Fast Categorization of Bacteriophage Protein Families using
... SAM (Sequence Alignment and Modeling) tells us that sequences are related, but there are times when the program is incorrect, and just by looking at a picture, we can tell it’s wrong, or vice versa. Therefore, we need a program to let a Human make the comparison on whether certain proteins are h ...
... SAM (Sequence Alignment and Modeling) tells us that sequences are related, but there are times when the program is incorrect, and just by looking at a picture, we can tell it’s wrong, or vice versa. Therefore, we need a program to let a Human make the comparison on whether certain proteins are h ...
Preface 1 PDF
... tools of the molecular biologist with those of the microscopist. From the molecular biology toolbox, this volume will present methods for antigen production by protein expression in bacterial cells and by expression of epitope tagged proteins in plant and animal cells. Methods for production of anti ...
... tools of the molecular biologist with those of the microscopist. From the molecular biology toolbox, this volume will present methods for antigen production by protein expression in bacterial cells and by expression of epitope tagged proteins in plant and animal cells. Methods for production of anti ...
16-17 Biology Fall Final Study Guide
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
... Passive transport (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion) Active transport (Bulk transport, Exocytosis, Endocytosis (Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis) Receptor-mediated) Central Dogma Differences between RNA and DNA Central dogma Where does each step occur? Transcription RNA Polymerase ...
Power Point Presentation on Cell Organelles
... Formed by the Golgi bodies Sac-like structures that contain digestive enzymes which break down large molecules & cell parts within the cytoplasm… The swelling & pain associated with arthritis have been linked to the seepage of this organelle…cortisone is thought to strengthen this organelles membran ...
... Formed by the Golgi bodies Sac-like structures that contain digestive enzymes which break down large molecules & cell parts within the cytoplasm… The swelling & pain associated with arthritis have been linked to the seepage of this organelle…cortisone is thought to strengthen this organelles membran ...
Erin Margaret Schuman
... proteins of interest, and not just in neurons. Schuman credits Susanne tom Dieck, a staff scientist in her group, for having the idea for the approach to ‘birth-date’ as well as label a protein. “Anything that is labeled can be retrospectively identified as having been synthesized during the labelin ...
... proteins of interest, and not just in neurons. Schuman credits Susanne tom Dieck, a staff scientist in her group, for having the idea for the approach to ‘birth-date’ as well as label a protein. “Anything that is labeled can be retrospectively identified as having been synthesized during the labelin ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Parts Powerpoint
... Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Mitochondria are found in plant & animal cells Functions as the cell’s “powerhouse” by converting energy stored in glucose to the cellular energy ATP Composed of 2 membranes: inner & outer The inner membrane is folded to increase surface area ...
... Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Mitochondria are found in plant & animal cells Functions as the cell’s “powerhouse” by converting energy stored in glucose to the cellular energy ATP Composed of 2 membranes: inner & outer The inner membrane is folded to increase surface area ...
Post-transcriptional processes - Department of Cellular and
... of cytoplasmic mRNA degradation [4]. Overshadowed all to frequently by examination of transcriptional events, RNA stability plays a major role in regulating the level of gene expression. Excluding contributions from altemative RNA splicing and RNA transport, gene transcription and RNA half life play ...
... of cytoplasmic mRNA degradation [4]. Overshadowed all to frequently by examination of transcriptional events, RNA stability plays a major role in regulating the level of gene expression. Excluding contributions from altemative RNA splicing and RNA transport, gene transcription and RNA half life play ...
Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein ab140735 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Upon delivery aliquot. Store at -20°C or 80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. pH: 8.00 Constituents: 0.02% DTT, 0.32% Tris HCl, 10% Glycerol, 0.58% Sodium chloride ...
... Shipped at 4°C. Store at +4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Upon delivery aliquot. Store at -20°C or 80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. pH: 8.00 Constituents: 0.02% DTT, 0.32% Tris HCl, 10% Glycerol, 0.58% Sodium chloride ...
Denaturation of proteins
... enzyme, then denaturation causes it to lose its enzymatic activity. If the protein was embedded in a cell membrane where it transported ions or molecules through the membrane, then denaturation destroys that ability. If the protein was an antibody, responsible for recognizing an infectious agent, de ...
... enzyme, then denaturation causes it to lose its enzymatic activity. If the protein was embedded in a cell membrane where it transported ions or molecules through the membrane, then denaturation destroys that ability. If the protein was an antibody, responsible for recognizing an infectious agent, de ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum
... – Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials, like water. – Plants have a large Central Vacuole, which takes up lots of water. ...
... – Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials, like water. – Plants have a large Central Vacuole, which takes up lots of water. ...
Affinity Chromatography
... Example: Human lens crystallins Human gene cloned into pET vector and expressed in E. coli. ...
... Example: Human lens crystallins Human gene cloned into pET vector and expressed in E. coli. ...
Isofocusing Chromatography
... chromatography technique that separates protein according to differences in their isoelectric point (PI). •Its a polishing step for partially purified samples. •Its a high resolution technique and can be used for analytical separation. •We can be used this technique as a complementary technique when ...
... chromatography technique that separates protein according to differences in their isoelectric point (PI). •Its a polishing step for partially purified samples. •Its a high resolution technique and can be used for analytical separation. •We can be used this technique as a complementary technique when ...
The Cell: Organelles and Functions
... surrounds chromatin Function: Cellular “Command Center” Difference between chromatin and chromosomes? ...
... surrounds chromatin Function: Cellular “Command Center” Difference between chromatin and chromosomes? ...
EXPLORING PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
Biological networks - Vanderbilt University
... allows the diploid cell to grow on selective media Pick colonies, isolate DNA, and sequence to identify the ORF interacting with the bait High-throughput Can detect transient interactions ...
... allows the diploid cell to grow on selective media Pick colonies, isolate DNA, and sequence to identify the ORF interacting with the bait High-throughput Can detect transient interactions ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... b) Name 2 types of protein secondary structure. For each type give a named example and its location in the cell. ...
... b) Name 2 types of protein secondary structure. For each type give a named example and its location in the cell. ...
Molecules and Life Quiz 3C
... blocks of many structures in organisms. Your muscles contain large amounts of protein. ...
... blocks of many structures in organisms. Your muscles contain large amounts of protein. ...
Biology 6 Study Guide – Exam #2
... regulation of the lac operon in response to lactose and glucose ...
... regulation of the lac operon in response to lactose and glucose ...
Document
... Signal Sequences Target Proteins for Secretion Signal sequence at the amino-terminal end of membrane proteins or secretory proteins are recognized by factors and receptors that mediate transmembrane transport. Signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase. ...
... Signal Sequences Target Proteins for Secretion Signal sequence at the amino-terminal end of membrane proteins or secretory proteins are recognized by factors and receptors that mediate transmembrane transport. Signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase. ...
Effect of protein aggregation and protein structure on magnetite
... in in vitro experiments, thereby demonstrating its potential as a candidate protein for the production of magnetite nanoparticles possibly useful in medical and other applications. However, the importance of the structure and aggregation state of the protein on the resulting biomimetic nanoparticles ...
... in in vitro experiments, thereby demonstrating its potential as a candidate protein for the production of magnetite nanoparticles possibly useful in medical and other applications. However, the importance of the structure and aggregation state of the protein on the resulting biomimetic nanoparticles ...
Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes
... Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes 1. Protein fate is determined by N-terminal signal sequences 15-30 amino acids long. All contain ~10 hydrophobic residues. 2. When 70-80 amino acids have been polymerised during translation, and the signal sequence has emerged into the cytosol, it is recognised b ...
... Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes 1. Protein fate is determined by N-terminal signal sequences 15-30 amino acids long. All contain ~10 hydrophobic residues. 2. When 70-80 amino acids have been polymerised during translation, and the signal sequence has emerged into the cytosol, it is recognised b ...
Biomolecules Review Game
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... Transcription: The process of copying a gene into mRNA RNA Polymerase: An enzyme that copies DNA into mRNA mRNA: AN RNA molecule that is a copy of a gene General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bin ...
... Transcription: The process of copying a gene into mRNA RNA Polymerase: An enzyme that copies DNA into mRNA mRNA: AN RNA molecule that is a copy of a gene General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bin ...
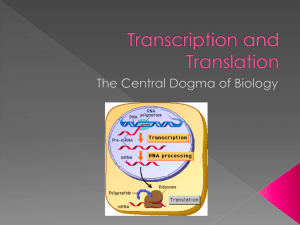
Transcription and Translation
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
Outline
... binding of the ligand ? • Introducing fluorophores at residues that exhibit changes in fluorescence emission • due to changes in conformation (open vs close) ...
... binding of the ligand ? • Introducing fluorophores at residues that exhibit changes in fluorescence emission • due to changes in conformation (open vs close) ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.