The Beliefs of Hinduism
... Maya (Illusion) • Which is real and which is illusion? • There is no correct answer—faces or chalices—because both possibilities can be seen. • Maya, or illusion, keeps us from knowing the truth. • For Hindus, maya keeps a person from seeing the divine oneness (Brahman) that surges through all thin ...
... Maya (Illusion) • Which is real and which is illusion? • There is no correct answer—faces or chalices—because both possibilities can be seen. • Maya, or illusion, keeps us from knowing the truth. • For Hindus, maya keeps a person from seeing the divine oneness (Brahman) that surges through all thin ...
IntrotoVedantaPhilosophy
... • Vedanta, then, also means “end of the Veda,” and in this sense can refer technically to the final sections of the four-fold Vedas, the so-called Upanishads (600 – 300 BCE) ...
... • Vedanta, then, also means “end of the Veda,” and in this sense can refer technically to the final sections of the four-fold Vedas, the so-called Upanishads (600 – 300 BCE) ...
Studying Latin American Philosophy
... First figure out what is the main question that the philosopher is addressing. Usually the best place to find this is in the title but sadly…not always. Then look for a thesis statement that gives you some clue where that philosopher wants to take you. Some philosophers are kind enough to use certai ...
... First figure out what is the main question that the philosopher is addressing. Usually the best place to find this is in the title but sadly…not always. Then look for a thesis statement that gives you some clue where that philosopher wants to take you. Some philosophers are kind enough to use certai ...
document
... – Some are Mashevara, Lord of Knowldedge. – Mahakala, Lord of time. • His city is Varanasi and anyone who dies there will go straight through death to Shiva. – Even if they are burdened by bad Karma • Shiva is often worshiped through the linga (male energy surrounded by the Yoni, the female source o ...
... – Some are Mashevara, Lord of Knowldedge. – Mahakala, Lord of time. • His city is Varanasi and anyone who dies there will go straight through death to Shiva. – Even if they are burdened by bad Karma • Shiva is often worshiped through the linga (male energy surrounded by the Yoni, the female source o ...
Becky Clay Dr. Doug Deaver 4-14
... conclusions. If one did agree that the components of reasoning were in accordance with reason and logic, it would likely be found that they believe being rational to be a “good” thing. On the contrary, if one did not believe that the components of reasoning were in accordance with reason and logic, ...
... conclusions. If one did agree that the components of reasoning were in accordance with reason and logic, it would likely be found that they believe being rational to be a “good” thing. On the contrary, if one did not believe that the components of reasoning were in accordance with reason and logic, ...
Yoga is one of our ancient Hindu sciences given to us by our
... Yoga is one of our ancient Hindu sciences given to us by our ancestors. It is a way of life and not just a few postures, meditation and breathing techniques. Yoga has originated from the ancient Hindu Scripture – Veda. The meaning of Veda is Gnaana or Knowledge. Sage Patanjali, has hand picked secti ...
... Yoga is one of our ancient Hindu sciences given to us by our ancestors. It is a way of life and not just a few postures, meditation and breathing techniques. Yoga has originated from the ancient Hindu Scripture – Veda. The meaning of Veda is Gnaana or Knowledge. Sage Patanjali, has hand picked secti ...
Name: PHI ISL – Introduction to Philosophy Ancient Philosophy
... starting point of Aristotle's metaphysics is his rejection of Plato's Theory of Forms. In Plato's theory, material objects are changeable and not real in themselves; rather, they correspond to an ideal, eternal, and immutable Form by a common name, and this Form can be perceived only by the intellec ...
... starting point of Aristotle's metaphysics is his rejection of Plato's Theory of Forms. In Plato's theory, material objects are changeable and not real in themselves; rather, they correspond to an ideal, eternal, and immutable Form by a common name, and this Form can be perceived only by the intellec ...
Hinduism
... Not many things have endured without interruption or major transformation for over 5,000 years. Hindu traditions such as these are great exceptions. Some say Hinduism is the oldest religion on Earth. One Faith, Many Paths Hinduism stands apart from all other religions for several reasons. It has no ...
... Not many things have endured without interruption or major transformation for over 5,000 years. Hindu traditions such as these are great exceptions. Some say Hinduism is the oldest religion on Earth. One Faith, Many Paths Hinduism stands apart from all other religions for several reasons. It has no ...
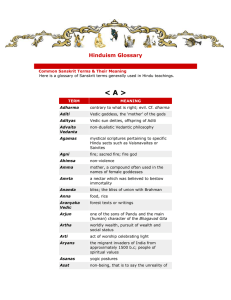
Hinduism Glossary - Vishva Shakti Durga Mandir
... existence, associated with the dissolver God Shiva and representing the quality of darkness and inertia in existence ...
... existence, associated with the dissolver God Shiva and representing the quality of darkness and inertia in existence ...
General principles of the philosophy East and West
... The main principles of Confucianism “Zhen” – “What do not wish for yourself, do not do to others” “Lee” – respectfulness. “Educated person makes demands to themselves, but inferior person makes demands to others”. “Cheng-min” – correction of names. “Everyone has to behave according to his own knowle ...
... The main principles of Confucianism “Zhen” – “What do not wish for yourself, do not do to others” “Lee” – respectfulness. “Educated person makes demands to themselves, but inferior person makes demands to others”. “Cheng-min” – correction of names. “Everyone has to behave according to his own knowle ...
PHILOSOPHY
... Do we have free will or are all our actions already determined for us? Is there a God? How do we know that the world we live in is real and not an illusion? Do ‘I’ exist and if so what am I? What does it mean to be a human? Are there really such things as good and evil? What is the best way to organ ...
... Do we have free will or are all our actions already determined for us? Is there a God? How do we know that the world we live in is real and not an illusion? Do ‘I’ exist and if so what am I? What does it mean to be a human? Are there really such things as good and evil? What is the best way to organ ...
A Study of Brahman
... beyond our intelligence and dreams. Then how can It be explained to the satisfaction of an intellectual and curious mind? The Rig Vedic seers themselves had this problem in their mind when they called Him vaguely as "IT" or "This" or "That". Know from this article why it is so difficult for the huma ...
... beyond our intelligence and dreams. Then how can It be explained to the satisfaction of an intellectual and curious mind? The Rig Vedic seers themselves had this problem in their mind when they called Him vaguely as "IT" or "This" or "That". Know from this article why it is so difficult for the huma ...
NAME: ENANG-EZEH FUNYI ADIAH DEPARTMENT: COMPUTER
... Epistemology identifies five major problems which are analytic problem, demarcations which is divided into internal and external problems. The third problem is method while the last is scepticism. Finally, in epistemology there is the problem of value which considers whether knowledge is worth havin ...
... Epistemology identifies five major problems which are analytic problem, demarcations which is divided into internal and external problems. The third problem is method while the last is scepticism. Finally, in epistemology there is the problem of value which considers whether knowledge is worth havin ...
Popular Hinduism
... Three “Heterodox” systems: Jainism, Buddhism, Carvaka (materialism) – These systems do not accept the authority of the Vedas (fundamental in Hism) – Interestingly, the Buddha is accepted as one of the avatars of Vishnu – [True Father could also be accepted as an avatar – The Kalkin Avatar] ...
... Three “Heterodox” systems: Jainism, Buddhism, Carvaka (materialism) – These systems do not accept the authority of the Vedas (fundamental in Hism) – Interestingly, the Buddha is accepted as one of the avatars of Vishnu – [True Father could also be accepted as an avatar – The Kalkin Avatar] ...
Josef Früchtl Professor in Philosophy University of Amsterdam
... in February 1995. In this book I took up a philosophical discussion which wasn’t only driven forward by postmodernism but also by the so called virtue ethics, i. e. by all those theories which oppose to a rigid philosophy of morality in the European Kantian and the Anglo-American utilitarian sense. ...
... in February 1995. In this book I took up a philosophical discussion which wasn’t only driven forward by postmodernism but also by the so called virtue ethics, i. e. by all those theories which oppose to a rigid philosophy of morality in the European Kantian and the Anglo-American utilitarian sense. ...
Vedanta philosophy – key ideas (Word)
... Vedanta philosophy - key ideas (The following information was provided by Mark Bhaghwandin (Hindu) who is recorded on a video clip speaking on the Hindu perspective on science and religion) this clip can be found on the CD-ROM Swami Vivekananda’s view was that the unmanifest, unified field, possessi ...
... Vedanta philosophy - key ideas (The following information was provided by Mark Bhaghwandin (Hindu) who is recorded on a video clip speaking on the Hindu perspective on science and religion) this clip can be found on the CD-ROM Swami Vivekananda’s view was that the unmanifest, unified field, possessi ...
12 Purva Mimamsa and Vedanta
... dependent upon the rope, So also, according to Shankara, the world is dependent upon Brahman but Brahman is not dependent upon the world. A classic example given as the purpose of philosophic thought is that of a thorn. If a thorn is stuck in one′s foot, we take another thorn and carefully remove it ...
... dependent upon the rope, So also, according to Shankara, the world is dependent upon Brahman but Brahman is not dependent upon the world. A classic example given as the purpose of philosophic thought is that of a thorn. If a thorn is stuck in one′s foot, we take another thorn and carefully remove it ...
Purva Mimamsa and Vedanta
... then, we must rely upon reason. Shankara’s advaita philosophy is deep and profound. Its insistence on rational thought and reason degenerated over the centuries into linguistic wrangling. Thus, in the 11th century, Ramanuja derived a form of “qualified” advaita known as visishtadvaita. It can be tho ...
... then, we must rely upon reason. Shankara’s advaita philosophy is deep and profound. Its insistence on rational thought and reason degenerated over the centuries into linguistic wrangling. Thus, in the 11th century, Ramanuja derived a form of “qualified” advaita known as visishtadvaita. It can be tho ...
Details - Indian Council of Philosophical Research
... elaborate and intensive debates (śāstrārtha) among themselves. This reminds us of the elaborate contests and disputes between Buddhism and Vedānta and the debates among various Upaniśadic schools themselves. These debates were mostly of traditional and textual nature. It was only after the advent of ...
... elaborate and intensive debates (śāstrārtha) among themselves. This reminds us of the elaborate contests and disputes between Buddhism and Vedānta and the debates among various Upaniśadic schools themselves. These debates were mostly of traditional and textual nature. It was only after the advent of ...