abiotic Non-living factors like rain, sun, minerals in soil, and
... a consumer which gets its energy by eating only meat/animal flesh the population that lives in the same area An organism that gets energy from eating other organisms. The variable in an experiment which is kept the same to ensure accuracy. An organism that gets its energy from breaking down decaying ...
... a consumer which gets its energy by eating only meat/animal flesh the population that lives in the same area An organism that gets energy from eating other organisms. The variable in an experiment which is kept the same to ensure accuracy. An organism that gets its energy from breaking down decaying ...
habitat place where an organism lives and that
... supplies nutrients to plants and is found mainly in topsoil. large, severe storm that forms over tropical oceans, has winds of at least 120 km/h, and loses power when it reaches land. an offspring that was given different genetic information for a trait from each parent. compound that has water chem ...
... supplies nutrients to plants and is found mainly in topsoil. large, severe storm that forms over tropical oceans, has winds of at least 120 km/h, and loses power when it reaches land. an offspring that was given different genetic information for a trait from each parent. compound that has water chem ...
Plant Notes
... o Adaptation of fibrous roots in the desert: Many _____________ have very long, fibrous roots which absorb moisture from the soil. Some, like ball cacti, have shorter, more compact roots that absorb dew water that falls off the cactus. ...
... o Adaptation of fibrous roots in the desert: Many _____________ have very long, fibrous roots which absorb moisture from the soil. Some, like ball cacti, have shorter, more compact roots that absorb dew water that falls off the cactus. ...
Beginner Age Division Horticulture Plant Parts Study Guide Roots
... Leaves are where the plant makes food. This process of making food is called photosynthesis. To make food, leaves use the energy of the sun and combine it with carbon dioxide and water the roots pull from the ground to make food for the plant. The leaves take in the carbon dioxide through tiny openi ...
... Leaves are where the plant makes food. This process of making food is called photosynthesis. To make food, leaves use the energy of the sun and combine it with carbon dioxide and water the roots pull from the ground to make food for the plant. The leaves take in the carbon dioxide through tiny openi ...
Taiwan_Marine_Technology_Micro_algae_+PSB
... Improve soil structure, improve soil fertility and promote crop growth. Most photosynthetic bacteria are nitrogen-fixing ability to improve soil nitrogen levels, soil composition of some organic, sulfide, ammonia nitrogen, and the promotion of harmful pollutants (such as pesticides and fertilizers ...
... Improve soil structure, improve soil fertility and promote crop growth. Most photosynthetic bacteria are nitrogen-fixing ability to improve soil nitrogen levels, soil composition of some organic, sulfide, ammonia nitrogen, and the promotion of harmful pollutants (such as pesticides and fertilizers ...
Origin Of Life On EARTH
... have selectively permeable membranes through which water molecules can pass. ...
... have selectively permeable membranes through which water molecules can pass. ...
9.2 Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Reading Guide
... The energy from the electrons moving down the chain is used to move H+ ions across the . inner membrane H+ ions build up in the space, making it positively charged and making the matrix negatively charged. intermembrane H+ ions move through channels of in the inner membrane.ATP synthase The ATP synt ...
... The energy from the electrons moving down the chain is used to move H+ ions across the . inner membrane H+ ions build up in the space, making it positively charged and making the matrix negatively charged. intermembrane H+ ions move through channels of in the inner membrane.ATP synthase The ATP synt ...
107 chem Assement Q
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
Biology 2.3 Carbon Compounds
... Amino Acids have Amino group (NH2) on one end, Carboxyllic acid group (COOH) on the other end ...
... Amino Acids have Amino group (NH2) on one end, Carboxyllic acid group (COOH) on the other end ...
Chapter 2 Notes: The Chemistry of Life
... Reactions that release energy often occur _________________________. Reactions that absorb energy will not occur _________________________ a source of energy. ...
... Reactions that release energy often occur _________________________. Reactions that absorb energy will not occur _________________________ a source of energy. ...
General Biology EOCT Review in ppt
... B. sperm cells C. four daughter cells D. haploid daughter cells E. tetraploid daughter cells ...
... B. sperm cells C. four daughter cells D. haploid daughter cells E. tetraploid daughter cells ...
CB098-008.34_Photosynthesis_B
... and NADPH), another input in the form of CO2, and involves certain outputs (C6H12O6 which is glucose, NADP+, H+, ADP, P+) The Calvin Cycle (occurring in the stroma) converts CO2 to sugar by using the energy in ATP and NADPH from the light reaction. The Calvin ...
... and NADPH), another input in the form of CO2, and involves certain outputs (C6H12O6 which is glucose, NADP+, H+, ADP, P+) The Calvin Cycle (occurring in the stroma) converts CO2 to sugar by using the energy in ATP and NADPH from the light reaction. The Calvin ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pass materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pass materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
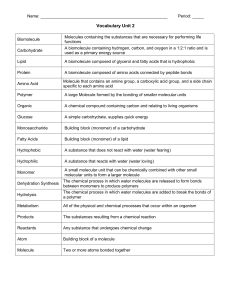
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... A small molecular unit that can be chemically combined with other small molecular units to form a larger molecule ...
... A small molecular unit that can be chemically combined with other small molecular units to form a larger molecule ...
Dark Reactions
... determining step of the Calvin cycle is fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase which make this enzyme a key enzyme in Calvin cycle regulation. Illumination of the chloroplasts activates photosynthetic electron transport, which generates reducing power in the form of NADPH and reduced ferredoxin. Several of the ...
... determining step of the Calvin cycle is fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase which make this enzyme a key enzyme in Calvin cycle regulation. Illumination of the chloroplasts activates photosynthetic electron transport, which generates reducing power in the form of NADPH and reduced ferredoxin. Several of the ...
Mathematics Semester 1 Study Guide
... reactions of photosynthesis and in cellular respiration? a. O2 in both. B. CO2 in both c. H2O in the light reactions and O2 in respiration d. NADP+ in the light reactions and NAD+ or FAD in respiration e. NADP+ in the light reactions and O2 in respiration Indicate if the following events occur durin ...
... reactions of photosynthesis and in cellular respiration? a. O2 in both. B. CO2 in both c. H2O in the light reactions and O2 in respiration d. NADP+ in the light reactions and NAD+ or FAD in respiration e. NADP+ in the light reactions and O2 in respiration Indicate if the following events occur durin ...
Plant structure and function
... Large area for absorption of light. Leaves are a plant's food factory. They are the main site of photosynthesis, where sugars are made from water and carbon dioxide, using sunlight energy that has been absorbed by chlorophyll. ...
... Large area for absorption of light. Leaves are a plant's food factory. They are the main site of photosynthesis, where sugars are made from water and carbon dioxide, using sunlight energy that has been absorbed by chlorophyll. ...
Chapter 8 Section 3 Notes
... When other organisms eat plants, they can use the energy and raw materials stored in these compounds. ...
... When other organisms eat plants, they can use the energy and raw materials stored in these compounds. ...
Robinson`s Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 10/19
... NATURE - Energy flow in ecosystems (e.g., energy pyramids and photosynthetic organisms to herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers) ...
... NATURE - Energy flow in ecosystems (e.g., energy pyramids and photosynthetic organisms to herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers) ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.