Taxonomy
... they use Genus species names instead of common names. Organisms may have more than one common name ...
... they use Genus species names instead of common names. Organisms may have more than one common name ...
Chapter 3: The Biosphere
... _____________________________________________________________ • If nutrients are in short supply, they are called ______________________ Ex: Nitrogen is often ___________ in water; if there is suddenly an input of N (_________________), organisms can grow rapidly (____________) ...
... _____________________________________________________________ • If nutrients are in short supply, they are called ______________________ Ex: Nitrogen is often ___________ in water; if there is suddenly an input of N (_________________), organisms can grow rapidly (____________) ...
Hughes respiration homework (2)
... Our bodies digest the food we eat by mixing it with fluids (acids and enzymes) in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. Glucose has energy stored in its chemical bonds,these bonds are bro ...
... Our bodies digest the food we eat by mixing it with fluids (acids and enzymes) in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. Glucose has energy stored in its chemical bonds,these bonds are bro ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 9 Cellular
... 1. During the redox reaction in glycolysis (step 6 in figure 9.9 in the orange book), which molecule acts as the oxidizing agent? The reducing agent? 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
... 1. During the redox reaction in glycolysis (step 6 in figure 9.9 in the orange book), which molecule acts as the oxidizing agent? The reducing agent? 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
Macromolecules - Dickinson ISD
... These atoms are usually in a ratio of 1:2:1. Living things use carbohydrates as a main source of energy. ...
... These atoms are usually in a ratio of 1:2:1. Living things use carbohydrates as a main source of energy. ...
Food Webs and Food Chains
... six molecules of water to form 1 molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. ...
... six molecules of water to form 1 molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. ...
STEM_Midterm Study Guide_2017
... What is needed for the light-independent reaction to take place? What is produced during the light-independent reaction? Describe what happens during the light-dependent reaction Describe what happens during the light-independent reaction Difference between photosystem I and photosystem II ...
... What is needed for the light-independent reaction to take place? What is produced during the light-independent reaction? Describe what happens during the light-dependent reaction Describe what happens during the light-independent reaction Difference between photosystem I and photosystem II ...
G:\CLASSES\BI 205\Biol205_S10\exams\Final_S10.wpd
... oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immediately upon removal of O2? ...
... oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. If the citric acid cycle (which does not use oxygen) and oxphos are separate processes, as they are, then why is it that the citric acid cycle stops almost immediately upon removal of O2? ...
AP Biology Topic 1 and 2 Test Preparation Assignment. Research
... human activity can increase atmospheric CO2. (4 points maximum) 2. Water is essential to all living things. (a) Discuss THREE properties of water. (6 points max) (b) Explain each of the following in terms of the properties of water. You are not limited to the three properties discussed in part (a): ...
... human activity can increase atmospheric CO2. (4 points maximum) 2. Water is essential to all living things. (a) Discuss THREE properties of water. (6 points max) (b) Explain each of the following in terms of the properties of water. You are not limited to the three properties discussed in part (a): ...
Document
... a. an animal cell to get energy from food. b. a cell to produce energy without oxygen. c. a plant to produce food (glucose). d. a plant leaf to turn green. Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
... a. an animal cell to get energy from food. b. a cell to produce energy without oxygen. c. a plant to produce food (glucose). d. a plant leaf to turn green. Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
The Respiratory System
... • During this process carbon dioxide and water are made. These products are then carried by the blood back to the lungs to be exhaled. ...
... • During this process carbon dioxide and water are made. These products are then carried by the blood back to the lungs to be exhaled. ...
File
... occur. First measure the oxygen concentration of water from the ocean, the bay, or a lake. Then fill the dark and light bottles with water from the ocean, the bay, or a lake. Let sit for 24 hours. Measure the oxygen concentration of the water in both the dark and light bottles. The light bottle shou ...
... occur. First measure the oxygen concentration of water from the ocean, the bay, or a lake. Then fill the dark and light bottles with water from the ocean, the bay, or a lake. Let sit for 24 hours. Measure the oxygen concentration of the water in both the dark and light bottles. The light bottle shou ...
6-3 Thyme - m7science
... 1. Photosynthesis takes carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water and turns them into plant food (sugar). 2. Plant food, or sugar is the product of photosynthesis. 3. Chloroplasts are the organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis. 4. Xylem transports water, an important part of photosynthesis, to ...
... 1. Photosynthesis takes carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water and turns them into plant food (sugar). 2. Plant food, or sugar is the product of photosynthesis. 3. Chloroplasts are the organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis. 4. Xylem transports water, an important part of photosynthesis, to ...
Name - XTEC Blocs
... d. Which part of the plant transport water and nutrients? ___The sap____________________________________________ e. Which part of the plant opens and becomes a flower? ...
... d. Which part of the plant transport water and nutrients? ___The sap____________________________________________ e. Which part of the plant opens and becomes a flower? ...
Geog595 Ecological Modeling
... 3. Numerical Experiment (1) Based on the main.c program and the functions used in the program, draw a flow diagram to show how net radiation, transpiration and photosynthesis are modeled. (2) Run the model for 2001 and compare the simulated net radiation, evapotranspiration and net photosynthesis wi ...
... 3. Numerical Experiment (1) Based on the main.c program and the functions used in the program, draw a flow diagram to show how net radiation, transpiration and photosynthesis are modeled. (2) Run the model for 2001 and compare the simulated net radiation, evapotranspiration and net photosynthesis wi ...
Photosynthesis
... • Efficient at transferring energy but not for storing energy over a long term ...
... • Efficient at transferring energy but not for storing energy over a long term ...
Unit 2 Metabolic Processes Expectations
... C3.1 explain the chemical changes and energy conversions associated with the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration (e.g., in aerobic cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of heat and ATP; in anaerobic cellular respir ...
... C3.1 explain the chemical changes and energy conversions associated with the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration (e.g., in aerobic cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of heat and ATP; in anaerobic cellular respir ...
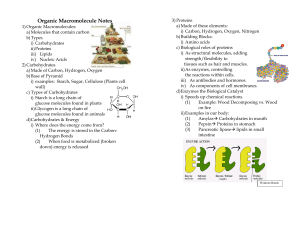
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
... a) Made of these elements: i) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen b) Building Blocks: i) Amino acids c) Biological roles of proteins i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies ...
S3 Level 4 Biology Course
... survive and pass on their characteristics to their offspring This theory was first proposed by Charles Darwin who called it ‘survival of the fittest’ Two organisms are said to be of the same species if they are able to breed and produce fertile offspring ...
... survive and pass on their characteristics to their offspring This theory was first proposed by Charles Darwin who called it ‘survival of the fittest’ Two organisms are said to be of the same species if they are able to breed and produce fertile offspring ...
... made of more than one polypeptide chain. 13. What are amino acids? building blocks (monomers) of proteins; twenty kinds 14. What are Reactants? Substances that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction. 15. What are Products? The substances that result from a recombination of atoms. 16. W ...
Botany terminology - Oregon State University Extension Service
... that are a plant's growing points. Mesophyll-A leaf's inner tissue, located between the upper and lower epidermis; contains the chloroplasts and other specialized cellular parts (organelles). ...
... that are a plant's growing points. Mesophyll-A leaf's inner tissue, located between the upper and lower epidermis; contains the chloroplasts and other specialized cellular parts (organelles). ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... identify them. How does chromatography work? Explain the function of plant pigments. Calculate Rf values, given a chromatogram and relevant distances traveled by solvent and pigments. Cellular Respiration 1. Notes and Worksheet: Cellular Respiration Reading Questions, Cellular Respiration Powe ...
... identify them. How does chromatography work? Explain the function of plant pigments. Calculate Rf values, given a chromatogram and relevant distances traveled by solvent and pigments. Cellular Respiration 1. Notes and Worksheet: Cellular Respiration Reading Questions, Cellular Respiration Powe ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.