Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations 2 Brochure
... Biocatalysts are increasingly used by chemists engaged in fine chemical synthesis within both industry and academia. Today, there exists a huge choice of high–tech enzymes and whole cell biocatalysts, which add enormously to the repertoire of synthetic possibilities. Practical Methods for Biocatalys ...
... Biocatalysts are increasingly used by chemists engaged in fine chemical synthesis within both industry and academia. Today, there exists a huge choice of high–tech enzymes and whole cell biocatalysts, which add enormously to the repertoire of synthetic possibilities. Practical Methods for Biocatalys ...
Calvin Cycle Flux, Pathway Constraints, and
... Since fumarate and malate have the same oxidation state, we grouped them as one metabolite to account for their simultaneous consumption and to better reflect the effects of intermediary metabolic fluxes on H2 yield. If we were to show the H2 yield as a proportion of fumarate consumed alone, without ...
... Since fumarate and malate have the same oxidation state, we grouped them as one metabolite to account for their simultaneous consumption and to better reflect the effects of intermediary metabolic fluxes on H2 yield. If we were to show the H2 yield as a proportion of fumarate consumed alone, without ...
Metabolism
... – Acetyl-CoA goes in and oxaloacetate comes out...which ironically is used to continue the cycle...? – Many B vitmins used as cofactors. – By-products go into the E- transport chain. ...
... – Acetyl-CoA goes in and oxaloacetate comes out...which ironically is used to continue the cycle...? – Many B vitmins used as cofactors. – By-products go into the E- transport chain. ...
Slide 1
... Prolyl-tRNA synthetases (ProRSs), which are class II synthetases that catalyze covalent attachment of proline to the 3´-end of the tRNAPro. ProRSs from all three kingdoms of life, have shown to misactivate noncognate alanine and cysteine, and form mischarged aminoacyl-tRNAPro. It has been found that ...
... Prolyl-tRNA synthetases (ProRSs), which are class II synthetases that catalyze covalent attachment of proline to the 3´-end of the tRNAPro. ProRSs from all three kingdoms of life, have shown to misactivate noncognate alanine and cysteine, and form mischarged aminoacyl-tRNAPro. It has been found that ...
Effects of oxygen on the growth and metabolism of Actinomyces
... such as ethanol and pyruvic, lactic, citric or glutamic acids were found (results not shown). In washed cell suspensions of aerobically grown cells oxygen was consumed at a considerable rate (101 nmol O 2- mg -1 dry weight, min -1) and with a high affinity ( K m = 1 # m o l . l - 1 ) , when glucose ...
... such as ethanol and pyruvic, lactic, citric or glutamic acids were found (results not shown). In washed cell suspensions of aerobically grown cells oxygen was consumed at a considerable rate (101 nmol O 2- mg -1 dry weight, min -1) and with a high affinity ( K m = 1 # m o l . l - 1 ) , when glucose ...
Pentose Phosphate Shunt
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis Or, if NADPH or ribose-5-P ...
... Cell’s Need for ATP, NADPH, and Rib-5-P Glucose can be a substrate either for glycolysis or for the pentose phosphate pathway The choice depends on the relative needs of the cell for biosynthesis and for energy from metabolism ATP can be made if G-6-P is sent to glycolysis Or, if NADPH or ribose-5-P ...
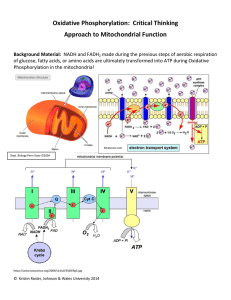
Oxidative Phosphorylation accompanying Oxidation of
... for the 02 dissolved in the medium. The 02 concentration in the medium was measured at -0-6v with a calomel reference electrode, and was determined by measuring the deflexion of the recorder pen with M-KCI saturated with air at 300 (International Critical Tables, 1928) followed by purging with 02-fr ...
... for the 02 dissolved in the medium. The 02 concentration in the medium was measured at -0-6v with a calomel reference electrode, and was determined by measuring the deflexion of the recorder pen with M-KCI saturated with air at 300 (International Critical Tables, 1928) followed by purging with 02-fr ...
Acids and Bases
... General rule: The conjugate base of a strong acid is a weak base. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a strong base is a weak acid. ...
... General rule: The conjugate base of a strong acid is a weak base. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a strong base is a weak acid. ...
9 essential amino acids your body can`t live without
... transporting essential oxygen around the body, accounts for 16%. Protein also has an essential function in every cell including in membranes, transporters, enzymes, components of the immune system, and is also a precursor to hormones. ...
... transporting essential oxygen around the body, accounts for 16%. Protein also has an essential function in every cell including in membranes, transporters, enzymes, components of the immune system, and is also a precursor to hormones. ...
Identification of GNB – IMViC Tests
... grown on a plate medium. Or, using a wooden applicator stick, a bacterial sample can either be rubbed on a Dry Slide Oxidase reaction area, on a KEY test strip, or filter paper moistened with the oxidase reagent. The light pink oxidase test reagent (Disk, strip, or Slide) serves as an artificial sub ...
... grown on a plate medium. Or, using a wooden applicator stick, a bacterial sample can either be rubbed on a Dry Slide Oxidase reaction area, on a KEY test strip, or filter paper moistened with the oxidase reagent. The light pink oxidase test reagent (Disk, strip, or Slide) serves as an artificial sub ...
2106lecture 6a powerpoint
... Definition of amino acid -building blocks of proteins Structure of amino acid -each amino acid has an amino group(NH2), an acid group(COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side group all of which are attached to central carbon atom -some amino acids also contain sulphur ...
... Definition of amino acid -building blocks of proteins Structure of amino acid -each amino acid has an amino group(NH2), an acid group(COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side group all of which are attached to central carbon atom -some amino acids also contain sulphur ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... Peripheral tissues possessing mitochondria can oxidize 3hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate, which can be reconverted to acetyl CoA, thus producing energy for the cell. Unlike fatty acids, ketone bodies can be utilized by the brain and, therefore, are important fuels during a fast. The liver lacks ...
... Peripheral tissues possessing mitochondria can oxidize 3hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate, which can be reconverted to acetyl CoA, thus producing energy for the cell. Unlike fatty acids, ketone bodies can be utilized by the brain and, therefore, are important fuels during a fast. The liver lacks ...
Aromatic amino acid catabolism by lactococci
... prepared from these strains were found to contain an œ-ketoglutarate-dependent aminotransferase activity with tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine. Tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine aminotransferase specifie activities (Il mol product formed/mg proteinlmin) ranged from 0.30 to 2.8 10-3, 0.93 ...
... prepared from these strains were found to contain an œ-ketoglutarate-dependent aminotransferase activity with tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine. Tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine aminotransferase specifie activities (Il mol product formed/mg proteinlmin) ranged from 0.30 to 2.8 10-3, 0.93 ...
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids
... relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several other amino acids are found in the body free or in combined states (i.e. not associated with peptides or proteins). These non-protein associated amino acids perform specialized functions. Several of the amino acids found in proteins ...
... relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several other amino acids are found in the body free or in combined states (i.e. not associated with peptides or proteins). These non-protein associated amino acids perform specialized functions. Several of the amino acids found in proteins ...
practice oxidative phosphorylation worksheet11
... Passive Transport is the flow of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration & uses NO energy to do so (spontaneous). Active Transport is the flow of particles from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration & USES energy to do so (not spontan ...
... Passive Transport is the flow of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration & uses NO energy to do so (spontaneous). Active Transport is the flow of particles from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration & USES energy to do so (not spontan ...
Journal: Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
... cycle and the nucleotide pools, revealed surprisingly similar dynamics for both cultivation conditions. Instead of a strong influence of the medium, we rather observed a growth phase-specific behavior in glycolysis and in the lower citric acid cycle. Furthermore, analysis of the lower part of glycol ...
... cycle and the nucleotide pools, revealed surprisingly similar dynamics for both cultivation conditions. Instead of a strong influence of the medium, we rather observed a growth phase-specific behavior in glycolysis and in the lower citric acid cycle. Furthermore, analysis of the lower part of glycol ...
very new glucogen me..
... Any substance can join to common pathway of gluconeogenesis is glycogenic ...
... Any substance can join to common pathway of gluconeogenesis is glycogenic ...
3-3.1 Indole Alkaloids
... Members related to lysergic acid (e.g. ergotamine and ergometrine) are levorotatory, more active and designated by suffix “ine”. ...
... Members related to lysergic acid (e.g. ergotamine and ergometrine) are levorotatory, more active and designated by suffix “ine”. ...
How do bacteria respond to their environment?
... starvation for nitrogen? Is there a protein that binds ALL amino acids? ...
... starvation for nitrogen? Is there a protein that binds ALL amino acids? ...
substrate specificities of octopine dehydrogenases
... only and could utilize oxaloacetate and ct-ketobutyrate as alternative substrates to replace pyruvate. Similar specificities were noted for two other bivalve species, Cerastoderma edule (Gade & Grieshaber, 1976) and the freshwater Anodonta cygnea (Gade & Grieshaber, 1975) although in neither case wa ...
... only and could utilize oxaloacetate and ct-ketobutyrate as alternative substrates to replace pyruvate. Similar specificities were noted for two other bivalve species, Cerastoderma edule (Gade & Grieshaber, 1976) and the freshwater Anodonta cygnea (Gade & Grieshaber, 1975) although in neither case wa ...
X - Genaxxon bioscience
... The amino acid analysis service encloses the total hydrolyis of a given sample, the chemical derivatisation of the free amino acids (either produced by the acid hydrolysis or of already free amino acids), the separation of the derivatised amino acids by reversed phase HPLC and subsequent interpretat ...
... The amino acid analysis service encloses the total hydrolyis of a given sample, the chemical derivatisation of the free amino acids (either produced by the acid hydrolysis or of already free amino acids), the separation of the derivatised amino acids by reversed phase HPLC and subsequent interpretat ...
Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas and Entner–Doudoroff pathways in
... [10,11], GAPN (a non-phosphorylating, highly allosteric GAPDH) [12,13] and GAPOR (a ferredoxin-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate oxidoreductase) [14], and (iv) three enzymes for phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate interconversion, a catabolic pyruvate kinase with low allosteric potential [15], an an ...
... [10,11], GAPN (a non-phosphorylating, highly allosteric GAPDH) [12,13] and GAPOR (a ferredoxin-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate oxidoreductase) [14], and (iv) three enzymes for phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate interconversion, a catabolic pyruvate kinase with low allosteric potential [15], an an ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.