4-6
... protein synthesis is depressed by ARF and protein degradation is increased even in the presence of insulin [9]. Acidosis was identified as an important factor in muscle protein breakdown. Metabolic acidosis activates the catabolism of protein and oxidation of amino acids independently of azotemia, a ...
... protein synthesis is depressed by ARF and protein degradation is increased even in the presence of insulin [9]. Acidosis was identified as an important factor in muscle protein breakdown. Metabolic acidosis activates the catabolism of protein and oxidation of amino acids independently of azotemia, a ...
INTRODUCING AMINO ACIDS
... If you look carefully, you will spot the abbreviations for glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) amongst the others. If you followed the protein chain all the way to its left-hand end, you would find an amino acid residue with an unattached -NH2 group. The N-terminal is always written on the left of a dia ...
... If you look carefully, you will spot the abbreviations for glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) amongst the others. If you followed the protein chain all the way to its left-hand end, you would find an amino acid residue with an unattached -NH2 group. The N-terminal is always written on the left of a dia ...
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of the chemol
... providing a link between glycolysis and the Kreb's cycle. The reaction takes place in several steps. In the first, pyruvate decarboxylase converts pyruvate to hydroxyethylthiamin pyrophosphate. Next the transacetylase shifts the two-carbon fragment from thiamin pyrophosphate to lipoic acid and from ...
... providing a link between glycolysis and the Kreb's cycle. The reaction takes place in several steps. In the first, pyruvate decarboxylase converts pyruvate to hydroxyethylthiamin pyrophosphate. Next the transacetylase shifts the two-carbon fragment from thiamin pyrophosphate to lipoic acid and from ...
References - The University of New Mexico
... of pyruvate vs. lactate. For pH conditions of 6.0 and 7.0, respectively, H+ coefficients (-‘ve values = H+ release) for the creatine kinase, adenylate kinase, AMP deaminase and ATPase reactions were 0.8 and 0.97, -0.13 and -0.02, 1.2 and 1.09, and -0.01 and -0.66, respectively. The glycolytic pathwa ...
... of pyruvate vs. lactate. For pH conditions of 6.0 and 7.0, respectively, H+ coefficients (-‘ve values = H+ release) for the creatine kinase, adenylate kinase, AMP deaminase and ATPase reactions were 0.8 and 0.97, -0.13 and -0.02, 1.2 and 1.09, and -0.01 and -0.66, respectively. The glycolytic pathwa ...
Poster
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism in Rhizobium trifolii
... Galactose may be catabolized via a different pathway, possibly involving an NADP+-linked galactose dehydrogenase. Pyruvate carboxylase was an important anaplerotic enzyme in R. trifolii required for growth on all carbon sources tested, except succinate. All the mutants, including a glk fup double mu ...
... Galactose may be catabolized via a different pathway, possibly involving an NADP+-linked galactose dehydrogenase. Pyruvate carboxylase was an important anaplerotic enzyme in R. trifolii required for growth on all carbon sources tested, except succinate. All the mutants, including a glk fup double mu ...
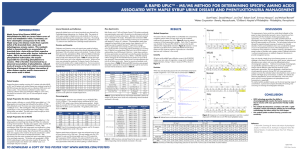
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... transferred to a 0.5mL microcentrifuge tube to which 100µL of Li220 diluting buffer was added. The tubes were mixed thoroughly at which time the samples were ready for analysis1. Sample Preparation for LC-MS/MS Plasma samples, calibrators or controls (50µL) were added to a 1.7mL polypropylene microc ...
... transferred to a 0.5mL microcentrifuge tube to which 100µL of Li220 diluting buffer was added. The tubes were mixed thoroughly at which time the samples were ready for analysis1. Sample Preparation for LC-MS/MS Plasma samples, calibrators or controls (50µL) were added to a 1.7mL polypropylene microc ...
Ch 3 Chemical Reactions 2013-Sept-08
... Metal Sulfides are black and metal sulfides come from the center of the earth. Sulfides are insoluble in water so they form a black mass in the deep ocean floor cracks. Chemical Reactions are the heart of Chemistry. This chapter is an introduction to symbols and chemical reactions. 3.1 Intro to Chem ...
... Metal Sulfides are black and metal sulfides come from the center of the earth. Sulfides are insoluble in water so they form a black mass in the deep ocean floor cracks. Chemical Reactions are the heart of Chemistry. This chapter is an introduction to symbols and chemical reactions. 3.1 Intro to Chem ...
Lecture 011, Respiration2 - SuperPage for Joel R. Gober, PhD.
... CO2. Now, what--where does this take place? >> [INDISTINCT] >> Could it be cytosol or mitochondria? I like mitochondria, that’s right. So, this is an enzyme that is contained within the mitochondria and as a matter of fact, nothing inside the mitochondria can happen without oxygen. So, this process ...
... CO2. Now, what--where does this take place? >> [INDISTINCT] >> Could it be cytosol or mitochondria? I like mitochondria, that’s right. So, this is an enzyme that is contained within the mitochondria and as a matter of fact, nothing inside the mitochondria can happen without oxygen. So, this process ...
Document
... ester; write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of an ester. Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products from acid and base hydrolysis of esters. Give the common names for amines; draw the condensed structural formulas when given their names. Classify amines as primary, sec ...
... ester; write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of an ester. Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products from acid and base hydrolysis of esters. Give the common names for amines; draw the condensed structural formulas when given their names. Classify amines as primary, sec ...
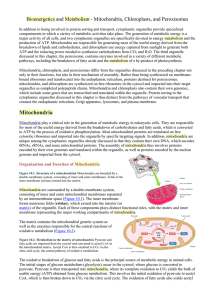
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
... respectively. Most of the energy derived from oxidative metabolism is then produced by the process of oxidative phosphorylation (discussed in detail in the next section), which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred through a se ...
... respectively. Most of the energy derived from oxidative metabolism is then produced by the process of oxidative phosphorylation (discussed in detail in the next section), which takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred through a se ...
ch.6
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Write in soft pencil. Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the answer sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each que ...
... Write in soft pencil. Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the answer sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each que ...
Role of Water soluble Vitamins in Food Industry
... coenzyme forms; addition of phosphate groups occurs in the activation of thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin B6; a shift in structure activates biotin, and formation of a complex between the free vitamin and parts of other molecules is involved in the activation of niacin, pantothenic acid, folic acid, ...
... coenzyme forms; addition of phosphate groups occurs in the activation of thiamin, riboflavin, and vitamin B6; a shift in structure activates biotin, and formation of a complex between the free vitamin and parts of other molecules is involved in the activation of niacin, pantothenic acid, folic acid, ...
View Full Article - PDF - International Research Journals
... stool (Groff et al., 1999). Diet with high fibre content have been used for weight control and fat reduction, as they give a sense of satiety even when small food is eaten (Ekop, 2004). Amino acids The results for this determination are in Table 2 which shows seventeen amino acid analysed. The resul ...
... stool (Groff et al., 1999). Diet with high fibre content have been used for weight control and fat reduction, as they give a sense of satiety even when small food is eaten (Ekop, 2004). Amino acids The results for this determination are in Table 2 which shows seventeen amino acid analysed. The resul ...
Chapter 2b Packet answers
... 3. The ability to move or change matter is __energy____________________. 4. All living things require a source of _energy_ to carry out their life activities. 5. The starting materials for chemical reactions are called _reactants__, while thenew substances that are formed are called __products__. 6. ...
... 3. The ability to move or change matter is __energy____________________. 4. All living things require a source of _energy_ to carry out their life activities. 5. The starting materials for chemical reactions are called _reactants__, while thenew substances that are formed are called __products__. 6. ...
Option A: Human nutrition and health (15 hours)
... • Instructions that are in red refer to what I expect to see in your notebook. Any extra information is fantastic! ...
... • Instructions that are in red refer to what I expect to see in your notebook. Any extra information is fantastic! ...
Enzymes - part 1
... Resulting species = product Enzyme acts on forward and reverse reactions Activity depends on protein’s native structure Regulated - by concentrations of substrate and substances other than substrate ...
... Resulting species = product Enzyme acts on forward and reverse reactions Activity depends on protein’s native structure Regulated - by concentrations of substrate and substances other than substrate ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier
... Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment materi ...
... Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment materi ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.