Parallel Faults on DC Microgrids - The University of Texas at Austin
... an order of magnitude longer in duration, and often damaged electrode structures, locally. ...
... an order of magnitude longer in duration, and often damaged electrode structures, locally. ...
Study Guide for the test on Electricity and Magnetism. Name Atoms
... The type of circuit allows electricity to flow through only one path is ____________________. The type of circuit that is typically used in homes and businesses is _________________. The type of circuit that allows electricity to flow in more than one path is _______________. The equation for power ...
... The type of circuit allows electricity to flow through only one path is ____________________. The type of circuit that is typically used in homes and businesses is _________________. The type of circuit that allows electricity to flow in more than one path is _______________. The equation for power ...
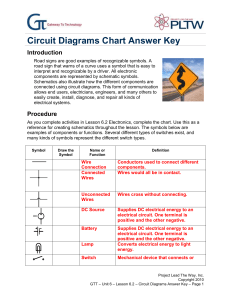
Circuit Diagrams Chart Answer Key
... Road signs are good examples of recognizable symbols. A road sign that warns of a curve uses a symbol that is easy to interpret and recognizable by a driver. All electronic components are represented by schematic symbols. Schematics also illustrate how the different components are connected using ci ...
... Road signs are good examples of recognizable symbols. A road sign that warns of a curve uses a symbol that is easy to interpret and recognizable by a driver. All electronic components are represented by schematic symbols. Schematics also illustrate how the different components are connected using ci ...
Electricity Review final - Hutchison
... c) _____ unlike charges repel one another d) _____ unlike charges attract one another 3. What particles are lost and gained when working with static electricity? ________________________ 4. Why do two different substances build up static charges when rubbed together? ________________________________ ...
... c) _____ unlike charges repel one another d) _____ unlike charges attract one another 3. What particles are lost and gained when working with static electricity? ________________________ 4. Why do two different substances build up static charges when rubbed together? ________________________________ ...
wel come to coe rac sector - ITI College
... current, a source of electrical energy is required. The torch battery is a source of electrical energy. The battery is said to have an E.M.F. which is available to drive the free electrons in the closed path in electrical circuit. The diff. in the distribution of electrons between the two terminal o ...
... current, a source of electrical energy is required. The torch battery is a source of electrical energy. The battery is said to have an E.M.F. which is available to drive the free electrons in the closed path in electrical circuit. The diff. in the distribution of electrons between the two terminal o ...
Chapter 7 - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... • The parts of a series circuit are wired one after another, so the amount of current is the same through every point. • Open circuit- if any part of a circuit is disconnected. No current flows through the circuit. For example- Christmas lights ...
... • The parts of a series circuit are wired one after another, so the amount of current is the same through every point. • Open circuit- if any part of a circuit is disconnected. No current flows through the circuit. For example- Christmas lights ...
Microcontroller based substation monitoring and control system
... The purpose of this project is to monitor and control various electrical devices within the substation. The parameters that will be monitored include the voltage, current, frequency and circuit breaker status. It can be extended to monitor the Transformer temperature. It also trips the circuit break ...
... The purpose of this project is to monitor and control various electrical devices within the substation. The parameters that will be monitored include the voltage, current, frequency and circuit breaker status. It can be extended to monitor the Transformer temperature. It also trips the circuit break ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... you rub two substances together you do work and thus you add energy. This removes electrons from one substance and adds it to the other. ...
... you rub two substances together you do work and thus you add energy. This removes electrons from one substance and adds it to the other. ...
Document
... electrons are rubbed loose from some atoms creating a positive charge, while other atoms gain electrons, creating a negative charge. Opposites attract--positive and negative charges attract each other creating static cling. When objects (such as your finger) are charged and then touch another object ...
... electrons are rubbed loose from some atoms creating a positive charge, while other atoms gain electrons, creating a negative charge. Opposites attract--positive and negative charges attract each other creating static cling. When objects (such as your finger) are charged and then touch another object ...
REVIEW SHEET – ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
... 12. a) How is an ammeter connected into a circuit? b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...
... 12. a) How is an ammeter connected into a circuit? b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...