* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
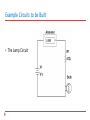
Download Week 3
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup