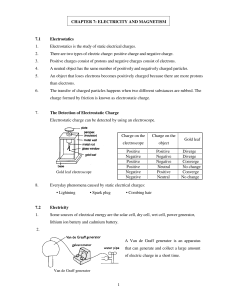
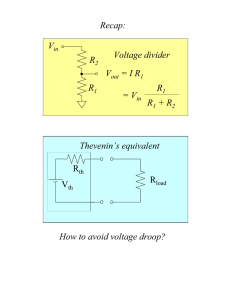
1 CHAPTER 7: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 7.1
... b. Inserting a laminated iron bar into the solenoid. c. Increasing the current flow. ...
... b. Inserting a laminated iron bar into the solenoid. c. Increasing the current flow. ...
Name_______________________Test Date
... In a parallel circuit, each bulb has its own pathway to the power source. For example, Christmas lights that remain lit when one bulb goes out is an example of a parallel circuit. A series circuit can have more than one receiver but all receivers will turn off when the wires are disconnected from th ...
... In a parallel circuit, each bulb has its own pathway to the power source. For example, Christmas lights that remain lit when one bulb goes out is an example of a parallel circuit. A series circuit can have more than one receiver but all receivers will turn off when the wires are disconnected from th ...
ILSCOPedia \ Electrical Industry Terminology
... SCCR (Short Circuit Current Rating) – Some connectors may say High SCCR. SERIES CIRCUIT - A circuit arrangement of two or more loads (or sources) connected end-to-end only allowing for one current path. Therefore, all components have the same current but can have different voltage. An open at any po ...
... SCCR (Short Circuit Current Rating) – Some connectors may say High SCCR. SERIES CIRCUIT - A circuit arrangement of two or more loads (or sources) connected end-to-end only allowing for one current path. Therefore, all components have the same current but can have different voltage. An open at any po ...
Electrical Chapter 1 Notes Name: Period__________ 1. The
... 1. The ________________ structure of an ___________ includes three basic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. 2. An electrical _____________________ is a material that contains free electrons and easily conducts electrical current. Copper is an excellent conductor used in automotive wiring. ...
... 1. The ________________ structure of an ___________ includes three basic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. 2. An electrical _____________________ is a material that contains free electrons and easily conducts electrical current. Copper is an excellent conductor used in automotive wiring. ...
CirCuits
... voltage is required to have the same current As current increases, resistance increases because the light bulb heats up Voltage ...
... voltage is required to have the same current As current increases, resistance increases because the light bulb heats up Voltage ...
Chapter 17 Section 1 1. Describe how an object is charged by
... cannot determine the type of charge (positive or negative) the object has. Explain why not. a. Like charges repel, but repulsion does not indicate what charge is involved. Therefore, the electroscope will behave the same, regardless of an object’s charge. 1. What is static electricity? Give an examp ...
... cannot determine the type of charge (positive or negative) the object has. Explain why not. a. Like charges repel, but repulsion does not indicate what charge is involved. Therefore, the electroscope will behave the same, regardless of an object’s charge. 1. What is static electricity? Give an examp ...
Distributed Generation at Clemson University
... • If DG is solidly grounded, voltage rise of healthy phases for single-phase faults can be less severe, but single-phase currents can increase drastically. • If DG is grounded through impedance, single-phase fault currents would get less severe, but voltage rise of healthy phases can get worse. • Fo ...
... • If DG is solidly grounded, voltage rise of healthy phases for single-phase faults can be less severe, but single-phase currents can increase drastically. • If DG is grounded through impedance, single-phase fault currents would get less severe, but voltage rise of healthy phases can get worse. • Fo ...
Definitions
... The statement which defines the Company's standard electric services, the rates for such services, and the rules and regulations governing the supply of such electric services, on file with, and accepted by, the State where electric service is offered. 2.37 THREE PHASE CIRCUIT A combination of circu ...
... The statement which defines the Company's standard electric services, the rates for such services, and the rules and regulations governing the supply of such electric services, on file with, and accepted by, the State where electric service is offered. 2.37 THREE PHASE CIRCUIT A combination of circu ...
Earth Fault Loop Impedance Testing For Traffic Signal Installations
... metres above ground level, for termination of low level lanterns. The box shall be a standard waterproof type with minimum dimensions of 305 mm x 160 mm x 160 mm and be made of aluminium or polycarbonate box and have rating of IP65. The terminal assembly box shall be fixed to the pole with a minimum ...
... metres above ground level, for termination of low level lanterns. The box shall be a standard waterproof type with minimum dimensions of 305 mm x 160 mm x 160 mm and be made of aluminium or polycarbonate box and have rating of IP65. The terminal assembly box shall be fixed to the pole with a minimum ...
A Method to Enhance Ground
... line-to-ground (DLG), and three-phase short-circuit (3SC). Among these types of faults, the SLG occurs most often while the 3SC is commonly deemed the most severe one with largest magnitude of fault current, significantly influencing the decision on the equipments and protective relays setting for p ...
... line-to-ground (DLG), and three-phase short-circuit (3SC). Among these types of faults, the SLG occurs most often while the 3SC is commonly deemed the most severe one with largest magnitude of fault current, significantly influencing the decision on the equipments and protective relays setting for p ...
Electricity (1)
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...