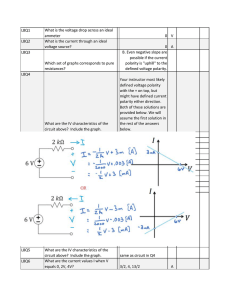
LOVOS-5 LOVOS-10 Low voltage surge arrester
... As results from statistical data (Fig. above) 90% of lightning currents have values not greater than 60 kA. In the overhead low voltage network a lightning stroke in the line usually leads to shock of all three phases due to small distances between conductors. Assuming that the lightning current flo ...
... As results from statistical data (Fig. above) 90% of lightning currents have values not greater than 60 kA. In the overhead low voltage network a lightning stroke in the line usually leads to shock of all three phases due to small distances between conductors. Assuming that the lightning current flo ...
PPT - School of Engineering and Applied Science
... • Decreased supply voltage: As supply voltage is reduced, the charge stored will be small. With larger subthreshold leakage current, coupling noise etc is will be a challenge to get circuits to operate properly. • Increased role of wiring resistance, inductance and capacitance. ...
... • Decreased supply voltage: As supply voltage is reduced, the charge stored will be small. With larger subthreshold leakage current, coupling noise etc is will be a challenge to get circuits to operate properly. • Increased role of wiring resistance, inductance and capacitance. ...
Name MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series
... A kilowatt is used to measure large amounts of electrical power. A kilowatt is equal to 1,000 watts, so the hair dryer uses 1,200 watts or 1.2 kilowatts of power. Directions: Try these problems using the information and formula from the top part of this sheet. (Give your answers in watts or kilowatt ...
... A kilowatt is used to measure large amounts of electrical power. A kilowatt is equal to 1,000 watts, so the hair dryer uses 1,200 watts or 1.2 kilowatts of power. Directions: Try these problems using the information and formula from the top part of this sheet. (Give your answers in watts or kilowatt ...
TD62M4501FG
... The absolute maximum rating of a semiconductor device are a set of specified parameter values that must not be exceeded during operation, even for an instant. If any of these ratings are exceeded during operation, the electrical characteristics of the device may be irreparably altered and the reliab ...
... The absolute maximum rating of a semiconductor device are a set of specified parameter values that must not be exceeded during operation, even for an instant. If any of these ratings are exceeded during operation, the electrical characteristics of the device may be irreparably altered and the reliab ...
Summary: Advanced Connections Questions
... Summary: Advanced Connections Questions 1. Many flashlights use two D-cells. Are the D-cells used in series or in parallel with the light bulb? Why? a. Flashlights use series circuits because voltage adds, so series D-cells provides more current, thus more light. 2. Would you recommend wiring string ...
... Summary: Advanced Connections Questions 1. Many flashlights use two D-cells. Are the D-cells used in series or in parallel with the light bulb? Why? a. Flashlights use series circuits because voltage adds, so series D-cells provides more current, thus more light. 2. Would you recommend wiring string ...
Power System Protection
... A systematic study of current responsive devices in an electrical power system. ...
... A systematic study of current responsive devices in an electrical power system. ...
Download the Quiz
... Which of the following is good practice for lightning protection grounds? A. They must be bonded to all buried water and gas lines B. Bends in ground wires must be made as close as possible to a right angle C. Lightning grounds must be connected to all ungrounded wiring D. They must be bonded togeth ...
... Which of the following is good practice for lightning protection grounds? A. They must be bonded to all buried water and gas lines B. Bends in ground wires must be made as close as possible to a right angle C. Lightning grounds must be connected to all ungrounded wiring D. They must be bonded togeth ...