FUNDAMENTALS OF WATER
... one receptacle/40 sft. for first 400 sft. subject to a minimum of one receptacle for every 10 lft. of wall length One receptacle per 100 sft. for area in excess of 400 sft. There shall not be more than 6 receptacles to a 20 A circuit in an office. Corridors should have a 20 A, 120 V receptacle every ...
... one receptacle/40 sft. for first 400 sft. subject to a minimum of one receptacle for every 10 lft. of wall length One receptacle per 100 sft. for area in excess of 400 sft. There shall not be more than 6 receptacles to a 20 A circuit in an office. Corridors should have a 20 A, 120 V receptacle every ...
File - Physical Science
... 3. Induction—Rearrangement of charge of a neutral object caused by a nearby charged object! ...
... 3. Induction—Rearrangement of charge of a neutral object caused by a nearby charged object! ...
Electric Motors
... • Mechatronics may alternatively be referred to as "electromechanical systems" or less often as "control and automation engineering". ...
... • Mechatronics may alternatively be referred to as "electromechanical systems" or less often as "control and automation engineering". ...
Glossary of Terms - Lyncole Grounding
... Main Ground Bar (MGB) - A metal bar, usually mounted in a dominant area of a structure, to which all other bus bars, grounding electrodes and grounding conductors are interconnected or bonded. See also Bus Bar. Mechanical Clamp - A device used to secure a conductor to a grounding element. Usually co ...
... Main Ground Bar (MGB) - A metal bar, usually mounted in a dominant area of a structure, to which all other bus bars, grounding electrodes and grounding conductors are interconnected or bonded. See also Bus Bar. Mechanical Clamp - A device used to secure a conductor to a grounding element. Usually co ...
CH 35 questions for HW
... A/An ____________ circuit cuts off electron flow A/An ___________ circuit allows electrons to flow A gap in a circuit is usually provided by an electric ________________. When connected in __________________, devices in a circuit form branches, each of which is a separate path for the flow of electr ...
... A/An ____________ circuit cuts off electron flow A/An ___________ circuit allows electrons to flow A gap in a circuit is usually provided by an electric ________________. When connected in __________________, devices in a circuit form branches, each of which is a separate path for the flow of electr ...
Low Voltage Power Circuit Breaker
... is to provide protection to circuit components and equipment. A short-time delay (STD) setting on a circuit breaker can negate the function of protecting the circuit components. A low voltage power circuit breaker with a short-time delay and without instantaneous trip, permits a fault to flow for th ...
... is to provide protection to circuit components and equipment. A short-time delay (STD) setting on a circuit breaker can negate the function of protecting the circuit components. A low voltage power circuit breaker with a short-time delay and without instantaneous trip, permits a fault to flow for th ...
Glossary of Terms - Advanced Protection Technologies
... IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) is an international society of engineers that develops its own standards. Impedance - Measured in ohms, impedance is the total opposition to current flow in a circuit where alternating current is flowing. This includes inductive reac ...
... IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) is an international society of engineers that develops its own standards. Impedance - Measured in ohms, impedance is the total opposition to current flow in a circuit where alternating current is flowing. This includes inductive reac ...
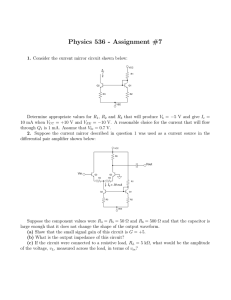
Physics 536 - Assignment #7
... Suppose the component values were R4 = R5 = 50 Ω and R6 = 500 Ω and that the capacitor is large enough that it does not change the shape of the output waveform. (a) Show that the small signal gain of this circuit is G = +5. (b) What is the output impedance of this circuit? (c) If the circuit were co ...
... Suppose the component values were R4 = R5 = 50 Ω and R6 = 500 Ω and that the capacitor is large enough that it does not change the shape of the output waveform. (a) Show that the small signal gain of this circuit is G = +5. (b) What is the output impedance of this circuit? (c) If the circuit were co ...
electrical transients:keeping the enemy out of your facility
... production facility, a shopping mall or a hospital -- are capable of producing magnitudes many times greater than internally generated transients. Lightning: Opposites Attract The most well-known external source of electrical disturbance is lightning. Contrary to what many of us learned in junior hi ...
... production facility, a shopping mall or a hospital -- are capable of producing magnitudes many times greater than internally generated transients. Lightning: Opposites Attract The most well-known external source of electrical disturbance is lightning. Contrary to what many of us learned in junior hi ...
Making an Earth Battery - United Scientific Supplies
... Have students create earth electrodes out of two dissimilar metals. Ask them to hypothesize what soil conditions are best for creating an earth battery. (Suggestions include: swamp or marsh muds, dry sand (no moisture), lawn soils, clay, sandy soils, acid forest soils, salty soils on roadsides after ...
... Have students create earth electrodes out of two dissimilar metals. Ask them to hypothesize what soil conditions are best for creating an earth battery. (Suggestions include: swamp or marsh muds, dry sand (no moisture), lawn soils, clay, sandy soils, acid forest soils, salty soils on roadsides after ...
File
... In most household wiring, the black wires are at 110 volts relative to ground The white wires are at zero volts because they are connected to ground • If you come into contact with an energized (live) black wire, and you are also in contact with the white grounded wire, current will pass through ...
... In most household wiring, the black wires are at 110 volts relative to ground The white wires are at zero volts because they are connected to ground • If you come into contact with an energized (live) black wire, and you are also in contact with the white grounded wire, current will pass through ...
Name - OnCourse
... Batteries contain only a limited amount of the chemicals needed to create this electric field. A battery is “dead” when ______________________________________________ ,_________________________________________________________________ ...
... Batteries contain only a limited amount of the chemicals needed to create this electric field. A battery is “dead” when ______________________________________________ ,_________________________________________________________________ ...