ELECTRICITY
... “oppose” the flow of electrons. -will change electrical energy into thermal energy and/or light. -all materials have some electrical resistance -measured in Ohms ( Ω ) -making wires thinner, longer or hotter increases the resistance. ...
... “oppose” the flow of electrons. -will change electrical energy into thermal energy and/or light. -all materials have some electrical resistance -measured in Ohms ( Ω ) -making wires thinner, longer or hotter increases the resistance. ...
Electricity & Magnetism
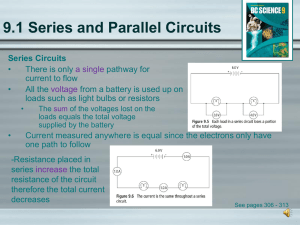
... There are 2 types of circuits: Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
... There are 2 types of circuits: Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. ...
PHY160-4
... number of batteries and electrical devices - That electric current must remain constant at all points in a series circuit - How placement of batteries and electrical devices in a series circuit affects the current ...
... number of batteries and electrical devices - That electric current must remain constant at all points in a series circuit - How placement of batteries and electrical devices in a series circuit affects the current ...
ELECTRICAL SURVEY REPORT
... the switchboard earth bar or terminal is continuous. For boats with an IT a.c. system, a continuously operating earth fault or insulation monitoring and alarm system is installed The main a.c. earthing conductor between the main a.c. switchboard and the boat electrical earth is continuous and the re ...
... the switchboard earth bar or terminal is continuous. For boats with an IT a.c. system, a continuously operating earth fault or insulation monitoring and alarm system is installed The main a.c. earthing conductor between the main a.c. switchboard and the boat electrical earth is continuous and the re ...
Layers of Earth Amazingly Earth is made up of four layers. There is
... Below the crust is the mantle. This is the thickest layer. Rocks can move or flow due to pressure and high temperatures. The mantle is partially molten. There is magnesium, iron, and also oxygen. The next layer is the outer core and it is a totally liquid layer. This layer is made of molten iron and ...
... Below the crust is the mantle. This is the thickest layer. Rocks can move or flow due to pressure and high temperatures. The mantle is partially molten. There is magnesium, iron, and also oxygen. The next layer is the outer core and it is a totally liquid layer. This layer is made of molten iron and ...
gc-10 : parallel path isolator
... • trailing-cable-fed equipment is in contact with the earth. If a ground path through earth parallels the ground conductor in a trailing cable, and if the resistance of the ground path through earth is less than the trip resistance of the ground-conductor monitor, the ground-conductor monitor will ...
... • trailing-cable-fed equipment is in contact with the earth. If a ground path through earth parallels the ground conductor in a trailing cable, and if the resistance of the ground path through earth is less than the trip resistance of the ground-conductor monitor, the ground-conductor monitor will ...
105U-4 / 105S-4 Installation Guide Statutory Requirements
... 105U-4 / 105S-4 Installation Power supply: (A) 12-24VAC 1.5 Amp CSA Certified Class 2 (B) 15-30VDC 1.5 Amp CSA Certified Class 2 (C) 11-15VDC Supply or battery (D) Solar panel with solar battery Choose option and wire as shown ...
... 105U-4 / 105S-4 Installation Power supply: (A) 12-24VAC 1.5 Amp CSA Certified Class 2 (B) 15-30VDC 1.5 Amp CSA Certified Class 2 (C) 11-15VDC Supply or battery (D) Solar panel with solar battery Choose option and wire as shown ...
BASIC ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (ELE 101/102)
... A 200 V, 50 Hz single phase supply is given to a series circuit comprising of a resistance of 50 and an inductive coil having an internal resistance ‘r’ and inductance ‘L’. The current through the circuit is 1.5 A which consumes a power of 135 Watts. Calculate (i) Values of ‘r’ and ‘L’, (ii) Voltage ...
... A 200 V, 50 Hz single phase supply is given to a series circuit comprising of a resistance of 50 and an inductive coil having an internal resistance ‘r’ and inductance ‘L’. The current through the circuit is 1.5 A which consumes a power of 135 Watts. Calculate (i) Values of ‘r’ and ‘L’, (ii) Voltage ...
ce-b36 metal clad - Casagrande Elettrocostruzioni SpA
... circuit making current when close to under load. The speed of the snap action closing operation is independent of controls. A manual switch operating lever is provided on the front of the switchbord. The device is provided with auxiliary switches for signalling the open and closed positions. ...
... circuit making current when close to under load. The speed of the snap action closing operation is independent of controls. A manual switch operating lever is provided on the front of the switchbord. The device is provided with auxiliary switches for signalling the open and closed positions. ...
Introduction to Switchgear
... circuit under all conditions viz. no load, full load and fault conditions. The Circuit breaker only can isolate the faulty part from healthy section. Relays: A relay is a device which detects the fault and supplies information to the breaker for circuit interruption. ...
... circuit under all conditions viz. no load, full load and fault conditions. The Circuit breaker only can isolate the faulty part from healthy section. Relays: A relay is a device which detects the fault and supplies information to the breaker for circuit interruption. ...
intake structures uptake 316(b) regulations
... Assume a 15 kV circuit breaker with both phase and ground relay protection (residual connection) in the example above is the protective device for the relevant circuit. If the circuit breaker inside the switchgear is programmed for 480 amp phase setting and 120 amp ground setting, the circuit breake ...
... Assume a 15 kV circuit breaker with both phase and ground relay protection (residual connection) in the example above is the protective device for the relevant circuit. If the circuit breaker inside the switchgear is programmed for 480 amp phase setting and 120 amp ground setting, the circuit breake ...
practice questions and answers
... 10. A device operating at a potential difference of 1.5 volts draws a current of 0.20 ampere. How much energy is used by the device in 60. seconds? (1) 4.5 J (3) 12 J (2) 8.0 J (4) 18 J 11. How much electrical energy is required to move a 4.00microcoulomb charge through a potential difference of 36. ...
... 10. A device operating at a potential difference of 1.5 volts draws a current of 0.20 ampere. How much energy is used by the device in 60. seconds? (1) 4.5 J (3) 12 J (2) 8.0 J (4) 18 J 11. How much electrical energy is required to move a 4.00microcoulomb charge through a potential difference of 36. ...