Theme 1 - NUI Galway
... surface hydrophobic patch.3 The architecture of the dimer interface makes Azurin an interesting test molecule for these studies. Using selective labelling via surface exposed cysteine residues,4 bulky hydrophobic molecules (FITC analogues) will be introduced at different sites in and around the hydr ...
... surface hydrophobic patch.3 The architecture of the dimer interface makes Azurin an interesting test molecule for these studies. Using selective labelling via surface exposed cysteine residues,4 bulky hydrophobic molecules (FITC analogues) will be introduced at different sites in and around the hydr ...
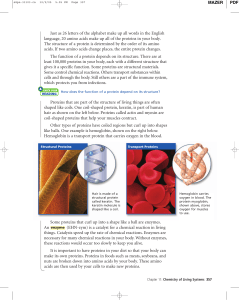
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
... language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein depends on its structure. There are at least 100,000 proteins in your b ...
word
... Consider what might happen to mutated protein (also pathways for degradation) Clathrin-coated vesicles Consider the basic import of proteins into nucleus, and the role of Ran, importins Consider import into mitochondria, into chloroplasts Consider what catalyzes the peptide bond on the ribosome – ev ...
... Consider what might happen to mutated protein (also pathways for degradation) Clathrin-coated vesicles Consider the basic import of proteins into nucleus, and the role of Ran, importins Consider import into mitochondria, into chloroplasts Consider what catalyzes the peptide bond on the ribosome – ev ...
Polypeptide: alpha-helix and beta
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
... Concept: Peptide chains tend to form orderly hydrogen-bonded arrangements. Materials: alpha-helix and beta-sheet models made by Prof. Ewing Procedure: Models may be used to help explain secondary protein structure. Related Information: Fibrous proteins are stringy, tough, and usually insoluble in ...
Coarse-Graining of Macromolecules
... Primary (amino acid sequence) Secondary (α-helices, β-strands) Tertiary (domains) Quaternary (active sites) ...
... Primary (amino acid sequence) Secondary (α-helices, β-strands) Tertiary (domains) Quaternary (active sites) ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, ...
... Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are prone to aggregating and sticking together, preventing them from performing their functions, ...
Prob_Set_2_2007
... - due Wednesday Feb 21 in class 1) Pick out a protein of known structure that is central to your research or is connected to your research interests. Download the coordinates from the Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org) and use a rendering program such as Chimera, Rasmol, Pymol, Molmol, iMol (Macs) etc ...
... - due Wednesday Feb 21 in class 1) Pick out a protein of known structure that is central to your research or is connected to your research interests. Download the coordinates from the Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org) and use a rendering program such as Chimera, Rasmol, Pymol, Molmol, iMol (Macs) etc ...
Slide 1
... • Long wavelength radiowaves are of low energy that is sufficient to ‘flip’ the spin of nuclei in a magnetic field (NMR). Nuclei interact weakly so spectral transitions between single, well defined energy levels are very sharp and well resolved. NMR is a vital technique for biological structure stud ...
... • Long wavelength radiowaves are of low energy that is sufficient to ‘flip’ the spin of nuclei in a magnetic field (NMR). Nuclei interact weakly so spectral transitions between single, well defined energy levels are very sharp and well resolved. NMR is a vital technique for biological structure stud ...
Chapter 3 (Protein structure and function)
... Proteins that have elongated, fibrous shapes Fibrous proteins e.g. alpha-keratin – intracellular collagen – extracellular Elastic fibers e.g. elastin – extracellular ...
... Proteins that have elongated, fibrous shapes Fibrous proteins e.g. alpha-keratin – intracellular collagen – extracellular Elastic fibers e.g. elastin – extracellular ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
... The incorporation of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen into biomolecules is readily accomplished by growth of a suitable microorganism in a medium containing biosynthetic precursors for both amino acids and nucleotides. The organism of choice is Escherichia coli, the most common bacterium used ...
... The incorporation of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen into biomolecules is readily accomplished by growth of a suitable microorganism in a medium containing biosynthetic precursors for both amino acids and nucleotides. The organism of choice is Escherichia coli, the most common bacterium used ...
Ch. 3 Study Guide
... 6. What is the common name for carbohydrates? What suffix is a clue that you are dealing with a carbohydrate? 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
... 6. What is the common name for carbohydrates? What suffix is a clue that you are dealing with a carbohydrate? 7. Carbohydrates perform three primary functions for cells. They are: A. B. C. 8. Compare and contrast monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides ...
Proteins as Supramolecular Building Blocks
... enzyme, representing the most common protein fold and therefore scaffold for activity; and the peroxiredoxins, a family of proteins that have already revealed themselves to have unique self-assembly properties controlled by a redox switch. Non-native architectures have been obtained and progress is ...
... enzyme, representing the most common protein fold and therefore scaffold for activity; and the peroxiredoxins, a family of proteins that have already revealed themselves to have unique self-assembly properties controlled by a redox switch. Non-native architectures have been obtained and progress is ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SEMINAR Professor Jeff Kelly Biological and Chemical Approaches to Adapt
... The cellular protein homeostasis, or proteostasis network, regulates proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, proteindegradation and the like. Stress responsive signaling pathways match proteostasis network capa ...
... The cellular protein homeostasis, or proteostasis network, regulates proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, proteindegradation and the like. Stress responsive signaling pathways match proteostasis network capa ...
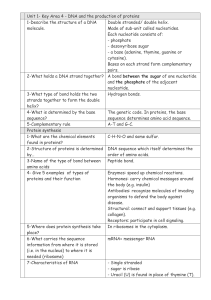
Unit1-KA4-Revision
... Each nucleotide consists of: - phosphate - desoxyribose sugar - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of b ...
... Each nucleotide consists of: - phosphate - desoxyribose sugar - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of b ...
proteins——Echo,Jason,Philip
... B)immune(means use antibodies to prevent something bad for us) C)genetic D)regulation Genetic effect comes from the nucleic acid rather than proteins. ...
... B)immune(means use antibodies to prevent something bad for us) C)genetic D)regulation Genetic effect comes from the nucleic acid rather than proteins. ...
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
Amino acid sequence fingerprints in divergent evolution of
... e-mail: [email protected] Proteins may basically be related by divergent or convergent evolution. In divergent evolution, i.e. the evolution from a common ancestor, there is only a small percentage of residues in the amino acid sequence of a protein, that have to be conserved in order the prot ...
... e-mail: [email protected] Proteins may basically be related by divergent or convergent evolution. In divergent evolution, i.e. the evolution from a common ancestor, there is only a small percentage of residues in the amino acid sequence of a protein, that have to be conserved in order the prot ...
SOLUGEL Protein Gummies Leaflet
... collagen protein in each gummy Triple your gummies’ protein content with SOLUGEL®! The traditional gummy bear contains around 6g of protein per 100g, entirely from its gelatin content. With SOLUGEL®, it is now possible to create a gummy rich in collagen protein that looks and tastes like any other g ...
... collagen protein in each gummy Triple your gummies’ protein content with SOLUGEL®! The traditional gummy bear contains around 6g of protein per 100g, entirely from its gelatin content. With SOLUGEL®, it is now possible to create a gummy rich in collagen protein that looks and tastes like any other g ...
Proteins - Kaikoura High School
... biochemical reactions in the body. • Are the structure of the body ...
... biochemical reactions in the body. • Are the structure of the body ...
Lecture 1
... From Sequence to Structure. Relatively primitive computational folding models have proved to be NP hard even in the 2-D case. ...
... From Sequence to Structure. Relatively primitive computational folding models have proved to be NP hard even in the 2-D case. ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... Please print out your brief, but complete, answers to these questions on separate pages and hand in Monday Aug. 28 in class 1. How are the purine bases chemically different from pyrimidine bases? 2. Distinguish between the following terms: base, nucleoside, nucleotide, and give an example of each. Y ...
... Please print out your brief, but complete, answers to these questions on separate pages and hand in Monday Aug. 28 in class 1. How are the purine bases chemically different from pyrimidine bases? 2. Distinguish between the following terms: base, nucleoside, nucleotide, and give an example of each. Y ...
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore and Angela Gronenborn at the NIH, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated.NMR involves the quantum mechanical properties of the central core (""nucleus"") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how the atoms are linked chemically, how close they are in space, and how rapidly they move with respect to each other. These properties are fundamentally the same as those used in the more familiar Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), but the molecular applications use a somewhat different approach, appropriate to the change of scale from millimeters (of interest to radiologists) to nano-meters (bonded atoms are typically a fraction of a nano-meter apart), a factor of a million. This change of scale requires much higher sensitivity of detection and stability for long term measurement. In contrast to MRI, structural biology studies do not directly generate an image, but rely on complex computer calculations to generate three-dimensional molecular models.Currently most samples are examined in a solution in water, but methods are being developed to also work with solid samples. Data collection relies on placing the sample inside a powerful magnet, sending radio frequency signals through the sample, and measuring the absorption of those signals. Depending on the environment of atoms within the protein, the nuclei of individual atoms will absorb different frequencies of radio signals. Furthermore the absorption signals of different nuclei may be perturbed by adjacent nuclei. This information can be used to determine the distance between nuclei. These distances in turn can be used to determine the overall structure of the protein.A typical study might involve how two proteins interact with each other, possibly with a view to developing small molecules that can be used to probe the normal biology of the interaction (""chemical biology"") or to provide possible leads for pharmaceutical use (drug development). Frequently, the interacting pair of proteins may have been identified by studies of human genetics, indicating the interaction can be disrupted by unfavorable mutations, or they may play a key role in the normal biology of a ""model"" organism like the fruit fly, yeast, the worm C. elegans, or mice. To prepare a sample, methods of molecular biology are typically used to make quantities by bacterial fermentation. This also permits changing the isotopic composition of the molecule, which is desirable because the isotopes behave differently and provide methods for identifying overlapping NMR signals.