HOW GOOD DO WE HAVE TO BE TO SOLVE THE PROTEIN FOLDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND SCORING PROBLEMS?
... challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of ...
... challenges remain both from the computational/theoretical and experimental perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of ...
File - SMIC Nutrition Science
... 6. The making of protein from 20 amino acids was compared in the chapter to the use of the English alphabet (26 letters) to make words and speak the English language. Why was this such a fitting analogy? ...
... 6. The making of protein from 20 amino acids was compared in the chapter to the use of the English alphabet (26 letters) to make words and speak the English language. Why was this such a fitting analogy? ...
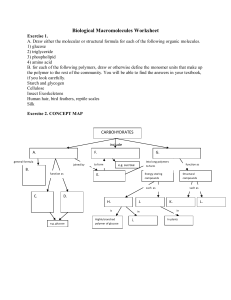
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... a. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in DNA b. the number _____ of different chemical classes of amino acids c. the number _____ of chains of nucleotides in a DNA molecule d. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in RNA e. the number _____ of different amino acids found in pr ...
... a. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in DNA b. the number _____ of different chemical classes of amino acids c. the number _____ of chains of nucleotides in a DNA molecule d. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in RNA e. the number _____ of different amino acids found in pr ...
CHEM 251L: Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Professor Jonathan
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
1 CHEM 251L: Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Professor Jonathan
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
L2_Principle of protein folding in the cellular environment
... synthesized protein chains to fold correctly within cells resides solely in the primary structure of the initial translation product. – Three families of molecular chaperone best known to interact with newly synthesized protein: hsp70, hsp40, and chaperonins ...
... synthesized protein chains to fold correctly within cells resides solely in the primary structure of the initial translation product. – Three families of molecular chaperone best known to interact with newly synthesized protein: hsp70, hsp40, and chaperonins ...
D6- Bulletin Board Powerful Protein
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
... • There are 9 essential amino acids that our bodies can’t make, so we need to get them from our food. • If a protein food has all 9 essential amino acids, it is called a complete protein. If it doesn’t, it is called an incomplete protein. • You can eat incomplete protein foods together to make sure ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in vegetarian diets? D. What ...
... 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetarian diets nutritionally sound? B. What should be my main concerns when planning a nutritionally sound vegetarian diet? C. Isn’t protein a problem in vegetarian diets? D. What ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... to detect conformational states of a single molecule such as misfolded protein during aggregation. ...
... to detect conformational states of a single molecule such as misfolded protein during aggregation. ...
BIOMOLECULES UNIT 3 Chemistry Review: Atoms
... Used in cell membranes, also a pre-cursor molecule for synthesis of vitamin D Also a class of hormones synthesized by the body Ex: estrogen, testosterone ...
... Used in cell membranes, also a pre-cursor molecule for synthesis of vitamin D Also a class of hormones synthesized by the body Ex: estrogen, testosterone ...
New high-throughput NMR
... ‘Unfortunately, typical drug targets are bigger and less soluble than one would like,’ he adds. The skeptics also point out that, so far, GFT NMR has only been tested using one small molecule, where the chemical shift assignments were already known.Therefore, they say that it remains to be seen whet ...
... ‘Unfortunately, typical drug targets are bigger and less soluble than one would like,’ he adds. The skeptics also point out that, so far, GFT NMR has only been tested using one small molecule, where the chemical shift assignments were already known.Therefore, they say that it remains to be seen whet ...
intracellular protein synthesis, post
... production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into the ER, and become associated with class I molecules. 20s and 2 6 s proteasomes degrade proteins pro ...
... production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into the ER, and become associated with class I molecules. 20s and 2 6 s proteasomes degrade proteins pro ...
Episode 23 0 Proetin: Structure and Function
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
Chapt 2
... 3. Chaperones are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. Chaperones are present in mitochondria 5. There is more than one class of proteins that assist with folding The structure that is formed when two subunits are held together by wrapping amphipathic alpha helices around each other: 1. Helix-loop ...
... 3. Chaperones are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. Chaperones are present in mitochondria 5. There is more than one class of proteins that assist with folding The structure that is formed when two subunits are held together by wrapping amphipathic alpha helices around each other: 1. Helix-loop ...
Genetic Engineering - USF :: Biological Sciences
... Department of Cell Biology, Microbiology, & Molecular Biology •Gene expression, Cloning, & Manipulation of Plasmids •Cell Culture •Transgenics •Mutagenesis •siRNA •Quantitative PCR •Generation of Antibodies •Use of Fluorescent Tags (i.e. GFP) •Protein Expression & Purification •High-throughput Techn ...
... Department of Cell Biology, Microbiology, & Molecular Biology •Gene expression, Cloning, & Manipulation of Plasmids •Cell Culture •Transgenics •Mutagenesis •siRNA •Quantitative PCR •Generation of Antibodies •Use of Fluorescent Tags (i.e. GFP) •Protein Expression & Purification •High-throughput Techn ...
Chapters 2 - 5 Exam Prep: What to Know
... What is “insoluble fiber?” What is the difference between alpha glycosidic linkages and beta glycosidic linkages? What type of linkages can humans digest? Saturated vs unsaturated fats: properties, number of hydrogens, be able to ID by their structure ...
... What is “insoluble fiber?” What is the difference between alpha glycosidic linkages and beta glycosidic linkages? What type of linkages can humans digest? Saturated vs unsaturated fats: properties, number of hydrogens, be able to ID by their structure ...
Crystallizing a clearer understanding of the protein
... They’ve been described as the workhorses of life at the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemi ...
... They’ve been described as the workhorses of life at the cellular level. Given the array of intelligent functions that proteins conduct in organisms, however, that moniker may not do them justice. Numbering in the millions, proteins—which are chains of amino acids—grow and repair cells, trigger chemi ...
College 5
... As a result of ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds, each type of protein has a particular three dimensional structure, which is determined by the order of the amino acids in the chain. ...
... As a result of ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds, each type of protein has a particular three dimensional structure, which is determined by the order of the amino acids in the chain. ...
Discussion Problem Set 3 C483 Spring 2014
... might you test the importance of an n-pi-star interaction? 2. What two things need to be minimized to have a stable alpha helix? 3. Which amino acid regularly adopts a cis peptide bond? Explain why this is possible. 4. What are the two major methods for determining protein structure. Describe two ma ...
... might you test the importance of an n-pi-star interaction? 2. What two things need to be minimized to have a stable alpha helix? 3. Which amino acid regularly adopts a cis peptide bond? Explain why this is possible. 4. What are the two major methods for determining protein structure. Describe two ma ...
To determine whether related genes appear in other species
... Many proteins contain compact units within the folding pattern of a single chain, that look as if they should have independent stability. The cell-surface protein CD4 consists of four similar domains ...
... Many proteins contain compact units within the folding pattern of a single chain, that look as if they should have independent stability. The cell-surface protein CD4 consists of four similar domains ...
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore and Angela Gronenborn at the NIH, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated.NMR involves the quantum mechanical properties of the central core (""nucleus"") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how the atoms are linked chemically, how close they are in space, and how rapidly they move with respect to each other. These properties are fundamentally the same as those used in the more familiar Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), but the molecular applications use a somewhat different approach, appropriate to the change of scale from millimeters (of interest to radiologists) to nano-meters (bonded atoms are typically a fraction of a nano-meter apart), a factor of a million. This change of scale requires much higher sensitivity of detection and stability for long term measurement. In contrast to MRI, structural biology studies do not directly generate an image, but rely on complex computer calculations to generate three-dimensional molecular models.Currently most samples are examined in a solution in water, but methods are being developed to also work with solid samples. Data collection relies on placing the sample inside a powerful magnet, sending radio frequency signals through the sample, and measuring the absorption of those signals. Depending on the environment of atoms within the protein, the nuclei of individual atoms will absorb different frequencies of radio signals. Furthermore the absorption signals of different nuclei may be perturbed by adjacent nuclei. This information can be used to determine the distance between nuclei. These distances in turn can be used to determine the overall structure of the protein.A typical study might involve how two proteins interact with each other, possibly with a view to developing small molecules that can be used to probe the normal biology of the interaction (""chemical biology"") or to provide possible leads for pharmaceutical use (drug development). Frequently, the interacting pair of proteins may have been identified by studies of human genetics, indicating the interaction can be disrupted by unfavorable mutations, or they may play a key role in the normal biology of a ""model"" organism like the fruit fly, yeast, the worm C. elegans, or mice. To prepare a sample, methods of molecular biology are typically used to make quantities by bacterial fermentation. This also permits changing the isotopic composition of the molecule, which is desirable because the isotopes behave differently and provide methods for identifying overlapping NMR signals.