History Project Hinduism
... • subdivided into a number of major denominations – Saivism (特麗卡 ), Shaktism (沙克蒂 ), Smartism (自由印度 教) , and Vaishnavism (神毗濕奴) . ...
... • subdivided into a number of major denominations – Saivism (特麗卡 ), Shaktism (沙克蒂 ), Smartism (自由印度 教) , and Vaishnavism (神毗濕奴) . ...
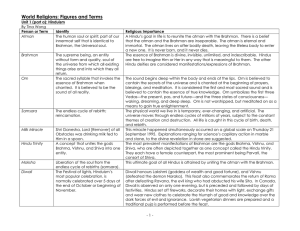
World Religions: Figures and Terms
... The organization of Hindu society into four classes called varnas (Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, Sudras), each with its own duties and expectations. ...
... The organization of Hindu society into four classes called varnas (Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, Sudras), each with its own duties and expectations. ...
Hinduism - WordPress.com
... Destroyer. Each god can take many forms, human or animal and each had a family ...
... Destroyer. Each god can take many forms, human or animal and each had a family ...
Hinduism - Spectrum Loves Social Studies
... • No single founder • No single sacred text • No single start-date – Hinduism probably began to form when Aryans combined their religious beliefs and gods with the gods of the Indus civilization – Later people added their own gods, beliefs, and traditions ...
... • No single founder • No single sacred text • No single start-date – Hinduism probably began to form when Aryans combined their religious beliefs and gods with the gods of the Indus civilization – Later people added their own gods, beliefs, and traditions ...
Hinduism
... Recognizes that paths to truth and salvation are many; Recognizes that there may be numerous gods and goddesses to worship [Henotheism]; Does not believe in a specific set of philosophic concepts. ...
... Recognizes that paths to truth and salvation are many; Recognizes that there may be numerous gods and goddesses to worship [Henotheism]; Does not believe in a specific set of philosophic concepts. ...
The Upanishads and Hindu Religious and Philosophical traditions
... • Theism (belief in a single Supreme personal being) emerges in many of the later Upanishads (8th-6th centuries BCE). • Theism is an important motif in the Epic literature of India beginning around the 5th century BCE. • The Bhagavad Gita (circa 300 BCE), for example, emphasized the ultimately perso ...
... • Theism (belief in a single Supreme personal being) emerges in many of the later Upanishads (8th-6th centuries BCE). • Theism is an important motif in the Epic literature of India beginning around the 5th century BCE. • The Bhagavad Gita (circa 300 BCE), for example, emphasized the ultimately perso ...
Hinduism - University of Mount Union
... the Brahmins began to expand their role as spiritual leaders and guides – there developed a body of religious literature, called the Vedas – the Vedas were written between 1200 and 300 BCE – There are other sacred text as well • Upanishads, Baghavad Gita ...
... the Brahmins began to expand their role as spiritual leaders and guides – there developed a body of religious literature, called the Vedas – the Vedas were written between 1200 and 300 BCE – There are other sacred text as well • Upanishads, Baghavad Gita ...
Buddhism and Hinduism
... 837 million followers worldwide (13 %) Over 80 % of India’s population Older than Christianity, Buddhism, & Islam No single founder Unique to India Why didn’t it spread? Geographical Barriers Doesn’t seek converts ...
... 837 million followers worldwide (13 %) Over 80 % of India’s population Older than Christianity, Buddhism, & Islam No single founder Unique to India Why didn’t it spread? Geographical Barriers Doesn’t seek converts ...
The Upanishads - Michael Sudduth
... • Although acknowledging many of the different gods of the Hindu pantheon, the Puranas demonstrate the rise in popularity of the worship of Vishnu and the worship of Shiva as the Supreme be ...
... • Although acknowledging many of the different gods of the Hindu pantheon, the Puranas demonstrate the rise in popularity of the worship of Vishnu and the worship of Shiva as the Supreme be ...
Hinduism is referred to as Sanātana Dharma, a Sanskrit phrase
... and has different paths according to each sect or denomination to realize the supreme. As Hinduism does not have a unified system of belief encoded in declaration of faith, It is therefore a very different kind of religion in these respects to the other traditions. Prominent themes in Hindu beliefs ...
... and has different paths according to each sect or denomination to realize the supreme. As Hinduism does not have a unified system of belief encoded in declaration of faith, It is therefore a very different kind of religion in these respects to the other traditions. Prominent themes in Hindu beliefs ...
Hinduism - hcworldreligions
... Basic Beliefs A. All living things have a soul. B. All souls are part of the eternal soul called atman. The goal in life is to unite atman with Brahman. C. Souls want to be part of Brahman but selfish desire ties them to the material world. D. Moksha - the goal of Hinduism - to leave the material w ...
... Basic Beliefs A. All living things have a soul. B. All souls are part of the eternal soul called atman. The goal in life is to unite atman with Brahman. C. Souls want to be part of Brahman but selfish desire ties them to the material world. D. Moksha - the goal of Hinduism - to leave the material w ...
Hindu - Berea College
... impersonal spirituality of Upanişads leads to renewed interest in popular, emotional, personal spirituality of bhakti (devotion) (c. 200 BCE-400 CE) New gods appear in multiple avataras (incarnations): Vishnu (best known as King Rama and Lord Krishna – associated with compassion, heroism, and mischi ...
... impersonal spirituality of Upanişads leads to renewed interest in popular, emotional, personal spirituality of bhakti (devotion) (c. 200 BCE-400 CE) New gods appear in multiple avataras (incarnations): Vishnu (best known as King Rama and Lord Krishna – associated with compassion, heroism, and mischi ...
33week2Hindu
... Upanishads Composed from 800 BCE- 600 CE. There are 200, 14 of which are most important. The teaching is Monistic (or pantheistic)- there is one RealityBrahman- the impersonal absolute- eternal, infinite, unknowable. Everything else is Maya- illusion. To attain liberation meditation (not sacrifice) ...
... Upanishads Composed from 800 BCE- 600 CE. There are 200, 14 of which are most important. The teaching is Monistic (or pantheistic)- there is one RealityBrahman- the impersonal absolute- eternal, infinite, unknowable. Everything else is Maya- illusion. To attain liberation meditation (not sacrifice) ...
Slide 1
... • The basic scriptures of Hinduism, are the Vedas (sometimes called the Rig Veda). • Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They were passed on from generation to generation orally for centuries before they were written down mostly in t ...
... • The basic scriptures of Hinduism, are the Vedas (sometimes called the Rig Veda). • Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They were passed on from generation to generation orally for centuries before they were written down mostly in t ...
Hinduism - TeacherWeb
... pleasure, success, and service provide temporary pleasure people who realize this begin to want more (that is, infinite life, knowledge, and joy) this liberation from death, ignorance, frustration, futility, and boredom is called moksha moksha gives us limitless being, consciousness, and bli ...
... pleasure, success, and service provide temporary pleasure people who realize this begin to want more (that is, infinite life, knowledge, and joy) this liberation from death, ignorance, frustration, futility, and boredom is called moksha moksha gives us limitless being, consciousness, and bli ...
16 Things to Know about The Sambodh Society
... motivation and happiness from one’s own self. The purpose of life is to realize one’s potential through a balanced mind while interacting with an ever-changing world. ...
... motivation and happiness from one’s own self. The purpose of life is to realize one’s potential through a balanced mind while interacting with an ever-changing world. ...
Week III Philosophy Excerpts- Mr F`s Philosophy Class Hindu
... contrary philosophical views associated with other Indian religious movements such as Buddhism or Jainism on issues of epistemology, metaphysics, logic, ethics or cosmology. Hence, historians of Indian philosophy typically understand the term “Hindu philosophy” as standing for the collection of phil ...
... contrary philosophical views associated with other Indian religious movements such as Buddhism or Jainism on issues of epistemology, metaphysics, logic, ethics or cosmology. Hence, historians of Indian philosophy typically understand the term “Hindu philosophy” as standing for the collection of phil ...
Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism
... Upanishads Composed from 800 BCE- 600 CE. There are 200, 14 of which are most important. The teaching is Monistic (or pantheistic)- there is one RealityBrahman- the impersonal absolute- eternal, infinite, unknowable. Everything else is Maya- illusion. To attain liberation meditation (not sacrifice) ...
... Upanishads Composed from 800 BCE- 600 CE. There are 200, 14 of which are most important. The teaching is Monistic (or pantheistic)- there is one RealityBrahman- the impersonal absolute- eternal, infinite, unknowable. Everything else is Maya- illusion. To attain liberation meditation (not sacrifice) ...
All Roads lead to God
... things everyone should do Saucha – keep clean Santosha – be content Tapas – self-discipline Svadhyaya – study wisdom of Hinduism Ishvara Pranidhana – surrender to God ...
... things everyone should do Saucha – keep clean Santosha – be content Tapas – self-discipline Svadhyaya – study wisdom of Hinduism Ishvara Pranidhana – surrender to God ...
Scriptures - World of Teaching
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
Scriptures - World of Teaching
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
Scriptures
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
... Yoga - Sage Patanjali Mimamsa - SageJaimini Vedanta – Sage Vyasa Nyaya - Sage Gautama Vaisheshika - Sage Kanada ...
Hinduism
... The goal of the individual soul is moksha. Moksha is liberation: the soul’s release from the cycle of death and rebirth. It occurs when the soul unites with Brahman by realizing its true nature. Several paths can lead to this realization and unity: the path of duty, the path of knowledge, and the pa ...
... The goal of the individual soul is moksha. Moksha is liberation: the soul’s release from the cycle of death and rebirth. It occurs when the soul unites with Brahman by realizing its true nature. Several paths can lead to this realization and unity: the path of duty, the path of knowledge, and the pa ...