponding Na-benzyloxycarbonyl derivative, an interm ediate of the Gastric ...
Document
... cholesterol biosynthesis are regulated. To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by c ...
... cholesterol biosynthesis are regulated. To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by c ...
A STUDY OF THE AMINO ACIDS ASSOCIATED WITH OVALBUMIN
... that free amino acids may be associated with ovalbumin. ...
... that free amino acids may be associated with ovalbumin. ...
file ini - Pusat Penelitian Biologi
... and capacity of phosphatases enzyme activity, as due to availability of phosphorous content in the medium identified by Barik & Purushothaman (1998). In the other hand, there is increasing evidence that phosphobacteria improve plant caused to biosynthesis of plant growth substances rather than their ...
... and capacity of phosphatases enzyme activity, as due to availability of phosphorous content in the medium identified by Barik & Purushothaman (1998). In the other hand, there is increasing evidence that phosphobacteria improve plant caused to biosynthesis of plant growth substances rather than their ...
The Effect of Actidione and other Antifungal Agents on Nucleic Acid
... bacteriocidal effect is located in the sequence of reactions leading to the synthesis of nucleic acid or protein. Fitzgerald, Bernheim & Fitzgerald (1948) reported the inhibition by streptomycin of the synthesis of the enzyme system involved in the adaptive utilization of benzoic acid by Mycobacteri ...
... bacteriocidal effect is located in the sequence of reactions leading to the synthesis of nucleic acid or protein. Fitzgerald, Bernheim & Fitzgerald (1948) reported the inhibition by streptomycin of the synthesis of the enzyme system involved in the adaptive utilization of benzoic acid by Mycobacteri ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.