Ecology - Choteau Schools
... – Organism that use light energy or energy stored in chemical compounds to make energy-rich compounds. – Example: Plants use sunlight to make energy during the process of photosynthesis. ...
... – Organism that use light energy or energy stored in chemical compounds to make energy-rich compounds. – Example: Plants use sunlight to make energy during the process of photosynthesis. ...
AP Biology - mvhs
... Sap transport in phloem – pressure-flow hypothesis, role of active transport and osmosis in loading at source and unloading at sink Redox reactions – LEO, GER; where do electrons originate, what pulls them away Light- Dependent Reactions – location, purpose; role of chlorophyll, water and photosyste ...
... Sap transport in phloem – pressure-flow hypothesis, role of active transport and osmosis in loading at source and unloading at sink Redox reactions – LEO, GER; where do electrons originate, what pulls them away Light- Dependent Reactions – location, purpose; role of chlorophyll, water and photosyste ...
Electron Transport Chain (1)
... The stage in between that connects the glycolysis to the Kreb cycle is by using oxygen. We need other proteins to connect with each other because electrons can’t pass through the cell membrane by itself. Free-energy change during electron transport: - Loses 2 electrons from breaking down NADH -> NAD ...
... The stage in between that connects the glycolysis to the Kreb cycle is by using oxygen. We need other proteins to connect with each other because electrons can’t pass through the cell membrane by itself. Free-energy change during electron transport: - Loses 2 electrons from breaking down NADH -> NAD ...
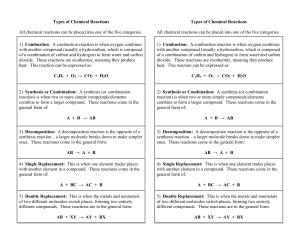
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
Contents - Garland Science
... 5 Photosynthetic Carbon Assimilation 93 Photosynthetic carbon assimilation produces most of the biomass on Earth Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through stomata but water is also lost in the process Carbon dioxide is converted to carbohydrates using energy derived from sunlight ...
... 5 Photosynthetic Carbon Assimilation 93 Photosynthetic carbon assimilation produces most of the biomass on Earth Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through stomata but water is also lost in the process Carbon dioxide is converted to carbohydrates using energy derived from sunlight ...
Cellular Respiration
... H+ ions are sequestered in the inner mitochondrial space H+ ions diffuse down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase Oxygen is the final electron acceptor molecule in the ETC The maximum amount of ATP produced is 36ATP ...
... H+ ions are sequestered in the inner mitochondrial space H+ ions diffuse down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase Oxygen is the final electron acceptor molecule in the ETC The maximum amount of ATP produced is 36ATP ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II State whether the following are true or false: ...
... II State whether the following are true or false: ...
Document
... • Fossil fuels are made when plants and other organic organisms die and decompose in the ground. Layers upon layers are formed over many years. Through chemical processes and pressure, fossil fuels are made. • 1.42 Sometimes, the environmental conditions are such that plants and marine organisms gro ...
... • Fossil fuels are made when plants and other organic organisms die and decompose in the ground. Layers upon layers are formed over many years. Through chemical processes and pressure, fossil fuels are made. • 1.42 Sometimes, the environmental conditions are such that plants and marine organisms gro ...
Cellular Respiration
... • A phosphate-containing compound transfers a phosphate group directly to ADP (makes 31 KJ/mol) • For each glucose molecule processed, 4 ATP (2 net) molecules are generated this way in glycolysis and 2 in Krebs cycle ...
... • A phosphate-containing compound transfers a phosphate group directly to ADP (makes 31 KJ/mol) • For each glucose molecule processed, 4 ATP (2 net) molecules are generated this way in glycolysis and 2 in Krebs cycle ...
LS2 ppt
... The major source of energy for ecosystems on Earth's surface is sunlight. Producers transform the energy of sunlight into the chemical energy of food through photosynthesis. This food energy is used by plants, and all other organisms to carry on life processes. Nearly all organisms on the surface of ...
... The major source of energy for ecosystems on Earth's surface is sunlight. Producers transform the energy of sunlight into the chemical energy of food through photosynthesis. This food energy is used by plants, and all other organisms to carry on life processes. Nearly all organisms on the surface of ...
Energy
... The dark reaction (Calvin Cycle): Carbon dioxide is changed into glucose(food) using ATP and the NADPH from the light reaction as energy. Occurs in stroma. ...
... The dark reaction (Calvin Cycle): Carbon dioxide is changed into glucose(food) using ATP and the NADPH from the light reaction as energy. Occurs in stroma. ...
The Calvin Cycle
... rxn has a net consumption of ATP decreases photosynthetic output by robbing Calvin cycle of organic material ...
... rxn has a net consumption of ATP decreases photosynthetic output by robbing Calvin cycle of organic material ...
A2 Populations and Environment JLL The Biochemistry of R
... B. During the link reaction and Krebs cycle, all 3 carbon atoms have been removed from pyruvate and are released as CO2 C. All the electrons removed from the 3 carbon atoms in the pyruvate have been transferred to NAD or FAD to produce reduced NAD and reduced FAD. In a series of oxidation-reduction ...
... B. During the link reaction and Krebs cycle, all 3 carbon atoms have been removed from pyruvate and are released as CO2 C. All the electrons removed from the 3 carbon atoms in the pyruvate have been transferred to NAD or FAD to produce reduced NAD and reduced FAD. In a series of oxidation-reduction ...
SBI3U - Hwdsb
... where the majority of ATP is produced – name it anaerobic cellular respiration understand why this process occurs (i.e.: in humans) Label the following Figure: ...
... where the majority of ATP is produced – name it anaerobic cellular respiration understand why this process occurs (i.e.: in humans) Label the following Figure: ...
Unit Test: Metabolism
... 17. Alanine can enter Cellular Respiration as which of the following? 18. In terms of direct ATP production, what is the advantage of a cell having mitochondria? 19. In terms of the spectrum of white light, which of the following is the least effective for photosynthesis? 20. What is the function of ...
... 17. Alanine can enter Cellular Respiration as which of the following? 18. In terms of direct ATP production, what is the advantage of a cell having mitochondria? 19. In terms of the spectrum of white light, which of the following is the least effective for photosynthesis? 20. What is the function of ...
Paleozoic Era
... increases as the frequency of the electromagnetic wave increases. a plant’s response to the lengths of daylight and darkness each day. lowest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000 K. process by which plants and many other producers use light energy to pro ...
... increases as the frequency of the electromagnetic wave increases. a plant’s response to the lengths of daylight and darkness each day. lowest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000 K. process by which plants and many other producers use light energy to pro ...
Name: MACROMOLECULES Date: I. ELEMENTS AND
... I. ELEMENTS AND MACROMOLECULES IN ORGANISMS: Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds ...
... I. ELEMENTS AND MACROMOLECULES IN ORGANISMS: Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be classified in two broad categories --- organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds ...
AP Bio Fall Final Study Guide
... This is where majority of the ATP is created. There is a rotator protein in the between the intermembrane space and the Mitochondrial Matrix. Here the Hydrogen ions move back into the mitochondrial space. They go through the rotator protein which has 1 ADP and 1 phosphate group ready to join. The hy ...
... This is where majority of the ATP is created. There is a rotator protein in the between the intermembrane space and the Mitochondrial Matrix. Here the Hydrogen ions move back into the mitochondrial space. They go through the rotator protein which has 1 ADP and 1 phosphate group ready to join. The hy ...
Energy - jpinks
... Respiration the bonds that hold the compound together are pulled apart, this releases energy. This energy is used to add a phosphate back on the ADP recharging it into an ATP. (Synthesis Reaction) 3. Sometimes another phosphate is pulled off of the ADP before it gets recharged. This forms an AMP mol ...
... Respiration the bonds that hold the compound together are pulled apart, this releases energy. This energy is used to add a phosphate back on the ADP recharging it into an ATP. (Synthesis Reaction) 3. Sometimes another phosphate is pulled off of the ADP before it gets recharged. This forms an AMP mol ...
- Mother Shipton`s Cave
... such as bees or butterflies, into the flower. The insects pick up pollen from the flower, and carry it to the next flower they visit. This is how most flowers are pollinated. ...
... such as bees or butterflies, into the flower. The insects pick up pollen from the flower, and carry it to the next flower they visit. This is how most flowers are pollinated. ...
Diversity of Organisms and Classification
... The smallest group of organisms classified which can interbreed with each other to produce fertile offspring; it is always written w/ a small letter. An example of man’s classification on the Genus level is Homo sapiens where the Genus name is always capitalized. Underline if handwritten. (Linneus?) ...
... The smallest group of organisms classified which can interbreed with each other to produce fertile offspring; it is always written w/ a small letter. An example of man’s classification on the Genus level is Homo sapiens where the Genus name is always capitalized. Underline if handwritten. (Linneus?) ...
Cellular Respiration - Home - Mrs. Guida's AP Biology Class
... • Autotrophs vs Heterotrophs • Cellular Respiration- the oxidation of organic compounds to extract energy from chemical bonds ...
... • Autotrophs vs Heterotrophs • Cellular Respiration- the oxidation of organic compounds to extract energy from chemical bonds ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.