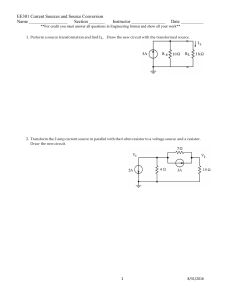
EE301 Current Sources and Source Conversion Name
... 1. Perform a source transformation and find IL. Draw the new circuit with the transformed source. ...
... 1. Perform a source transformation and find IL. Draw the new circuit with the transformed source. ...
Fluid flow analogy
... 7-2 The natural response of an RC circuit • An RC circuit is analogous to an RL circuit • The switch has been in the position for a long time such that all the elements in the circuit reach a steady-state condition . • A source voltage exists between the terminals. • Circuit after switching is show ...
... 7-2 The natural response of an RC circuit • An RC circuit is analogous to an RL circuit • The switch has been in the position for a long time such that all the elements in the circuit reach a steady-state condition . • A source voltage exists between the terminals. • Circuit after switching is show ...
SNC1P - MsKhan
... 13.3 - Electric Current Electric current (I) is the rate of electron flow at any point in a circuit. It is measured in ________________ (A) by an ammeter. An ammeter is connected in series with the load to measure the current flowing through the load. If there is too much current flowing through a c ...
... 13.3 - Electric Current Electric current (I) is the rate of electron flow at any point in a circuit. It is measured in ________________ (A) by an ammeter. An ammeter is connected in series with the load to measure the current flowing through the load. If there is too much current flowing through a c ...
Electrical shock
... continuous or System Ground – primarily designed to protect machines and tools against damage ...
... continuous or System Ground – primarily designed to protect machines and tools against damage ...
Protection of the People and Equipments in the Electric
... covering of insulating material such as rubber or plastic. -protective earthling: hazardous electrical paths are enclosed in a conductive housing which is then connected to earth by a separate conductor. -separation: human contact with conductor is prevented by physical separation, enforced by physi ...
... covering of insulating material such as rubber or plastic. -protective earthling: hazardous electrical paths are enclosed in a conductive housing which is then connected to earth by a separate conductor. -separation: human contact with conductor is prevented by physical separation, enforced by physi ...
startco - ElectricalManuals.net
... The SE-105 is a combination ground-fault and ground-check monitor for resistance-grounded systems in non-hazardous applications. The ground-fault circuit is latching and the ground-check circuit is typically non-latching. One output contact is provided for contactor control, or for shunt or undervol ...
... The SE-105 is a combination ground-fault and ground-check monitor for resistance-grounded systems in non-hazardous applications. The ground-fault circuit is latching and the ground-check circuit is typically non-latching. One output contact is provided for contactor control, or for shunt or undervol ...
PS1: Overcurrent Protection of a Substation Power Transformer
... using the computers available in the lab. Students can conduct the experiments at any time as long as the lab is available. Reports are due at the specified date. Preparation of the report: The report must include the following: A brief introduction to the hydrothermal coordination problem The M ...
... using the computers available in the lab. Students can conduct the experiments at any time as long as the lab is available. Reports are due at the specified date. Preparation of the report: The report must include the following: A brief introduction to the hydrothermal coordination problem The M ...
Electrical Circuits
... What is an electric circuit? An electric circuit is a path for electric charge to flow along. Like all electrical devices, this portable MP3 player contains electric circuits to enable it to play music. What is needed for an electric circuit to work? source of energy ...
... What is an electric circuit? An electric circuit is a path for electric charge to flow along. Like all electrical devices, this portable MP3 player contains electric circuits to enable it to play music. What is needed for an electric circuit to work? source of energy ...
WordWise
... 1. A property that causes subatomic particles such as protons and electrons to attract or repel other matter 2. The attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects 3. Charge transfer without contact between materials 4. Law that total charge in an isolated system is constant 5. A contin ...
... 1. A property that causes subatomic particles such as protons and electrons to attract or repel other matter 2. The attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects 3. Charge transfer without contact between materials 4. Law that total charge in an isolated system is constant 5. A contin ...
AT-6000 GDS Ground Fault Detection System
... The system detects the occurrence of ground fault leakage current between the generator field circuit and rotor ground, and transmits a good/bad fault determination (based upon a fixed leakage current threshold) from the rotor transmitter to the non-rotating receiver. Note: Although the AT-6000 is a ...
... The system detects the occurrence of ground fault leakage current between the generator field circuit and rotor ground, and transmits a good/bad fault determination (based upon a fixed leakage current threshold) from the rotor transmitter to the non-rotating receiver. Note: Although the AT-6000 is a ...
ELG4125: Symmetrical Faults
... momentary power outages but, more important, if a protective action is not taken, can cause permanent damage to transmission equipment such as the transmission line itself and/or the transformer. ...
... momentary power outages but, more important, if a protective action is not taken, can cause permanent damage to transmission equipment such as the transmission line itself and/or the transformer. ...
generators - ingles-escrito-uah-08
... An electric network is excited when there is an answer, that means, there are currents on the electric branches and voltage on its branch points. ...
... An electric network is excited when there is an answer, that means, there are currents on the electric branches and voltage on its branch points. ...
Electric Motors - MSU College of Engineering
... • Mechatronics may alternatively be referred to as "electromechanical systems" or less often as "control and automation engineering". ...
... • Mechatronics may alternatively be referred to as "electromechanical systems" or less often as "control and automation engineering". ...
electric circuits 2 and 3
... 1. A television runs on 120 volts and has a resistance of 60 ohms. What current does it draw? 2. A television remote control uses a current of 0.04 Amps when the power button is pressed. The resistance inside the remote is 75 Ω. What battery voltage is needed to make the remote work? 3. A hair dryer ...
... 1. A television runs on 120 volts and has a resistance of 60 ohms. What current does it draw? 2. A television remote control uses a current of 0.04 Amps when the power button is pressed. The resistance inside the remote is 75 Ω. What battery voltage is needed to make the remote work? 3. A hair dryer ...
Episode 100
... Most students will be familiar with concepts of charge, current and voltage from their previous work at pre-16 level. However, these ideas are often muddled and this can be a real obstacle to progress so it is well worth reinforcing simple ideas and providing basic training in the use of ammeters, v ...
... Most students will be familiar with concepts of charge, current and voltage from their previous work at pre-16 level. However, these ideas are often muddled and this can be a real obstacle to progress so it is well worth reinforcing simple ideas and providing basic training in the use of ammeters, v ...