Mitochondrial Medicine Arrives to Prime Time in Clinical Care
... into pyruvate/lactate; (2) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex— enzymatic and nutrient-dependent conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA; (3) Krebs/citric acid cycle—intramitochondrial enzymatic degradation of acetyl-CoA into its constituent carbon and hydrogen atoms to fuel ATP production; leading finally ...
... into pyruvate/lactate; (2) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex— enzymatic and nutrient-dependent conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA; (3) Krebs/citric acid cycle—intramitochondrial enzymatic degradation of acetyl-CoA into its constituent carbon and hydrogen atoms to fuel ATP production; leading finally ...
Mitochondrial Medicine Arrives to Prime Time in Clinical Care
... into pyruvate/lactate; (2) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex— enzymatic and nutrient-dependent conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA; (3) Krebs/citric acid cycle—intramitochondrial enzymatic degradation of acetyl-CoA into its constituent carbon and hydrogen atoms to fuel ATP production; leading finally ...
... into pyruvate/lactate; (2) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex— enzymatic and nutrient-dependent conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA; (3) Krebs/citric acid cycle—intramitochondrial enzymatic degradation of acetyl-CoA into its constituent carbon and hydrogen atoms to fuel ATP production; leading finally ...
NEISSERIAE
... 2. Carbohydrate utilization The various species of Neisseria can be differentiated according to carbohydrate utilization patterns. Neisseria species do not produce acid from carbohydrate fermentation but rather by an oxidative pathway. These tests are done using a media with single carbohydrates ( g ...
... 2. Carbohydrate utilization The various species of Neisseria can be differentiated according to carbohydrate utilization patterns. Neisseria species do not produce acid from carbohydrate fermentation but rather by an oxidative pathway. These tests are done using a media with single carbohydrates ( g ...
AMP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetases in Archaea show
... truncated protein of about 63 kDa was heterologously produced in E. coli but did not exhibit ACS activity (data not shown). This size is consistent with the position of the stop codon indicated in the published genome sequence. The sequence of the cloned M. thermautotrophicus ΔH ACS1 gene (determine ...
... truncated protein of about 63 kDa was heterologously produced in E. coli but did not exhibit ACS activity (data not shown). This size is consistent with the position of the stop codon indicated in the published genome sequence. The sequence of the cloned M. thermautotrophicus ΔH ACS1 gene (determine ...
Print this article - Journals at the University of Arizona
... reservoir carbon and hence allow us to identify the presence of multiple carbon reservoirs in human bone, and to do so without recourse to the dating of associated materials (if possible). This hypothesis initiated the Oxford Radiocarbon Accelerator Unit’s (ORAU) novel approach to 14C dating single ...
... reservoir carbon and hence allow us to identify the presence of multiple carbon reservoirs in human bone, and to do so without recourse to the dating of associated materials (if possible). This hypothesis initiated the Oxford Radiocarbon Accelerator Unit’s (ORAU) novel approach to 14C dating single ...
8/18/2015 1 BCMB 3100
... c. Another method for aa composition analysis is to treat protein hydrolysate with phenylisothiocyanate (PITC) at pH 9.0 to yield PITC-aa derivatives, separate by HPLC via hydrophobic attraction of aa side chains to hydrocarbon matrix of column and quantitate by OD 254 nm (due to PTC moiety). (The f ...
... c. Another method for aa composition analysis is to treat protein hydrolysate with phenylisothiocyanate (PITC) at pH 9.0 to yield PITC-aa derivatives, separate by HPLC via hydrophobic attraction of aa side chains to hydrocarbon matrix of column and quantitate by OD 254 nm (due to PTC moiety). (The f ...
Phosphate stabilizing compositions
... The compositions are synergistic because, although polyaspartic acids are not effective phosphate stabilizers, blending polyaspartic acid with known polymer phosphate inhibitors improves the performance of known phosphate stabilizers. This was surprising because polyaspartic acid alone does not have ...
... The compositions are synergistic because, although polyaspartic acids are not effective phosphate stabilizers, blending polyaspartic acid with known polymer phosphate inhibitors improves the performance of known phosphate stabilizers. This was surprising because polyaspartic acid alone does not have ...
View/Open
... Metabolism can be defined as the sum total of all chemical transformations that occur in cells (Stanier, Adelberg & Ingraham 1980). Fermentation is a metabolic process in which carbohydrates and related compounds are oxidised with the release of energy in the absence of any external electron accepto ...
... Metabolism can be defined as the sum total of all chemical transformations that occur in cells (Stanier, Adelberg & Ingraham 1980). Fermentation is a metabolic process in which carbohydrates and related compounds are oxidised with the release of energy in the absence of any external electron accepto ...
Black and White Nucleotide Metabolism english document for
... 1. De novo synthesis pathway is the pathway involves with different enzymes to create nucleotide molecule. 2. Salvage pathway is the pathway that relies on recycling of degradative product of DNA or RNA molecule. ...
... 1. De novo synthesis pathway is the pathway involves with different enzymes to create nucleotide molecule. 2. Salvage pathway is the pathway that relies on recycling of degradative product of DNA or RNA molecule. ...
Escherichia coli ATP Synthase
... Overall, F1 Fo -ATP synthase is structurally and functionally similar among sources with only a few exceptions such as in chloroplasts, where there are two isoforms, and in mitochondria, where there are 7–9 additional subunits. ATP hydrolysis and synthesis occur on three catalytic sites in the F1 se ...
... Overall, F1 Fo -ATP synthase is structurally and functionally similar among sources with only a few exceptions such as in chloroplasts, where there are two isoforms, and in mitochondria, where there are 7–9 additional subunits. ATP hydrolysis and synthesis occur on three catalytic sites in the F1 se ...
Glycolysis Lecture
... Welcome to the Department of Clinical Biochemistry. The aim of this course guide is to provide you with clear description of the course objectives, contents of each topic together with its lectures, tutorials and practicals, which are presented in a sequential manner. Also it states clearly what is ...
... Welcome to the Department of Clinical Biochemistry. The aim of this course guide is to provide you with clear description of the course objectives, contents of each topic together with its lectures, tutorials and practicals, which are presented in a sequential manner. Also it states clearly what is ...
articles - Geoscience Research Institute
... the nature of which depends upon the number and order (sequence) of the amino acids within the molecules. The order is critical. In some instances, having one amino acid out of position will cause a protein to be non-functional. Proteins act as enzymes, which are catalysts involved in all biological ...
... the nature of which depends upon the number and order (sequence) of the amino acids within the molecules. The order is critical. In some instances, having one amino acid out of position will cause a protein to be non-functional. Proteins act as enzymes, which are catalysts involved in all biological ...
Manipulation of yeast respiration using acetic acid to demonstrate
... almost certainly have a different texture. In yeast breads leavening is a result of CO2 production by yeast cells as they metabolize sugars through aerobic respiration and fermentation (Fig. 1). In the presence of oxygen, yeast cells actively take up and metabolize glucose using aerobic respiration, ...
... almost certainly have a different texture. In yeast breads leavening is a result of CO2 production by yeast cells as they metabolize sugars through aerobic respiration and fermentation (Fig. 1). In the presence of oxygen, yeast cells actively take up and metabolize glucose using aerobic respiration, ...
Calculation of hydrophobicities
... Critique. While this method gives equal errors for all amino acids, it might give to high overall errors. One possibility would be to relax the equalities in Eq. 7 to –say- 5% between them, instead of precise equality or too tight matching. The adoption of this method depends on the actual result of ...
... Critique. While this method gives equal errors for all amino acids, it might give to high overall errors. One possibility would be to relax the equalities in Eq. 7 to –say- 5% between them, instead of precise equality or too tight matching. The adoption of this method depends on the actual result of ...
University of Groningen Operation of the purine nucleotide cycle in
... compound seemed to be required. Carter & Cohen ( I 955) partially purified the enzyme from yeast which catalyses reaction (3). T h e authors rightly assumed adenylosuccinate to be an intermediate in the mechanism for incorporation of the amino group in adenine nucleotides. Subsequently, Lieberman ( ...
... compound seemed to be required. Carter & Cohen ( I 955) partially purified the enzyme from yeast which catalyses reaction (3). T h e authors rightly assumed adenylosuccinate to be an intermediate in the mechanism for incorporation of the amino group in adenine nucleotides. Subsequently, Lieberman ( ...
Presentations in Biochemistry for MS 1
... glucose and lipid-derived ketone bodies, including acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid. Glucose cannot be synthesized from lipids, and is instead made from amino acids such as alanine in the process of gluconeogenesis. Serum alanine (choice B) drops dramatically in starvation, due to its c ...
... glucose and lipid-derived ketone bodies, including acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid. Glucose cannot be synthesized from lipids, and is instead made from amino acids such as alanine in the process of gluconeogenesis. Serum alanine (choice B) drops dramatically in starvation, due to its c ...
Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine
... been made, 17 amino acids were compared in this study using competitive kinetic principles. The experimental results showed that (1) most amino acids have similar initial reactivities at neutral pH; (2) amino acids with thiol groups such as methionine and cysteine are exceptionally reactive and prod ...
... been made, 17 amino acids were compared in this study using competitive kinetic principles. The experimental results showed that (1) most amino acids have similar initial reactivities at neutral pH; (2) amino acids with thiol groups such as methionine and cysteine are exceptionally reactive and prod ...
Muscle Energetics and Fatigue - Dr. Feher
... Each activation of the muscle requires fast ATP hydrolysis Larger EMG amplitudes (recorded in volts) indicate greater number of muscle fibers that are firing action potentials. Each muscle fiber, when activated, is activated completely. The control of force for the entire muscle is achieved by the t ...
... Each activation of the muscle requires fast ATP hydrolysis Larger EMG amplitudes (recorded in volts) indicate greater number of muscle fibers that are firing action potentials. Each muscle fiber, when activated, is activated completely. The control of force for the entire muscle is achieved by the t ...
Lecture 53-
... (cholecalciferol) requires conversion to 1,25dihydroxy vitamin D3 to form the active compound. • Effect of Deficiency: Rickets, osteomalacia - Oral manifestations: Deficiency associated with incomplete mineralization of teeth. Excess associated with pulp calcification • Sources: UV irradiation of 7- ...
... (cholecalciferol) requires conversion to 1,25dihydroxy vitamin D3 to form the active compound. • Effect of Deficiency: Rickets, osteomalacia - Oral manifestations: Deficiency associated with incomplete mineralization of teeth. Excess associated with pulp calcification • Sources: UV irradiation of 7- ...
Plant Physiology 66:
... integuments of the ovule release a nutrient-rich fluid that fills the embryo sac and bathes the expanding embryo asymmetrically (18). A clear distinction may be drawn between this liquid, originating from the integuments, and the endosperm, which is transient and never becomes fully cellular (17, 18 ...
... integuments of the ovule release a nutrient-rich fluid that fills the embryo sac and bathes the expanding embryo asymmetrically (18). A clear distinction may be drawn between this liquid, originating from the integuments, and the endosperm, which is transient and never becomes fully cellular (17, 18 ...
corrected Amino acids and Protein
... Amino acids are building blocks of proteins. More than100 amino acids have been isolated and identified but only 25 are obtained upon hydrolysis of typical proteins. All 25 except 2 are αamino acids; the two exceptions are proline and hydroxy proline, which are imino acids. Only 20 amino acids are o ...
... Amino acids are building blocks of proteins. More than100 amino acids have been isolated and identified but only 25 are obtained upon hydrolysis of typical proteins. All 25 except 2 are αamino acids; the two exceptions are proline and hydroxy proline, which are imino acids. Only 20 amino acids are o ...
1958 Shorland: RECENT WORK ON ANIMAL FATS
... into the citric acid cycle to be oxidized into carbon dioxide and water. The level of fatty acid oxidation is therefore determined by the rate at which oxaloacetate I,ecomes nvailab1.e. If this rate falls off through depression of carbohydrate metabolism as in diabetes, then acetyl coenzyme A cannot ...
... into the citric acid cycle to be oxidized into carbon dioxide and water. The level of fatty acid oxidation is therefore determined by the rate at which oxaloacetate I,ecomes nvailab1.e. If this rate falls off through depression of carbohydrate metabolism as in diabetes, then acetyl coenzyme A cannot ...
The Enterobacteriaceae
... conversion of glucose to pyruvate NADH2 in turn reduces pyruvate with oxidation of NADH2 to NAD which supports continued anaerobic glycolysis, and generation from pyruvate of alcohols, carboxylic acids, and CO2 gas End products of glucose fermentation: organic acids and CO2 gas Fermentation detected ...
... conversion of glucose to pyruvate NADH2 in turn reduces pyruvate with oxidation of NADH2 to NAD which supports continued anaerobic glycolysis, and generation from pyruvate of alcohols, carboxylic acids, and CO2 gas End products of glucose fermentation: organic acids and CO2 gas Fermentation detected ...
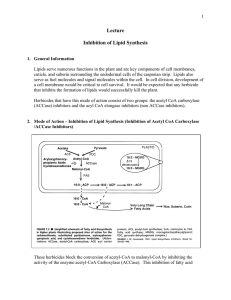
Lecture Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis
... and ICI Plant Protection (Zeneca/Syngenta) and was first tested in the U.S. in 1981. Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhib ...
... and ICI Plant Protection (Zeneca/Syngenta) and was first tested in the U.S. in 1981. Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhib ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.