* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bus-bars of Substations Bus-bars
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
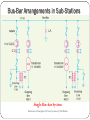
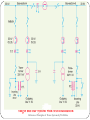
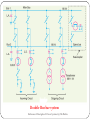
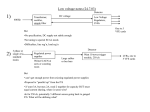
Bus bars in a Sub Station Bus-bars of Substations Bus-bars • Bus-bars are used as the common electrical point where a number of lines operating at same voltage are electrically connected directly • The bus-bar operates at constant voltage and the incoming and outgoing lines in a substations are connected to the bus-bars • Types of bus-bar arrangement (i) Single bus-bar (ii) Double bus-bar (ii) Single bus-bar system with sectionalisation 11 Bus-Bar Arrangements in Sub-Stations Single Bus-bar System Reference: Principles of Power Systems by V K Mehta Single Bus-bar System • It consists of a single bus-bar and incoming and outgoing lines are connected to it. They are often used for 11 kV indoor substation and are not used for voltages exceeding 33 kV • They have initial low cost, less maintenance, and simple operation • If repair has to be done the power supply is interrupted Single bus-bar System with Sectionalisation Reference: Principles of Power Systems by V K Mehta Single bus-bar System with Sectionalisation • The single bus-bar is divided into sections and load is equally distributed on all sections. Any two sections of the bus bar are connected by a circuit breaker • If the fault occurs on any section of the bus, that section can be isolated without affecting the supply from other sections. Double Bus bar system Reference: Principles of Power Systems by V K Mehta Double Bus bar system This system consists of two bus-bars, a “main” bus-bar and a “spare” bus-bar. Each bus-bar has the capacity to take up the entire sub-station load. The incoming and outgoing lines can be connected to either busbar with the help of a bus-bar coupler which consists of a circuit breaker and isolators. Ordinarily, the incoming and outgoing lines remain connected to the main bus-bar. However, in case of repair of main bus-bar or fault occuring on it, the continuity of supply to the circuit can be maintained by transferring it to the spare bus-bar. For voltages exceeding 33kV, double bus-bar system is frequently used. Key Diagram of 66/11 kV Sub-Station Reference: Principles of Power Systems by V K Mehta Key Diagram of 11 kV/400 V Indoor Sub-Station Reference: Principles of Power Systems by V K Mehta