Study Guide #3: The Rise of the Sumerian Empire
... Study Guide #3: The Rise of the Sumerian Empire Ancient Sumer: ( ___________B.C to 2006 B.C) -Located in __________________Mesopotamia. -___________Mesopotamia is better for farming than the _________ ...
... Study Guide #3: The Rise of the Sumerian Empire Ancient Sumer: ( ___________B.C to 2006 B.C) -Located in __________________Mesopotamia. -___________Mesopotamia is better for farming than the _________ ...
1-2 PowerPoint
... • Irrigation = method of bringing water to a field from another place to water the crops • City-state = independent state made up of city and the land and villages surrounding it. Like a mini country. ...
... • Irrigation = method of bringing water to a field from another place to water the crops • City-state = independent state made up of city and the land and villages surrounding it. Like a mini country. ...
Mesopotamia - Socials ZEhn
... The Phase of the Moon The phase of the annual agricultural cycle Equinoxes and solstices The local mythos and its divine Patrons The success of the reigning Monarch Commemoration of specific historical events (founding, military ...
... The Phase of the Moon The phase of the annual agricultural cycle Equinoxes and solstices The local mythos and its divine Patrons The success of the reigning Monarch Commemoration of specific historical events (founding, military ...
Mesopotamia - School District 34 Abbotsford
... The Phase of the Moon The phase of the annual agricultural cycle Equinoxes and solstices The local mythos and its divine Patrons The success of the reigning Monarch Commemoration of specific historical events (founding, military ...
... The Phase of the Moon The phase of the annual agricultural cycle Equinoxes and solstices The local mythos and its divine Patrons The success of the reigning Monarch Commemoration of specific historical events (founding, military ...
Mesopotamia - TeacherWeb
... 1. List the four territorial states that flourished in Mesopotamia (and timeframes). 2. What role did nature, climate and geography have on the influence of religion? 3. What was the most significant historical moment according to records in Mesopotamia? Why? 4. What were ziggurats? 5. Mesopotamia w ...
... 1. List the four territorial states that flourished in Mesopotamia (and timeframes). 2. What role did nature, climate and geography have on the influence of religion? 3. What was the most significant historical moment according to records in Mesopotamia? Why? 4. What were ziggurats? 5. Mesopotamia w ...
Mesopotamia - cloudfront.net
... soil in the Middle East where the agricultural revolution took place Tigris and Euphrates had unpredictable flooding ...
... soil in the Middle East where the agricultural revolution took place Tigris and Euphrates had unpredictable flooding ...
Period 5`s Awesome Chapter 2 Study Guide
... Period 5’s Awesome Chapter 2 Study Guide Key terms, people and places Scribe City-state Polytheism Empire Bazaar Myth Monotheism Caravan Sumer Mesopotamia Babylonia Fertile Crescent Hammurabi Euphrates River Cuneiform Famine Tigris River ...
... Period 5’s Awesome Chapter 2 Study Guide Key terms, people and places Scribe City-state Polytheism Empire Bazaar Myth Monotheism Caravan Sumer Mesopotamia Babylonia Fertile Crescent Hammurabi Euphrates River Cuneiform Famine Tigris River ...
ANCIENT CIVILIZATION UNIT TEST
... Completion: Choose the correct name to complete each sentence: Mesopotamia polytheists ...
... Completion: Choose the correct name to complete each sentence: Mesopotamia polytheists ...
Mesopotamia Notes
... 4. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN HUMANS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT - What do the people do to the environment? What does the environment do for the people? Farmers used water to irrigate their fields. The rivers would flood and deposit silt, small particles of soil, that are good for farming. ...
... 4. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN HUMANS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT - What do the people do to the environment? What does the environment do for the people? Farmers used water to irrigate their fields. The rivers would flood and deposit silt, small particles of soil, that are good for farming. ...
First civilizations
... Akkadians – Northern Mesopotamia The king of the Akkadians was Sargon He conquered ALL of Mesopotamia and established the worlds first empire The empire would last 200 yrs ...
... Akkadians – Northern Mesopotamia The king of the Akkadians was Sargon He conquered ALL of Mesopotamia and established the worlds first empire The empire would last 200 yrs ...
Summary - Junta de Andalucía
... ARCHITECTURE: The Mesopotamians were great constructors. But, due to the fact that they built with brick and cement, there are not many remains left nowadays. They used arcs and vaults. • Temples: owned all the land and they workshops of the city, it was the headquarters of the government, the court ...
... ARCHITECTURE: The Mesopotamians were great constructors. But, due to the fact that they built with brick and cement, there are not many remains left nowadays. They used arcs and vaults. • Temples: owned all the land and they workshops of the city, it was the headquarters of the government, the court ...
Mesopotamian Civilization
... governments, art, religion, class divisions, and a writing system. Rivers were important because they made for good farming conditions. They also made it easy for people to travel and trade. Governments were formed because someone had to make plans and decisions for the common good. Mesopotami ...
... governments, art, religion, class divisions, and a writing system. Rivers were important because they made for good farming conditions. They also made it easy for people to travel and trade. Governments were formed because someone had to make plans and decisions for the common good. Mesopotami ...
Mesopotamia
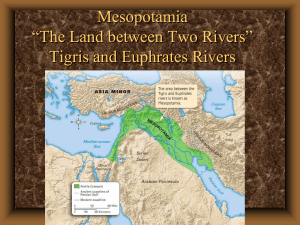
... Mesopotamia = “land between the rivers” In between Tigris and Euphrates River Little rain, needed irrigation Fertile Crescent - area of land where soil was fertile due to flooding ...
... Mesopotamia = “land between the rivers” In between Tigris and Euphrates River Little rain, needed irrigation Fertile Crescent - area of land where soil was fertile due to flooding ...
Chapter 2 Outline - Judson Independent School District
... First cities emerge, 4000 B.C.E. a. Between 3200 and 2350 B.C.E., they evolve into city-states (control of surrounding region) b. Governments sponsor building projects and irrigation c. Attacks by others led to wall building and military development ...
... First cities emerge, 4000 B.C.E. a. Between 3200 and 2350 B.C.E., they evolve into city-states (control of surrounding region) b. Governments sponsor building projects and irrigation c. Attacks by others led to wall building and military development ...
Chapter 3, Section 2 “The Rise of Sumer”
... in a particular task, a division of labor is created. Large projects were undertaken, which led to the need for structure and rules. Settlements grew in size, creating cities between 4000 and 3000 B.C. ...
... in a particular task, a division of labor is created. Large projects were undertaken, which led to the need for structure and rules. Settlements grew in size, creating cities between 4000 and 3000 B.C. ...
File
... Sargon’s soldiers defeated all the city-states of Sumer. They also conquered northern Mesopotamia, finally bringing the entire region under his rule. With these conquests, ____________ established the world’s first ____________, or land with different territories and peoples under a single rule. Thi ...
... Sargon’s soldiers defeated all the city-states of Sumer. They also conquered northern Mesopotamia, finally bringing the entire region under his rule. With these conquests, ____________ established the world’s first ____________, or land with different territories and peoples under a single rule. Thi ...
The Ancient Fertile Crescent
... to development • Traders use the rivers or go overland • Wealth builds Sumerian cities ...
... to development • Traders use the rivers or go overland • Wealth builds Sumerian cities ...
Mesopotamia and Egypt Notes
... Tigris & Euphrates Rivers, present day Iraq • It is also part of the Fertile Crescent • Sumerian City-states began to develop around 3000 B.C.E. (after the Neolithic Revolution) ...
... Tigris & Euphrates Rivers, present day Iraq • It is also part of the Fertile Crescent • Sumerian City-states began to develop around 3000 B.C.E. (after the Neolithic Revolution) ...
Study Guide #2: Mesopotamia
... -These rivers would flow into the ___________ Gulf. -Located in modern day ____________. Framework of Civilization (4 Parts) -Civilization is people living together in _________ societies. Part 1: Large ___________ Communities -These would be called _____/states -Independent cities with fields for _ ...
... -These rivers would flow into the ___________ Gulf. -Located in modern day ____________. Framework of Civilization (4 Parts) -Civilization is people living together in _________ societies. Part 1: Large ___________ Communities -These would be called _____/states -Independent cities with fields for _ ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.