105U-2, 105S-2 Installation Guide Statutory Requirements
... EC: Unlicensed operation limits the radio power. High gain aerials may only be used to compensate for cable losses. ...
... EC: Unlicensed operation limits the radio power. High gain aerials may only be used to compensate for cable losses. ...
RCCB-ID B type - Schneider Electric
... protection of persons against electric shock by direct contact (30 mA), protection of persons against electric shock by indirect contact (u 300 mA), protection of installations against the risk of fire (300 mA or 500 mA). ...
... protection of persons against electric shock by direct contact (30 mA), protection of persons against electric shock by indirect contact (u 300 mA), protection of installations against the risk of fire (300 mA or 500 mA). ...
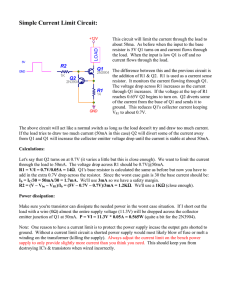
6. 8. A 10. A Summing up power supply load conducting
... 5. Electrical resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for electric charge to flow through part of a circuit. 6. Conductors of electricity have very little resistance. 7. In metallic conductors, as long as the temperature remains fairly constant, a graph of voltage drop versus electri ...
... 5. Electrical resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for electric charge to flow through part of a circuit. 6. Conductors of electricity have very little resistance. 7. In metallic conductors, as long as the temperature remains fairly constant, a graph of voltage drop versus electri ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... More than one resistor in multiple paths Electrons may go through any path More electrons will go through path with less resistance Overall resistance goes down because more than one electron can get through at once ...
... More than one resistor in multiple paths Electrons may go through any path More electrons will go through path with less resistance Overall resistance goes down because more than one electron can get through at once ...
An Explanation of Discrimination
... Circuit protection whether by fuse, circuit breaker or relays cannot prevent faults from occurring, however they can limit the damage that could occur if the fault current was allowed to continue to flow. When considering the co-ordination of circuit protection devices, we must not lose sight of the ...
... Circuit protection whether by fuse, circuit breaker or relays cannot prevent faults from occurring, however they can limit the damage that could occur if the fault current was allowed to continue to flow. When considering the co-ordination of circuit protection devices, we must not lose sight of the ...
Electrical
... • Disclaimer: Some of the photos or videos used in this presentation are from numerous sources, most of which are not identifiable. We do not claim any ownership of these videos. Not do we have any association with the owners. And only use them to illustrate the concepts of our safety programs. If ...
... • Disclaimer: Some of the photos or videos used in this presentation are from numerous sources, most of which are not identifiable. We do not claim any ownership of these videos. Not do we have any association with the owners. And only use them to illustrate the concepts of our safety programs. If ...
Electric Hazards Homework
... 11. Foolishly trying to fish a burning piece of bread from a toaster with a metal butter knife, a man comes into contact with 120-V AC. He does not even feel it since, luckily, he is wearing rubber-soled shoes. What is the minimum resistance of the path the current follows through the person? (OpenS ...
... 11. Foolishly trying to fish a burning piece of bread from a toaster with a metal butter knife, a man comes into contact with 120-V AC. He does not even feel it since, luckily, he is wearing rubber-soled shoes. What is the minimum resistance of the path the current follows through the person? (OpenS ...
Benefits of Memristor
... maintains a functional relationship between the time integrals of current and voltage. ...
... maintains a functional relationship between the time integrals of current and voltage. ...