Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
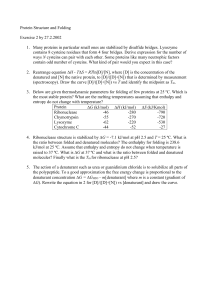
... DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure i ...
... DNA is a specific nucleic acid that directs protein making in all living things Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure i ...
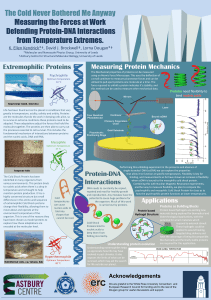
The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
... temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock proteins change their flexibility, allowing them to move about and operate at the environment temperature of the organism. ...
... temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock proteins change their flexibility, allowing them to move about and operate at the environment temperature of the organism. ...
Characterization
... Each material has a unique “molecular fingerprint”, allowing identification of through spectra comparison, and provides information on polymer structure and composition ...
... Each material has a unique “molecular fingerprint”, allowing identification of through spectra comparison, and provides information on polymer structure and composition ...
Structural Studies of Sgt2, a Component of the GET Pathway that
... diffusion technique. Crystals diffracted to 2.6-Å resolution on a home X-ray source, and belonged to the orthorhombic space group, C2221 with unit cell dimensions a= 72.378. Å, b= 81.413 Å, c= 109.349 Å, and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure was determined by molecular replacement and contained two m ...
... diffusion technique. Crystals diffracted to 2.6-Å resolution on a home X-ray source, and belonged to the orthorhombic space group, C2221 with unit cell dimensions a= 72.378. Å, b= 81.413 Å, c= 109.349 Å, and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure was determined by molecular replacement and contained two m ...
G Protein Coupled Receptors
... GTP exchange leads to a conformational change in the switch region. This leads to dissociation of Gß and it destabilizes the region where the G protein N- and Cterminus come together with the GPCR C-terminus, which leads to G protein dissociation. ...
... GTP exchange leads to a conformational change in the switch region. This leads to dissociation of Gß and it destabilizes the region where the G protein N- and Cterminus come together with the GPCR C-terminus, which leads to G protein dissociation. ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
Pipe Cleaner Protein
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
... ◦ DNA sequence written out ◦ mRNA sequence written out ◦ Amino acid sequence written out ...
37151
... Proteomics is usually carried out to study the complement of protein expressed by a cell at any one time or at a particular stage ...
... Proteomics is usually carried out to study the complement of protein expressed by a cell at any one time or at a particular stage ...
D. E. Shaw Research is seeking postdoctoral fellows of exceptional... Postdoctoral Fellowships at D. E. Shaw Research
... physics, or in a relevant area of computer science or applied mathematics. Relevant areas of experience might include the study of allosteric interactions or other functionally important conformational changes in biological molecules, structure prediction or design for proteins or RNA, the study of ...
... physics, or in a relevant area of computer science or applied mathematics. Relevant areas of experience might include the study of allosteric interactions or other functionally important conformational changes in biological molecules, structure prediction or design for proteins or RNA, the study of ...
Lecture 1
... Molecular Chaperones bind to unfolded proteins and prevent non-native conformations ...
... Molecular Chaperones bind to unfolded proteins and prevent non-native conformations ...
051507
... – Exploit differences in physical/chemical characteristics (arising from…?) to separate proteins – Ion exchange – Gel filtration/Size exclusion – Affinity ...
... – Exploit differences in physical/chemical characteristics (arising from…?) to separate proteins – Ion exchange – Gel filtration/Size exclusion – Affinity ...
Proteins for Growth and Repair
... are essential to life and must be added to the diet. They are found in animal foods like meat, fish, milk cheese and eggs. Vegans and vegetarians can get shortages of the essential amino acids lysine and threonine if they are not observant. Lysine can be found in soy beans, chickpeas, kidney and oat ...
... are essential to life and must be added to the diet. They are found in animal foods like meat, fish, milk cheese and eggs. Vegans and vegetarians can get shortages of the essential amino acids lysine and threonine if they are not observant. Lysine can be found in soy beans, chickpeas, kidney and oat ...
Proteins
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
Typical IP Protocol
... 5. Elute with sample buffer 6. SDS-PAGE 7. Detection • protein stain • radioactivity ...
... 5. Elute with sample buffer 6. SDS-PAGE 7. Detection • protein stain • radioactivity ...
circular dichroism
... CD has an important role in the structural determinants of proteins. However, the effort expended in determining secondary structure elements is usually not worth it because it is somewhat unreliable. The real power of CD is in the analysis of structural and conformational changes in a protein upon ...
... CD has an important role in the structural determinants of proteins. However, the effort expended in determining secondary structure elements is usually not worth it because it is somewhat unreliable. The real power of CD is in the analysis of structural and conformational changes in a protein upon ...
Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging
... field is removed (turned off), or the sample is removed from the magnet. c. Normally, an NMR sample is diamagnetic, i.e., all electrons in the molecule are paired up, or, there is no net magnetization from the electrons. d. A quadrupole spin means it has very large magnetic moment. e. The majority o ...
... field is removed (turned off), or the sample is removed from the magnet. c. Normally, an NMR sample is diamagnetic, i.e., all electrons in the molecule are paired up, or, there is no net magnetization from the electrons. d. A quadrupole spin means it has very large magnetic moment. e. The majority o ...
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore and Angela Gronenborn at the NIH, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated.NMR involves the quantum mechanical properties of the central core (""nucleus"") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how the atoms are linked chemically, how close they are in space, and how rapidly they move with respect to each other. These properties are fundamentally the same as those used in the more familiar Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), but the molecular applications use a somewhat different approach, appropriate to the change of scale from millimeters (of interest to radiologists) to nano-meters (bonded atoms are typically a fraction of a nano-meter apart), a factor of a million. This change of scale requires much higher sensitivity of detection and stability for long term measurement. In contrast to MRI, structural biology studies do not directly generate an image, but rely on complex computer calculations to generate three-dimensional molecular models.Currently most samples are examined in a solution in water, but methods are being developed to also work with solid samples. Data collection relies on placing the sample inside a powerful magnet, sending radio frequency signals through the sample, and measuring the absorption of those signals. Depending on the environment of atoms within the protein, the nuclei of individual atoms will absorb different frequencies of radio signals. Furthermore the absorption signals of different nuclei may be perturbed by adjacent nuclei. This information can be used to determine the distance between nuclei. These distances in turn can be used to determine the overall structure of the protein.A typical study might involve how two proteins interact with each other, possibly with a view to developing small molecules that can be used to probe the normal biology of the interaction (""chemical biology"") or to provide possible leads for pharmaceutical use (drug development). Frequently, the interacting pair of proteins may have been identified by studies of human genetics, indicating the interaction can be disrupted by unfavorable mutations, or they may play a key role in the normal biology of a ""model"" organism like the fruit fly, yeast, the worm C. elegans, or mice. To prepare a sample, methods of molecular biology are typically used to make quantities by bacterial fermentation. This also permits changing the isotopic composition of the molecule, which is desirable because the isotopes behave differently and provide methods for identifying overlapping NMR signals.