Earthing
... • To protect buildings, machinery & appliances under fault conditions ie. To ensure that all exposed conductive parts do not reach a dangerous potential. • To provide safe path to dissipate lightning and short circuit currents. • To provide stable platform for operation of sensitive electronic equip ...
... • To protect buildings, machinery & appliances under fault conditions ie. To ensure that all exposed conductive parts do not reach a dangerous potential. • To provide safe path to dissipate lightning and short circuit currents. • To provide stable platform for operation of sensitive electronic equip ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... current is complete and unbroken. An open circuit is one in which the pathway of the electrical current is broken. A switch is a device in the circuit in which the circuit can be closed (turned on) or open (turned off). ...
... current is complete and unbroken. An open circuit is one in which the pathway of the electrical current is broken. A switch is a device in the circuit in which the circuit can be closed (turned on) or open (turned off). ...
Question 3 - cloudfront.net
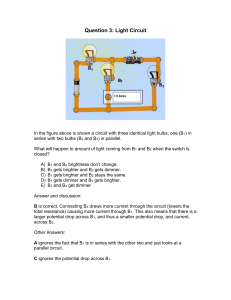
... total resistance) causing more current through B1. This also means that there is a larger potential drop across B1, and thus a smaller potential drop, and current, across B2. Other Answers: A ignores the fact that B1 is in series with the other two and just looks at a parallel circuit. C ignores the ...
... total resistance) causing more current through B1. This also means that there is a larger potential drop across B1, and thus a smaller potential drop, and current, across B2. Other Answers: A ignores the fact that B1 is in series with the other two and just looks at a parallel circuit. C ignores the ...
Electrical engineering presentation
... • Wires rigidly anchored at both ends of the wire run • Tension in the wire varies with temperature • Wire sags down at high temperatures – Regulated Tension • Tension is the wire is held approximately constant ...
... • Wires rigidly anchored at both ends of the wire run • Tension in the wire varies with temperature • Wire sags down at high temperatures – Regulated Tension • Tension is the wire is held approximately constant ...
Electricity
... • Generators: device that spins coiled wire within a magnetic field producing electricity by transferring heat energy to mechanical energy – The mechanical energy of a spinning turbine is transformed into electrical energy for human use – Primary method for producing the electricity in homes, school ...
... • Generators: device that spins coiled wire within a magnetic field producing electricity by transferring heat energy to mechanical energy – The mechanical energy of a spinning turbine is transformed into electrical energy for human use – Primary method for producing the electricity in homes, school ...
Static electricity
... Static electricity occurs when an object that has negatively charged particles meets an object with positively charged particles . There are also objects that are electrically neutral , meaning that they have the same number of positive and negative charges . Rubbing is a way to create static electr ...
... Static electricity occurs when an object that has negatively charged particles meets an object with positively charged particles . There are also objects that are electrically neutral , meaning that they have the same number of positive and negative charges . Rubbing is a way to create static electr ...
city of surrey electrical inspection report for primary unit substations
... Step & touch voltages (signed and sealed letter required from P. Eng.) Grounding requirements for water, sprinkler, waste, etc. Ground pad location and identification (each conductor connected to ground pad to be identified in a permanent manner) A Field Review report from the design engineer is to ...
... Step & touch voltages (signed and sealed letter required from P. Eng.) Grounding requirements for water, sprinkler, waste, etc. Ground pad location and identification (each conductor connected to ground pad to be identified in a permanent manner) A Field Review report from the design engineer is to ...
Future developments in the IEE Wiring Regulations
... disconnect the electrical supply when an imbalance is detected between live conductors. In the case of a single-phase circuit, the device monitors the difference in currents between the line and neutral conductors. If a line to earth fault develops, a portion of the line conductor current will not r ...
... disconnect the electrical supply when an imbalance is detected between live conductors. In the case of a single-phase circuit, the device monitors the difference in currents between the line and neutral conductors. If a line to earth fault develops, a portion of the line conductor current will not r ...
Electrical Circuits - WHSFreshmanScience
... • Negative charges are attracted to positive charges the same way mice are attracted to cheese. – Any time there is a natural attraction between two things we can use it to make the objects do work. – The negative charges (mice) will gladly do work in order to get to the positive charges (cheese). ...
... • Negative charges are attracted to positive charges the same way mice are attracted to cheese. – Any time there is a natural attraction between two things we can use it to make the objects do work. – The negative charges (mice) will gladly do work in order to get to the positive charges (cheese). ...