* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism Glossary - Vishva Shakti Durga Mandir
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
Vaishnavism wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
2013 Bangladesh anti-Hindu violence wikipedia , lookup
Sri Vaishnavism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu nationalism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
Dayananda Saraswati wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu philosophy wikipedia , lookup
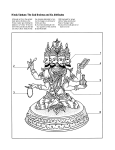
Hinduism Glossary Common Sanskrit Terms & Their Meaning Here is a glossary of Sanskrit terms generally used in Hindu teachings. <A> TERM MEANING Adharma contrary to what is right; evil. Cf. dharma Aditi Vedic goddess, the 'mother' of the gods Adityas Vedic sun deities, offspring of Aditi Advaita Vedanta non-dualistic Vedantic philosophy Agamas mystical scriptures pertaining to specific Hindu sects such as Vaisnavaites or Saivites Agni fire; sacred fire; fire god Ahimsa non-violence Amma mother, a compound often used in the names of female goddesses Amrta a nectar which was believed to bestow immortality Ananda bliss; the bliss of union with Brahman Anna food, rice Aranyaka Vedic forest texts or writings Arjun one of the sons of Pandu and the main (human) character of the Bhagavad Gita Artha worldly wealth, pursuit of wealth and social status Arti act of worship celebrating light Aryans the migrant invaders of India from approximately 1500 b.c; people of spiritual values Asanas yogic postures Asat non-being, that is to say the unreality of the world as opposed to the true Being (sat) which is Brahman. Ashram hermitage, retreat or place of quiet and solitude, often in a forest, where a Hindu sage lives alone or with his disciples Asramas the four stages of life in Hinduism Asvamedha probably the most prestigious of Vedic sacrificial rites, where a horse is sacrificed in a yajna by the king whose supremacy has been acknowledged by the neighbouring kings Atharva Veda 'Knowledge of Incantations', the fourth Veda Atman the presence of Brahman as the deepest essence of the self in all entities; the Divine Self, a synonym of Brahman Aum the sacred sound and symbol which represents Brahman in its unmanifest and manifest aspects Avatar literally 'descents', incarnation of God, usually the incarnations of Visnu and his consort Laksmi Avidya ignorance Ayurveda Vedic Medicine <B> TERM MEANING Bhagavad Gita Hindu scripture of the avatar Krishna dated to approximately the first two centuries b.c Bhajans hymns in praise of a deity Bhakta ardent devotee of a deity who expresses loving-devotion to the divine Bhakti ecstatic loving-devotion to the Almighty Bhakti marga the path of devotion Bhakti Yoga Yoga of Devotion Bhuktis planetary time periods, minor Bindi mark (usually a round, red) worn on the centre of the forehead to show that a woman is married Brahma form of the Hindu trinity governing creation or the Creator God Brahmachari young boy at the first of the four stages of life, the stage of the student Brahmacharya control of sexual energy; state of life of learning and purity Brahman the Absolute or ultimate reality Brahmanas Vedic ritualistic texts or manuals of instruction on the Vedas Brahmins a priest and member of the most privileged of the four social classes of Hinduism Brihaspati Vedic God of the ritual, the planet Jupiter Buddha ninth avatar of Vishnu Buddhism non-orthodox form of Vedic / Aryan teaching founded by the Buddha or enlightened one <C> TERM MEANING Chakras nerve centers of the subtle body; non-dualistic Vedantic philosophy Charvakas materialistic philosophers of ancient India Chela disciple and student of a guru Cit the Pure Consciousness equated with moksa when the egoistic <D> TERM MEANING Dalit person outside the class system of Hinduism who was formerly termed as Untouchable Darsanas writings of the six philosophical schools of Hindu religious thought Darshan literally 'view' or 'sight of' referring to audience with a deity Dashas planetary time periods Deva male deity; literally 'shining one' Devi female deity Dharana yogic concentration or attention Dharma what is right for the self - moral piety, religion, honor, the clan, karma or work, society and the universe Dharma Sastras Law Books forming part of the scriptures of Hinduism Dhatus bodily tissues in Ayurvedic Medicine Dhyana meditation Divali Hindu festival of lights Doshas biological humors of Ayurvedic medicine Durga the Goddess as the destroyer of demons, one of the energy forms of Siva Dussehra Hindu festival that celebrates the defeat of the demon King Ravan at the hands of Lord Ram (found in the epic Ramayana ). It is also the worship of goddess Durga. Dvandva dualities; pairs of opposites Dvija twice-born, referring to the Brahmins, (formerly even the Ksatriyas and Vaisyas), who undergo initiation into the Hindu religion at a sacred-thread ceremony <G> TERM MEANING Ganesha elephant-headed God who takes away all obstacles and is the God of good fortune Ganesh Chaturthi worship of god Ganesha in the month of September Garbagriha literally 'womb-house', the central part of a temple where the main deity is enshrined Gauna the ceremony marking the departure of a bride for the home of her new husband Gayatri Vedic chant for awakening the soul Gopis cowherdesses (celebrated in the myths of Lord Krishna) Gramadevatas village deities Grihastha person at the second of the four stages of life, the stage of the householder Gunas prime three qualities of nature - sattva (spiritual), rajas (worldly) and tamas (unholy), which constitute all life Guru enlightened spiritual teacher <H> TERM MEANING Hanuman the monkey God, protagonist in Ramayana Hanuman Chalisa the book containing prayers/hymns for the deified monkey God Hanuman Havan an offering of fire in Hindu worship Hatha Yoga Yoga of the physical body Hinduism Vedic knowledge and teachings Holi Hindu festival of colours Homa Vedic worship, Fire offerings Hum great mantra of Agni and Shiva <I> TERM MEANING Indra Vedic God of storm and thunder who was also king of the gods Ishtadevata chosen deity Ishvara or Lord, the term used of God in manifest Ishwara form; the cosmic Creator Itihasas Hindu epics or scriptures which convey historical and mythological sagas and tales <J> TERM MEANING Jainism Aryan teaching emphasizing non-violence Jati birth and the caste system Jivatman the personality self Jnana intuitive knowledge Jnana Marga the path of knowledge Jnana Yoga of Knowledge Yoga Jutha the 'left-overs' of food offered to a deity, the deity having extracted the essence of the food Jyotish Vedic Astrology <K> TERM MEANING Kailash the world mountain Kalash brass pot containing water, representative of a goddess Kali the dark form of the Goddess, characterized by ferocious appearance Kali Yuga dark or iron age Kalki tenth avatar of Vishnu Kama pursuit of desire and pleasure, particularly sexual pleasure Kapha biological water humor Kapila great Hindu sage, founder of the Sankhya system of philosophy Karakas planetary significators Karma literally 'action' but also the law of cause and effect; action and reaction Karma Marga the path of egoless action Karma Yoga Yoga of Work or Service Karma Yogi person who is selflessly devoted to work Kashmiri Shaivism Shaivite philosophy of medieval Kashmir Katcha poor quality, impure food Ketu south node of the Moon, dragon's tail Kirtan hymn in praise of a deity Krishna eighth avatar of Vishnu KrishnaJanamastami Hindu festival celebrating the birth of Lord Krishna Kriya Yoga Yoga of technique Kshatriya people of political values, belonging to the second of the four Hindu classes of society, traditionally a warrior, ruler or administrator Kundalini serpent power, power of subtle body <L> TERM MEANING Lakshman the brother of Lord Ram in the epic Ramayana Lakshmi Goddess of prosperity, fortune and beauty; consort of Vishnu, sometimes called Sri Lalita Goddess of bliss Laya Yoga Yoga of absorption of sound-current (nada) Linga phallic symbol associated with the God Shiva Loka place; realm, as the deva loka, the realm of the gods <M> TERM MEANING Mahabharata the epic of Krishna, Pandavas & Kauravas Mahadeva 'Great God', one of the names of the deity Shiva Mahadevi 'Great Goddess', the Mother Goddess of Hinduism Mahashivratri Hindu festival devoted to Lord Shiva Mahavakyas great sayings of Vedantic knowledge Mahayana great vehicle, northern school of Buddhism Manas mind or emotion Mandal Hindu temple which can also be used for socio-cultural purposes Mandap/mandva the canopy under which a wedding ceremony takes place Mandir a Hindu temple Mantra spiritual or sacred syllables or sounds which contain in their essence divine cosmic power Manu Vedic original man, founder of human culture Marmas sensitive body zones in Ayurvedic treatment Mata mother, a compound often used in the names of female goddesses Maya illusion, particularly the illusion of the transient, impermanent, phenomenal world Mayavada doctrine that the world is unreal Mehndi long-lasting pattern made with henna dye on the hands of a woman at her wedding and sometimes at festive occasions Meru the poles Mimamsa ritualistic form of Vedic philosophy Moksha pursuit of liberation from the cycle of reincarnation, loss of the egoistic self, and union with Brahman Monism the theory that everything in the cosmos is a unity and is equated with the divine Monotheism belief in one personal god or goddess Murti the image and representation of a deity in a temple, shrine or in the home <N> TERM MEANING Nada sound current of the subtle body Nadis nerves of the subtle body Namaskar Namaste 'I bow to you', the greeting which acknowledges the atman in another person Nataraj Shiva as lord of the cosmic dance Navaratri a nine-day Hindu festival devoted to the goddess Durga Neti Neti literally 'not this, not this', the expression used to denote that Brahman is beyond all dualities and human thought Nirakara 'without form', referring to Brahman as Unmanifest Nirguna 'without gunas', without qualities, referring to Brahman as Unmanifest Nirvana liberation, the state of peace Nitya 'obligatory', referring to aspects of religious practice. Niyamas yogic observances Nyaya & Vaisheshika Hindu philosophies <P> TERM MEANING Pancha Karma five Ayurvedic purification methods Panda a temple priest at a pilgrimage site Panentheism the belief that the divine is in all things and unifies all things but is ultimately greater than all things Pantheism the belief that the divine is in all things and is equated with the totality of all Parashurama sixth avatar of Vishnu Parvati goddess, the consort of God Shiva Patanjali main teacher of classical Yoga system Pinda four balls of rice prepared on the twelfth day after someone has died to symbolize the union of the deceased with his or her forebears Pitta biological fire humor Polytheism belief in many personal gods and /or goddesses Prakriti great Nature, matter Prana breath or life-force Pranayama yogic control of the breath Prana Yoga Yoga of the life-force Prasad the grace of the deity given to the worshipper in the form of food after worship: see also jutha Pratyahara yogic control of mind and senses Puja Hindu honour, respect or worship of a deity, flower offerings Pujari temple or shrine priest who performs puja Pukka good quality food which is considered ritually pure Puranas Hindu mythological texts Purohit a family priest or guru Purusha literally 'person': the original, primeval being the sacrifice of which was believed to create from its body the phenomenal world, in particular the four classes. It is the pure consciousness, or the spirit which is also synonymous of Brahman and therefore of atman <R> TERM MEANING Radha a cowherdess who was the favourite of Lord Krishna and an incarnation of the Goddess Lakshmi, also a Goddess in her own right Rahu north node of the Moon; dragon's head Raja a tribal chieftain, local ruler or monarch Rajas one of the three gunas or qualities in existence, associated with the creator God Brahma and representing the active energy or agitation in the universe Raja Yoga integral or royal yoga path of Patanjali Rakhi a band symbolizing protection which is tied round the wrists of males by girls at the festival of Raksha Bandhan Raksha Bandhan Hindu festival of tying Rakhi or band around wrists Rama seventh avatar of Vishnu and hero of the epic The Ramayana Ramayana Hindu epic scripture dealing with the heroic exploits of Lord Rama Ram Navami Hindu festival celebrating the birthday of Lord Rama Rasayana Ayurvedic rejuvenation methods Rig Veda/Rg Veda 'Royal Knowledge', Veda of chant, one of the four Vedas, the major and oldest Aryan Hindu scripture Rishis ancient Vedic seers, enlightened men who composed Vedic hymns and Upanishads Rta the Vedic cosmic norm which regulated all existence and to which all had to conform Rudra terrible or wrathful form of Shiva <S> TERM MEANING Sadharana Dharma what is right in terms of the common duties and obligations to one's fellow human beings Saguna manifest, referring to manifest aspects of Brahman Saivites devotees of the deity Shiva Sakara 'with form', referring to the manifest aspects of Brahman Sakti the female active energy in the universe Samadhi absorption, bliss, trance Sama Veda 'Knowledge of Chants', one of the four Vedas Samsara worldly life or reincarnation Samskaras rituals and rites in one's life cycle Sanatana Dharma what is right for the universe; it is also synonymous with Hinduism Sankhya Vedic philosophy of cosmic principles Sannyasin/Sannyasa person at the last of the four stages of life, the stage of the wandering ascetic, stage of life of renunciation and liberation Sanskrit Vedic and mantric language Santana Dharma the eternal teaching; traditional name for the Hindu religion Santosi Ma a modern Hindu goddess of prosperity and wish-fulfilment Saptapadi the seven steps taken by a couple during their marriage ceremony symbolizing seven different wishes for the future Saraswati Goddess of speech, learning, knowledge and wisdom Sari traditional dress for women consisting of a piece of material of five or six metres long which is draped around the body Sat the Being, Truth and Reality associated with Brahman as opposed to the non-being (asat) of the phenomenal world Sati voluntary burning of a widow on her husband's funeral pyre Sati consort of the God Shiva, also called Uma Sattva quality of truth or light; one of the three gunas or qualities in existence, associated with the preserving God Vishnu and representing light and spiritual evolution Sautrantika Buddhist philosophy of the momentariness of all things Savitar Vedic Sun god as the guide of Yoga Savitr Vedic solar deity Shakti the power of consciousness and spiritual evolution Shankara the great philsopher of nondualistic Vedanta Shiva form of the Hindu trinity governing destruction and transcendence Shudras people of sensate values Shunyavada Buddhist philosophy that everything is void Sita the wife of Rama in the Hindu epic the Ramayana and an avatar of the Goddess Lakshmi Shiva one of the three trinities in Hinduism, the god of Destruction Skanda the God of war Smrti literally 'memory' or 'remembered': a category of sacred scriptures which contains much popular and devotional literature So'ham natural mantric sound of the breath Soma Vedic God of bliss or equated also with a potent hallucinogenic drink Sraddha ceremonies for the deceased in the twelve days following cremation Srauta official sacrificial ritual of the Vedic period Sri the Goddess Lakshmi, consort of Lord Vishnu Srotas channel systems used in Ayurvedic medicine Sruti category of sacred scriptures which are 'heard' or cognized by the ancient seers Sudra the fourth of the Hindu four classes, traditionally the servant class Surya Vedic Sun God or god of the enlightened mind Svadharma what is right for an individual <T> TERM MEANING Tamas one of the three gunas or qualities in existence, associated with the dissolver God Shiva and representing the quality of darkness and inertia in existence Tantra medieval yogic and ritualistic Indian texts; esoteric, mystical teachings Tara the Goddess in her role as savior Tat Tvam Asi 'That art thou', the equating of the atman and every being in total identity with That, which is Brahman Theism belief in a personal god, goddess, gods or goddesses Tilak the mark (usually vertical) placed on the forehead of a devotee during ritual worship Trimurti literally 'three-form',the Hindu trinity of three deities, Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, the Creator, the Preserver and the Destroyer, respectively <U> TERM MEANING Ugadi Hindu festival Uma consort of the male deity Shiva Upanayama ceremony of the sacred thread undertaken by the top three classes of the Hindu society Upangas literature concerned with ritual and logical thought Upanishads Vedic philosophical texts or scriptures occuring at the end of the Vedas characterised by mystical and philosophical speculation on the nature of the self and ultimate Reality Upavedas additions to the Vedic scriptures Ushas Vedic goddess of dawn <V> TERM MEANING Vaishnavites devotees of the deity Vishnu Vaishyas person belonging to the third of the four Hindu classes of society, traditionally an artisan or skilled labourer, people of commercial values Vak Divine Word, the Goddess Vanaprastha person at the third of the four stages of life, hermitage or forestdweller stage of life Varna literally 'colour', the word for the four social values or class system in Hinduism, Varnasramadharma what is right for class and stage of life Varuna Vedic deity of cosmic order Vata biological air humor Veda knowledge Vedangas rules on ritual, astronomy, morals, grammar and phonetics Vedas the four Vedic ancient scriptures of India, namely the Rg, Sama, Yajur and Atharva Vedanta Vedic philosophy of Self-knowledge Vedic Science integral spiritual science of the Vedas Vidya knowledge Vijnana intelligence Vijnanavada Buddhist philosophy that consciousness alone exists Vishnu God or form of the Hindu trinity governing preservation <Y > TERM MEANING Yajna sacrifice, sacred ritual Yajur Veda 'Knowledge of Sacrificial Ritual', one of the four Vedas Yama God of Death; ruler of the realm of the dead the 'Land of the Fathers': he was the first man to die and therefore the welcomer of others to his realm Yamas yogic attitudes Yantra geometrical meditation designs Yatra pilgrimage Yoga techniques of developing and integrating energy; discipline or 'yoking' of the senses and the ego more... Yoga Sutras classical text of Patanjali on Yoga Yogi practitioner of yoga Yugas world-ages